| BLOCK Function |
BLOCK(
matrix1 <, matrix2, ..., matrix15> )
;
The BLOCK function forms a block-diagonal matrix. The blocks are defined by the arguments to the function. Up to 15 matrices can be specified. The matrices are combined diagonally to form a new matrix.
For example, if 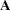 ,
, 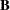 , and
, and  are any matrices, then the block matrix formed from these matrices has the following form:
are any matrices, then the block matrix formed from these matrices has the following form:
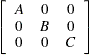 |
The following statements produce a block-diagonal matrix composed of three blocks, shown in Figure 23.50:
a = 1;
b = {2 2,
3 3};
c = {4 4 4,
5 5 5};
d = block(a, b, c);
print d;
Figure 23.50
Block Matrix
| d | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 5 | 5 |