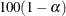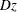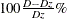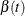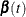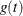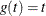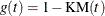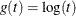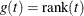-
ALPHA=number
-
specifies the level of significance  for
for 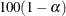 % confidence intervals. The value number must be between 0 and 1; the default value is 0.05, which results in 95% intervals. This value is used as the default confidence
level for limits computed by the BASELINE, BAYES, CONTRAST, HAZARDRATIO, and MODEL statements. You can override this default
by specifying the ALPHA= option in the separate statements.
% confidence intervals. The value number must be between 0 and 1; the default value is 0.05, which results in 95% intervals. This value is used as the default confidence
level for limits computed by the BASELINE, BAYES, CONTRAST, HAZARDRATIO, and MODEL statements. You can override this default
by specifying the ALPHA= option in the separate statements.
-
ATRISK
-
displays a table that contains the number of units at risk at each event time and the corresponding number of events in the
risk sets. For example, the following risk set information is displayed if the ATRISK option is specified in the example in
the section Getting Started: PHREG Procedure.
|
Risk Set Information
|
| |
Number of Units
|
|
Days
|
At Risk
|
Event
|
|
142
|
40
|
1
|
|
143
|
39
|
1
|
|
156
|
38
|
1
|
|
|

|

|
|
296
|
5
|
2
|
|
304
|
3
|
1
|
|
323
|
2
|
1
|
-
COVOUT
-
adds the estimated covariance matrix of the parameter estimates to the OUTEST= data set. The COVOUT option has no effect unless
the OUTEST= option is specified.
-
COVM
-
requests that the model-based covariance matrix (which is the inverse of the observed information matrix) be used in the analysis
if the COVS option is also specified. The COVM option has no effect if the COVS option is not specified.
-
COVSANDWICH <(AGGREGATE)>
COVS <(AGGREGATE)>
-
requests the robust sandwich estimate of Lin and Wei (1989) for the covariance matrix. When this option is specified, this robust sandwich estimate is used in the Wald tests for testing
the global null hypothesis, null hypotheses of individual parameters, and the hypotheses in the CONTRAST and TEST statements.
In addition, a modified score test is computed in the testing of the global null hypothesis, and the parameter estimates table
has an additional StdErrRatio column, which contains the ratios of the robust estimate of the standard error relative to the
corresponding model-based estimate. Optionally, you can specify the keyword AGGREGATE enclosed in parentheses after the COVSANDWICH
(or COVS) option, which requests a summing up of the score residuals for each distinct ID pattern in the computation of the
robust sandwich covariance estimate. This AGGREGATE option has no effect if the ID statement is not specified.
-
DATA=SAS-data-set
-
names the SAS data set that contains the data to be analyzed. If you omit the DATA= option, the procedure uses the most recently
created SAS data set.
-
EV
-
requests the Schemper-Henderson measure (Schemper and Henderson 2000) of the proportion of variation that is explained by a Cox regression. This measure of explained variation (EV) is the ratio
of distance measures between the 1/0 survival processes and the fitted survival curves with and without covariates information.
The distance measure is referred to as the predictive inaccuracy, because the smaller the predictive inaccuracy, the better
the prediction. When you specify this option, PROC PHREG creates a table that has three columns: one presents the predictive
inaccuracy without covariates (D); one presents the predictive inaccuracy with covariates (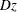 ); and one presents the EV measure, computed according to
); and one presents the EV measure, computed according to 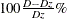 .
.
-
FAST
-
uses an alternative algorithm to speed up the fitting of the Cox regression for a large data set that has the counting process
style of input. Simonsen (2014) has demonstrated the efficiency of this algorithm when the data set contains a large number of observations and many distinct
event times. The algorithm requires only one pass through the data to compute the Breslow or Efron partial log-likelihood
function and the corresponding gradient and Hessian. PROC PHREG ignores the FAST option if you specify a TIES= option value
other than BRESLOW or EFRON, or if you specify programming statements for time-varying covariates. You might not see much
improvement in the optimization time if your data set has only a moderate number of observations.
-
INEST=SAS-data-set
-
names the SAS data set that contains initial estimates for all the parameters in the model. BY-group processing is allowed
in setting up the INEST= data set. For more information, see the section INEST= Input Data Set.
-
MULTIPASS
-
requests that, for each Newton-Raphson iteration, PROC PHREG recompile the risk sets that correspond to the event times for
the (start,stop) style of response and recomputes the values of the time-dependent variables defined by the programming statements
for each observation in the risk sets. If the MULTIPASS option is not specified, PROC PHREG computes all risk sets and all
the variable values and saves them in a utility file. The MULTIPASS option decreases required disk space at the expense of
increased execution time; however, for very large data, it might actually save time, because it is time-consuming to write
and read large utility files. This option has an effect only when the (start,stop) style of response is used or when there
are time-dependent explanatory variables.
-
NAMELEN=n
-
specifies the length of effect names in tables and output data sets to be n characters, where n is a value between 20 and 200. The default length is 20 characters.
-
NOPRINT
-
suppresses all displayed output. Note that this option temporarily disables the Output Delivery System (ODS); for more information
about ODS, see Chapter 20: Using the Output Delivery System.
-
NOSUMMARY
-
suppresses the summary display of the event and censored observation frequencies.
-
OUTEST=SAS-data-set
-
creates an output SAS data set that contains estimates of the regression coefficients.
The data set also contains the convergence status and the log likelihood. If you use the COVOUT option, the data set also
contains the estimated covariance matrix of the parameter estimators.
For more information, see the section OUTEST= Output Data Set.
-
PLOTS<(global-plot-options)> = plot-request
PLOTS<(global-plot-options)> = (plot-request <…<plot-request>>)
-
controls the baseline functions plots produced through ODS Graphics. Each observation in the COVARIATES= data set in the BASELINE
statement represents a set of covariates for which a curve is produced for each plot-request and for each stratum. You can use the ROWID=
option in the BASELINE statement to specify a variable in the COVARIATES= data set for identifying the curves produced for
the covariate sets. If the ROWID=
option is not specified, the curves produced are identified by the covariate values if there is only a single covariate or
by the observation numbers of the COVARIATES= data set if the model has two or more covariates. If the COVARIATES= data set
is not specified, a reference set of covariates consisting of the reference levels for the CLASS variables and the average
values for the continuous variables is used. For plotting more than one curve, you can use the OVERLAY= option to group the
curves in separate plots. When you specify one plot-request, you can omit the parentheses around the plot request. Here are some examples:
plots=survival
plots=(survival cumhaz)
ODS Graphics must be enabled before plots can be requested. For example:
ods graphics on;
proc phreg plots(cl)=survival;
model Time*Status(0)=X1-X5;
baseline covariates=One;
run;
For more information about enabling and disabling ODS Graphics, see the section Enabling and Disabling ODS Graphics in Chapter 21: Statistical Graphics Using ODS.
The global-plot-options include the following:
-
CL<=EQTAIL | HPD>
-
displays the pointwise interval limits for the specified curves. For the classical analysis, CL displays the confidence limits.
For the Bayesian analysis, CL=EQTAIL displays the equal-tail credible limits and CL=HPD displays the HPD limits. Specifying
just CL in a Bayesian analysis defaults to CL=HPD.
-
OVERLAY <=overlay-option>
-
specifies how the curves for the various strata and covariate sets are overlaid. If the STRATA statement is not specified,
specifying OVERLAY without any option will overlay the curves for all the covariate sets. The available overlay-options are as follows:
-
BYGROUP
GROUP
-
overlays, for each stratum, all curves for the covariate sets that have the same GROUP=
value in the COVARIATES= data set in the same plot.
-
INDIVIDUAL
IND
-
displays, for each stratum, a separate plot for each covariate set.
-
BYROW
ROW
-
displays, for each covariate set, a separate plot containing the curves for all the strata.
-
BYSTRATUM
STRATUM
-
displays, for each stratum, a separate plot containing the curves for all sets of covariates.
The default is OVERLAY=BYGROUP if the GROUP=
option is specified in the BASELINE statement or if the COVARIATES= data set contains the _GROUP_ variable; otherwise the
default is OVERLAY=INDIVIDUAL.
-
TIMERANGE=(<min> <,max>)
TIMERANGE=<min> <,max>
RANGE=(<min> <,max>)
RANGE=<min> <,max>
-
specifies the range of values on the time axis to clip the display. The min and max values are the lower and upper bounds of the range. By default, min is 0 and max is the largest event time.
You can specify the following plot-requests:
-
CIF
-
plots the estimated cumulative incidence function (CIF) for each set of covariates in the COVARIATES= data set in the BASELINE
statement. If the COVARIATES= data set is not specified, the estimated CIF is plotted for the reference set of covariates,
which consists of reference levels for the CLASS variables and average values for the continuous variables.
-
CUMHAZ
-
plots the estimated cumulative hazard function for each set of covariates in the COVARIATES= data set in the BASELINE statement.
If the COVARIATES= data set is not specified, the estimated cumulative hazard function is plotted for the reference set of
covariates, which consists of reference levels for the CLASS variables and average values for the continuous variables.
-
MCF
-
plots the estimated mean cumulative function for each set of covariates in the COVARIATES= data set in the BASELINE statement.
If the COVARIATES= data set is not specified, the estimated mean cumulative function is plotted for the reference set of covariates,
which consists of reference levels for the CLASS variables and average values for the continuous variables.
-
NONE
-
suppresses all the plots in the procedure. Specifying this option is equivalent to disabling ODS Graphics for the entire procedure.
-
SURVIVAL
-
plots the estimated survivor function for each set of covariates in the COVARIATES= data set in the BASELINE statement. If
COVARIATES= data set is not specified, the estimated survivor function is plotted for the reference set of covariates, which
consists of reference levels for the CLASS variables and average values for the continuous variables.
-
SIMPLE
-
displays simple descriptive statistics (mean, standard deviation, minimum, and maximum) for each explanatory variable in the
MODEL statement.
-
ZPH<(zph-options)>
-
requests diagnostics based on the weighted Schoenfeld residuals for checking the proportional hazards assumption (for more
information, see ZPH Diagnostics). For each predictor, PROC PHREG presents a plot of the time-varying coefficients in addition to a correlation test between
the weighted residuals and failure times in a given scale. You can specify the following zph-options:
-
FIT=NONE | LOESS | SPLINE
-
displays a fitted smooth curve in a plot of time-varying coefficients. FIT=LOESS displays a loess curve. FIT=SPLINE fits a
penalized B-spline curve. If you do not want to display a fitted curve, specify FIT=NONE. By default, FIT=SPLINE.
-
GLOBAL
-
computes the global correlation test.
-
NOPLOT
-
suppresses the plots of the time-varying coefficients 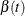 .
.
-
NOTEST
-
suppresses the correlation tests.
-
OUT=SAS-data-set
-
names the output data set that contains the time-varying coefficients 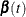 , one row per event time. The variables that contain
, one row per event time. The variables that contain 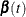 have the same names as the predictors. The data set also contains the transformed event times
have the same names as the predictors. The data set also contains the transformed event times 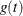 .
.
-
TRANSFORM=IDENTITY | KM | LOG | RANK
-
specifies how the failure times should be transformed in the diagnostic plots and correlation tests. You can choose from the
following transformations:
- IDENTITY
-
specify the identity transformation, 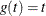 .
.
- KM
-
specifies the complement of the Kaplan-Meier estimate transformation, 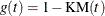 .
.
- LOG
-
specifies the log transformation, 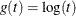 .
.
- RANK
-
specifies the rank transformation, 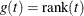 .
.

 PROC PHREG StatementASSESS StatementBASELINE StatementBAYES StatementBY StatementCLASS StatementCONTRAST StatementEFFECT StatementESTIMATE StatementFREQ StatementHAZARDRATIO StatementID StatementLSMEANS StatementLSMESTIMATE StatementMODEL StatementOUTPUT StatementProgramming StatementsRANDOM StatementSTRATA StatementSLICE StatementSTORE StatementTEST StatementWEIGHT Statement
PROC PHREG StatementASSESS StatementBASELINE StatementBAYES StatementBY StatementCLASS StatementCONTRAST StatementEFFECT StatementESTIMATE StatementFREQ StatementHAZARDRATIO StatementID StatementLSMEANS StatementLSMESTIMATE StatementMODEL StatementOUTPUT StatementProgramming StatementsRANDOM StatementSTRATA StatementSLICE StatementSTORE StatementTEST StatementWEIGHT Statement Failure Time DistributionTime and CLASS Variables UsagePartial Likelihood Function for the Cox ModelCounting Process Style of InputLeft-Truncation of Failure TimesThe Multiplicative Hazards ModelProportional Rates/Means Models for Recurrent EventsThe Frailty ModelProportional Subdistribution Hazards Model for Competing-Risks DataHazard RatiosNewton-Raphson MethodFirth’s Modification for Maximum Likelihood EstimationRobust Sandwich Variance EstimateTesting the Global Null HypothesisType 3 Tests and Joint TestsConfidence Limits for a Hazard RatioUsing the TEST Statement to Test Linear HypothesesAnalysis of Multivariate Failure Time DataModel Fit StatisticsSchemper-Henderson Predictive MeasureResidualsDiagnostics Based on Weighted ResidualsInfluence of Observations on Overall Fit of the ModelSurvivor Function EstimatorsCaution about Using Survival Data with Left TruncationEffect Selection MethodsAssessment of the Proportional Hazards ModelThe Penalized Partial Likelihood Approach for Fitting Frailty ModelsSpecifics for Bayesian AnalysisComputational ResourcesInput and Output Data SetsDisplayed OutputODS Table NamesODS Graphics
Failure Time DistributionTime and CLASS Variables UsagePartial Likelihood Function for the Cox ModelCounting Process Style of InputLeft-Truncation of Failure TimesThe Multiplicative Hazards ModelProportional Rates/Means Models for Recurrent EventsThe Frailty ModelProportional Subdistribution Hazards Model for Competing-Risks DataHazard RatiosNewton-Raphson MethodFirth’s Modification for Maximum Likelihood EstimationRobust Sandwich Variance EstimateTesting the Global Null HypothesisType 3 Tests and Joint TestsConfidence Limits for a Hazard RatioUsing the TEST Statement to Test Linear HypothesesAnalysis of Multivariate Failure Time DataModel Fit StatisticsSchemper-Henderson Predictive MeasureResidualsDiagnostics Based on Weighted ResidualsInfluence of Observations on Overall Fit of the ModelSurvivor Function EstimatorsCaution about Using Survival Data with Left TruncationEffect Selection MethodsAssessment of the Proportional Hazards ModelThe Penalized Partial Likelihood Approach for Fitting Frailty ModelsSpecifics for Bayesian AnalysisComputational ResourcesInput and Output Data SetsDisplayed OutputODS Table NamesODS Graphics Stepwise RegressionBest Subset SelectionModeling with Categorical PredictorsFirth’s Correction for Monotone LikelihoodConditional Logistic Regression for m:n MatchingModel Using Time-Dependent Explanatory VariablesTime-Dependent Repeated Measurements of a CovariateSurvival CurvesAnalysis of ResidualsAnalysis of Recurrent Events DataAnalysis of Clustered DataModel Assessment Using Cumulative Sums of Martingale ResidualsBayesian Analysis of the Cox ModelBayesian Analysis of Piecewise Exponential ModelAnalysis of Competing-Risks Data
Stepwise RegressionBest Subset SelectionModeling with Categorical PredictorsFirth’s Correction for Monotone LikelihoodConditional Logistic Regression for m:n MatchingModel Using Time-Dependent Explanatory VariablesTime-Dependent Repeated Measurements of a CovariateSurvival CurvesAnalysis of ResidualsAnalysis of Recurrent Events DataAnalysis of Clustered DataModel Assessment Using Cumulative Sums of Martingale ResidualsBayesian Analysis of the Cox ModelBayesian Analysis of Piecewise Exponential ModelAnalysis of Competing-Risks Data