| NORMAL Function |
The NORMAL function generates pseudorandom numbers from the standard normal distribution. The seed argument is a numeric matrix or literal. The elements of the seed argument can be any integer value up to 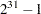 .
.
The NORMAL function returns pseudorandom numbers from a normal distribution with a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1. The NORMAL function returns a matrix with the same dimensions as the argument. The first argument on the first call is used for the seed; if that value is 0, the system time is used for the seed. This function is equivalent to the DATA step function RANNOR.
The Box-Muller transformation of the UNIFORM function deviates is used to generate the numbers. The following statements produce the output shown in Figure 23.204:
seed = 123456; c = j(5, 1, seed); /* generate 5 number from the same seed */ b = normal(c); print b;
| b |
|---|
| -0.109483 |
| -0.348785 |
| 1.1202546 |
| -2.513766 |
| 1.3630022 |
For generating millions of pseudorandom numbers, use the RANDGEN subroutine.