Statements, Functions, and Subroutines by Category
Mathematical Functions
- ALLCOMB
generates all combinations of
 elements taken
elements taken 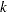 at a time
at a time - ALLPERM
generates all permutations of
 elements
elements - ABS function
computes the absolute value
- EXP function
applies the exponential function
- INT function
truncates a value
- LOG function
computes the natural logarithm
- MOD function
computes the modulo (remainder)
- SQRT function
computes the square root
- RANCOMB
returns random combinations of
 elements taken
elements taken 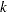 at a time
at a time - RANPERM
returns random permutations of
 elements
elements
You can also call any function in Base SAS software, such as those documented in the following sections:
Reduction Functions
- MAX function
finds the maximum value of a matrix
- MIN function
finds the smallest element of a matrix
- PROD function
multiplies all elements
- SSQ function
computes the sum of squares of all elements
- SUM function
sums all elements
Matrix Inquiry Functions
- ALL function
checks for all nonzero elements
- ANY function
checks for any nonzero elements
- COUNTMISS function
returns the number of missing values
- COUNTN function
returns the number of nonmissing values
- COUNTUNIQUE function
returns the number of unique values
- CHOOSE function
conditionally chooses and changes elements
- LOC function
finds indices for the nonzero elements of a matrix
- NCOL function
finds the number of columns of a matrix
- NLENG function
finds the size of an element
- NROW function
finds the number of rows of a matrix
- TYPE function
determines the type of a matrix
Matrix Sorting and BY-Group Processing Functions
- SORT call
sorts a matrix by specified columns
- SORTNDX call
creates a sorted index for a matrix
- UNIQUEBY function
finds locations of unique BY groups in a sorted or indexed matrix
Matrix Reshaping Functions
- BLOCK function
forms block-diagonal matrices
- BTRAN function
computes a block transpose
- DIAG function
creates a diagonal matrix
- DO function
produces an arithmetic series
- FULL function
converts a matrix stored in a sparse format into a full (dense) matrix
- I function
creates an identity matrix
- INSERT function
inserts one matrix inside another
- J function
creates a matrix of identical values
- REMOVE function
discards elements from a matrix
- REPEAT function
creates a new matrix of repeated values
- SHAPE function
reshapes and repeats values
- SHAPECOL function
reshapes and repeats values by columns
- SPARSE function
converts a matrix that contains many zeros into a matrix stored in a sparse format
- SQRSYM function
converts a symmetric matrix to a square matrix
- SQRVECH function
converts a symmetric matrix which is stored columnwise to a square matrix
- SYMSQR function
converts a square matrix to a symmetric matrix
- T function
transposes a matrix
- VECH function
creates a vector from the columns of the lower triangular elements of a matrix
- VECDIAG function
creates a vector from a diagonal
Character Manipulation Functions
- BYTE function
translates numbers to ordinal characters
- CHANGE call
replaces text
- CHAR function
produces a character representation of a matrix
- CONCAT function
concatenates elementwise strings
- CSHAPE function
reshapes and repeats character values
- LENGTH function
finds the lengths of character matrix elements
- NAME function
lists the names of arguments
- NUM function
produces a numeric representation of a character matrix
- ROWCAT function
concatenates rows without using blank compression
- ROWCATC function
concatenates rows by using blank compression
- SUBSTR function
takes substrings of matrix elements
You can also call functions in Base SAS software such as those documented in Character and Formatting Functions and Character String Matching Functions and Subroutines.
Functions for Random Number Generation
- NORMAL function
generates a pseudorandom normal deviate
- RANDGEN call
generates random numbers from specified distributions
- RANDSEED call
initializes seed for subsequent RANDGEN calls
- UNIFORM function
generates pseudorandom uniform deviates
You can also call functions in Base SAS software such as those documented in Random Number Functions and Subroutines.
Statistical Functions
- BIN function
divides numeric values into a set of disjoint intervals
- BRANKS function
computes bivariate ranks
- CORR function
computes correlation statistics
- COUNTMISS function
counts the number of missing values
- COUNTN function
counts the number of nonmissing values
- COUNTUNIQUE function
returns the number of unique values
- COV function
computes a sample variance-covariance matrix
- CUSUM function
computes cumulative sums
- CUPROD function
computes cumulative products
- DESIGN function
creates a design matrix
- DESIGNF function
creates a full-rank design matrix
- GEOMEAN function
computes geometric means
- HADAMARD function
creates a Hadamard matrix
- HARMEAN function
computes harmonic means
- IPF call
performs an iterative proportional fit of a contingency table
- LAV call
performs linear least absolute value regression by solving the
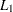 norm minimization problem
norm minimization problem - LMS call
performs robust least median of squares (LMS) regression
- LTS call
performs robust least trimmed squares (LTS) regression
- MAD function
finds the univariate (scaled) median absolute deviation
- MARG call
evaluates marginal totals in a multiway contingency table
- MAXQFORM call
computes the subsets of a matrix system that maximize the quadratic form
- MCD call
finds the minimum covariance determinant estimator
- MEAN function
computes sample means
- MVE call
finds the minimum volume ellipsoid estimator
- OPSCAL function
rescales qualitative data to be a least squared fit to qualitative data
- QNTL call
computes sample quantiles (percentiles)
- RANGE function
returns the range of values for a set of matrices.
- RANK function
ranks elements of a matrix, breaking ties arbitrarily
- RANKTIE function
ranks elements of a matrix
- SEQ call
performs discrete sequential tests
- SEQSCALE call
performs estimates of scales associated with discrete sequential tests
- SEQSHIFT call
performs estimates of means associated with discrete sequential tests
- STD function
computes a sample standard deviation
- TABULATE call
counts the number of unique values in a vector
- SWEEP function
sweeps a matrix
- VAR function
computes a sample variance
You can also call functions in Base SAS software such as those documented in Descriptive Statistics Functions and Subroutines.
Time Series Functions
- ARMACOV call
computes an autocovariance sequence for an autoregressive moving average (ARMA) model
- ARMALIK call
computes the log likelihood and residuals for an ARMA model
- ARMASIM function
simulates an ARMA series
- CONVEXIT function
computes convexity of a noncontingent cash flow
- COVLAG function
computes autocovariance estimates for a vector time series
- DIF function
computes the difference between a value and a lagged value
- DURATION function
computes modified duration of a noncontingent cash flow
- FARMACOV call
computes the autocovariance function for an autoregressive fractionally integrated moving average (ARFIMA) model of the form ARFIMA(
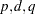 )
) - FARMAFIT call
estimates the parameters of an ARFIMA(
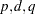 ) model
) model - FARMALIK call
computes the log-likelihood function of an ARFIMA(
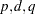 ) model
) model - FARMASIM call
generates an ARFIMA(
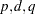 ) process
) process - FDIF call
computes a fractionally differenced process
- FORWARD function
computes forward rates
- KALCVF call
computes the one-step prediction
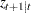 and the filtered estimate
and the filtered estimate 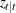 , in addition to their covariance matrices. The call uses forward recursions, and you can also use it to obtain
, in addition to their covariance matrices. The call uses forward recursions, and you can also use it to obtain 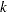 -step estimates.
-step estimates. - KALCVS call
uses backward recursions to compute the smoothed estimate
 and its covariance matrix,
and its covariance matrix, 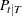 , where
, where 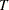 is the number of observations in the complete data set
is the number of observations in the complete data set - KALDFF call
computes the one-step forecast of state vectors in a state space model (SSM) by using the diffuse Kalman filter. The call estimates the conditional expectation of
 , and it also estimates the initial random vector,
, and it also estimates the initial random vector, 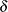 , and its covariance matrix.
, and its covariance matrix. - KALDFS call
computes the smoothed state vector and its mean squares error matrix from the one-step forecast and mean squares error matrix computed by the KALDFF subroutine.
- LAG function
computes lagged values
- PV function
computes the present value
- RATES function
converts interest rates from one base to another
- SPOT function
computes spot rates
- TSBAYSEA call
performs Bayesian seasonal adjustment modeling
- TSDECOMP call
analyzes nonstationary time series by using smoothness priors modeling
- TSMLOCAR call
analyzes nonstationary or locally stationary time series by using a method that minimizes Akaike’s information criterion (AIC)
- TSMLOMAR call
analyzes nonstationary or locally stationary multivariate time series by using a method that minimizes Akaike’s information criterion (AIC)
- TSMULMAR call
estimates vector autoregressive (VAR) processes by minimizing the AIC
- TSPEARS call
analyzes periodic autoregressive (AR) models by minimizing the AIC
- TSPRED call
provides predicted values of univariate and multivariate ARMA processes when the ARMA coefficients are given
- TSROOT call
computes AR and moving average (MA) coefficients from the characteristic roots of the model, or computes the characteristic roots of the model from the AR and MA coefficients
- TSTVCAR call
analyzes time series that are nonstationary in the covariance function
- TSUNIMAR call
determines the order of an AR process by minimizing the AIC, and estimates the AR coefficients
- VARMACOV call
computes the theoretical cross-covariance matrices for a stationary vector autoregressive moving average (VARMA(
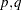 )) model
)) model - VARMALIK call
computes the log-likelihood function for a VARMA(
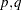 ) model
) model - VARMASIM call
generates VARMA(
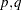 ) time series
) time series - VNORMAL call
generates multivariate normal random series
- VTSROOT call
computes the characteristic roots for a VARMA(
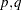 ) model
) model - YIELD function
computes yield-to-maturity of a cash-flow stream
You can also call functions in Base SAS software such as those documented in Financial Functions.
Numerical Analysis Functions
- BSPLINE function
computes a B-spline basis
- FFT function
performs the finite Fourier transform
- IFFT function
computes the inverse finite Fourier transform
- JROOT function
computes the first nonzero roots of a Bessel function of the first kind and the derivative of the Bessel function at each root
- ODE call
performs numerical integration of first-order vector differential equations with initial boundary conditions
- ORPOL function
generates orthogonal polynomials on a discrete set of data
- ORTVEC call
provides columnwise orthogonalization by the Gram-Schmidt process and stepwise QR decomposition by the Gram-Schmidt process
- POLYROOT function
finds zeros of a real polynomial
- PRODUCT function
multiplies matrices of polynomials
- QUAD call
performs numerical integration of scalar functions in one dimension over infinite, connected semi-infinite, and connected finite intervals
- RATIO function
divides matrix polynomials
- SPLINE call
fits a cubic spline to data
- SPLINEC call
fits a cubic spline to data and returns the spline coefficients
- SPLINEV function
evaluates a cubic spline at new data points
- TPSPLINE call
computes thin-plate smoothing splines
- TPSPLNEV call
evaluates the thin-plate smoothing spline at new data points
Linear Algebra functions
- APPCORT call
computes a complete orthogonal decomposition
- COMPORT call
computes a complete orthogonal decomposition by Householder transformations
- CVEXHULL function
finds a convex hull of a set of planar points
- DET function
computes the determinant of a square matrix
- ECHELON function
reduces a matrix to row-echelon normal form
- EIGEN call
computes eigenvalues and eigenvectors
- EIGVAL function
computes eigenvalues
- EIGVEC function
computes eigenvectors
- GENEIG call
computes eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a generalized eigenproblem
- GINV function
computes a generalized inverse
- GSORTH call
computes the Gram-Schmidt orthonormalization
- HALF function
computes the Cholesky decomposition
- HANKEL function
generates a Hankel matrix
- HDIR function
performs a horizontal direct product
- HERMITE function
reduces a matrix to Hermite normal form
- HOMOGEN function
solves homogeneous linear systems
- INV function
computes the inverse
- INVUPDT function
updates a matrix inverse
- ITSOLVER call
solves a sparse general linear system by iteration
- LUPDT call
provides updating and downdating for rank-deficient linear least squares solutions, complete orthogonal factorization, and Moore-Penrose inverses
- QR call
computes the QR decomposition of a matrix by Householder transformations
- RDODT call
downdates and updates QR and Cholesky decompositions
- ROOT function
performs the Cholesky decomposition of a matrix
- RUPDT call
updates QR and Cholesky decompositions
- RZLIND call
updates QR and Cholesky decompositions
- SOLVE function
solves a system of linear equations
- SOLVELIN call
solves a sparse symmetric system of linear equations by direct decomposition
- SVD call
computes the singular value decomposition
- TOEPLITZ function
generates a Toeplitz or block-Toeplitz matrix
- TRACE function
sums diagonal elements
- TRISOLV function
solves linear systems with triangular matrices
- XMULT function
performs extended-precision matrix multiplication
Optimization Subroutines
- LCP call
solves the linear complementarity problem
- LP call
solves the linear programming problem
- NLPCG call
performs nonlinear optimization by conjugate gradient method
- NLPDD call
performs nonlinear optimization by double-dogleg method
- NLPFDD call
approximates derivatives by finite-differences method
- NLPFEA call
computes feasible points subject to constraints
- NLPHQN call
computes hybrid quasi-Newton least squares
- NLPLM call
computes Levenberg-Marquardt least squares
- NLPNMS call
performs nonlinear optimization by Nelder-Mead simplex method
- NLPNRA call
performs nonlinear optimization by Newton-Raphson method
- NLPNRR call
performs nonlinear optimization by Newton-Raphson ridge method
- NLPQN call
performs nonlinear optimization by quasi-Newton method
- NLPQUA call
performs nonlinear optimization by quadratic method
- NLPTR call
performs nonlinear optimization by trust-region method
-
Nonlinear optimization and related subroutines
lists the nonlinear optimization and related subroutines in SAS/IML software
Set functions
- ELEMENT function
finds elements that are contained in a set
- SETDIF function
compares elements of two matrices
- UNION function
performs unions of sets
- UNIQUE function
sorts and removes duplicates
- XSECT function
intersects sets
Control Statements
- ABORT statement
ends PROC IML
- APPLY function
applies a module to arguments
- CALL statement
calls a subroutine or function
- DO statement
groups statements as a unit
- DO, iterative statement
iteratively executes a DO group
- DO UNTIL statement
iteratively executes statements until a condition is satisfied
- DO WHILE statement
iteratively executes statements while a condition is satisfied
- END statement
ends a DO loop or DO statement
- EXECUTE call
executes statements at run time
- FINISH statement
denotes the end of a module
- FREE statement
frees matrix storage space
- GOTO statement
jumps to a new statement
-
IF-THEN/ELSE statement
conditionally executes statement
- LINK statement
jumps to another statement
- MATTRIB statement
associates printing attributes with matrices
- PAUSE statement
interrupts module execution
- PRINT statement
prints matrix values
- PURGE statement
removes observations marked for deletion and renumbers records
- PUSH call
pushes statements to the beginning of the command input stream
- QUEUE call
queues statements at the end of the command input stream
- QUIT statement
exits from PROC IML
- REMOVE statement
removes matrices from storage
- RESET statement
sets processing options
- RESUME statement
resumes execution
- RETURN statement
returns to caller
- RUN statement
executes statements in a module
- SHOW statement
prints system information
- SOUND call
produces a tone
- START statement
defines a module
- STOP statement
stops execution of statements
- STORAGE function
lists names of matrices and modules in storage
- STORE statement
stores matrices and modules in library storage
- VALSET call
performs indirect assignment
- VALUE function
assigns values by indirect reference
Data Set and File Functions
- APPEND statement
adds observations to SAS data set
- CLOSE statement
closes a SAS data set
- CLOSEFILE statement
closes a file
- CONTENTS function
returns the variables in a SAS data set
- CREATE statement
creates a new SAS data set
- DATASETS function
obtains the names of SAS data sets
- DELETE call
deletes a SAS data set
- DELETE statement
marks observations in a data set for deletion
- DO DATA statement
repeats a loop until an end of file occurs
- EDIT statement
opens a SAS data set for editing
- FILE statement
opens or points to an external file
- FIND statement
finds observations
- FORCE statement
is an alias for the SAVE statement
- INDEX statement
indexes a variable in a SAS data set
- INFILE statement
opens a file for input
- INPUT statement
inputs data
- LIST statement
displays observations of a data set
- LOAD statement
loads modules and matrices from library storage
- PUT statement
writes data to an external file
- READ statement
reads observations from a data set
- RENAME call
renames a SAS data set
- REPLACE statement
replaces values in observations and updates observations
- SAVE statement
saves data
- SETIN statement
makes a data set current for input
- SETOUT statement
makes a data set current for output
- SORT statement
sorts a SAS data set
- SUMMARY statement
computes summary statistics for SAS data sets
- USE statement
opens a SAS data set for reading
Graphics and Window functions
- DISPLAY statement
displays fields in a display window
- GBLKVP call
defines a blanking viewport
- GBLKVPD call
deletes the blanking viewport
- GCLOSE call
closes the graphics segment
- GDELETE call
deletes a graphics segment
- GDRAW call
draws a polyline
- GDRAWL call
draws individual lines
- GGRID call
draws a grid
- GINCLUDE call
includes a graphics segment
- GOPEN call
opens a graphics segment
- GPIE call
draws pie slices
- GPIEXY call
converts from polar to world coordinates
- GPOINT call
plots points
- GPOLY call
draws and fills a polygon
- GPORT call
defines a viewport
- GPORTPOP call
pops the viewport
- GPORTSTK call
stacks the viewport
- GSCALE call
computes round numbers for labeling axes
- GSCRIPT call
writes multiple text strings with special fonts
- GSET call
sets attributes for a graphics segment
- GSHOW call
shows a graph
- GSTART call
initializes the graphics system
- GSTOP call
deactivates the graphics system
- GSTRLEN call
finds the string length
- GTEXT call
places text horizontally on a graph
- GVTEXT call
places text vertically on a graph
- GWINDOW call
defines the data window
- GXAXIS call
draws a horizontal axis
- GYAXIS call
draws a vertical axis
- PGRAF call
produces scatter plots
- ODSGRAPH call
renders a graph by using ODS Statistical Graphics
- WINDOW statement
opens a display window
Wavelet Analysis functions
- WAVFT call
computes a wavelet transform of one dimensional data
- WAVGET call
returns requested information about a wavelet transform
- WAVIFT call
inverts a wavelet transform after applying thresholding to the detail coefficients
- WAVPRINT call
displays information about a wavelet transform
- WAVTHRSH call
applies specified thresholding to the detail coefficients of a wavelet transform
Genetic Algorithm functions
- GAEND call
terminates a genetic algorithm and frees memory resources
- GAGETMEM call
gets requested members and objective values from the current solution population
- GAGETVAL call
gets objective function values for a requested member of current solution population
- GAINIT call
initializes the initial solution population
- GAREEVAL call
reevaluates the objective function for all solutions in the current population
- GASETCRO call
specifies a current crossover operator
- GASETMUT call
specifies a current mutation operator
- GASETOBJ call
specifies a current objective function
- GASETSEL call
specifies a current selection parameters
- GASETUP function
sets up a specific genetic algorithm optimization problem
Calling External Modules
- MODULEI call
calls an external routine that has no return code
- MODULEIC call
calls an external routine that returns a character
- MODULEIN call
calls an external routine that returns a numeric value
Calling SAS statements or R Functions
- SUBMIT statement
calls SAS procedures, DATA steps, or macros. You can also use the R option to call functions in the R language.
- ENDSUBMIT statement
defines a block of submitted statements. All statements between the SUBMIT and ENDSUBMIT statements are sent to the SAS System or R for processing.
- EXPORTDATASETTOR call
transfers data from a SAS data set into an R data frame
- EXPORTMATRIXTOR call
transfers data from a SAS/IML matrix into an R matrix
- IMPORTDATASETFROMR call
transfers data from a matrix or data frame into a SAS data set
- IMPORTMATRIXFROMR call
transfers data from a matrix or data frame into a SAS/IML matrix