| BTRAN Function |
BTRAN(
x, n, m )
;
The BTRAN function computes the block transpose of a partitioned matrix. The arguments to the BTRAN function are as follows:
- x
is an
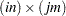 numeric matrix.
numeric matrix. - n
is a scalar with a value that specifies the row dimension of the submatrix blocks.
- m
is a scalar with a value that specifies the column dimension of the submatrix blocks.
The argument x is a partitioned matrix formed from submatrices of dimension 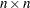 . If the
. If the 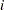 th,
th, 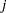 th submatrix of the argument x is denoted
th submatrix of the argument x is denoted 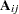 , then the
, then the 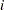 th,
th, 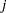 th submatrix of the result is
th submatrix of the result is  .
.
The value returned by the BTRAN function is a 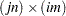 matrix, the block transpose of x, where the blocks are
matrix, the block transpose of x, where the blocks are 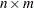 .
.
For example, the following statements compute the block transpose of a matrix:
a11 = {1 1, /* a 3 x 2 matrix */
1 1,
1 1};
a12 = 1 + a11;
a13 = 2 + a11;
a21 = 3 + a11;
a22 = 4 + a11;
a23 = 5 + a11;
x = (a11 || a12 || a13) // /* a partitioned matrix */
(a21 || a22 || a23); /* each submatrix is a 3 x 2 block */
z = btran(x, 3, 2); /* transpose the blocks */
print z;
Figure 23.54
Block Transpose of a Partitioned Matrix
| z | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 4 | 4 |
| 1 | 1 | 4 | 4 |
| 1 | 1 | 4 | 4 |
| 2 | 2 | 5 | 5 |
| 2 | 2 | 5 | 5 |
| 2 | 2 | 5 | 5 |
| 3 | 3 | 6 | 6 |
| 3 | 3 | 6 | 6 |
| 3 | 3 | 6 | 6 |