The MCMC Procedure
-
Overview

-
Getting Started

-
Syntax

-
Details
 How PROC MCMC WorksBlocking of ParametersSampling MethodsTuning the Proposal DistributionDirect SamplingConjugate SamplingInitial Values of the Markov ChainsAssignments of ParametersStandard DistributionsUsage of Multivariate DistributionsSpecifying a New DistributionUsing Density Functions in the Programming StatementsTruncation and CensoringSome Useful SAS FunctionsMatrix Functions in PROC MCMCCreate Design MatrixModeling Joint LikelihoodAccess Lag and Lead VariablesCALL ODE and CALL QUAD SubroutinesRegenerating Diagnostics PlotsCaterpillar PlotAutocall Macros for PostprocessingGamma and Inverse-Gamma DistributionsPosterior Predictive DistributionHandling of Missing DataFunctions of Random-Effects ParametersFloating Point Errors and OverflowsHandling Error MessagesComputational ResourcesDisplayed OutputODS Table NamesODS Graphics
How PROC MCMC WorksBlocking of ParametersSampling MethodsTuning the Proposal DistributionDirect SamplingConjugate SamplingInitial Values of the Markov ChainsAssignments of ParametersStandard DistributionsUsage of Multivariate DistributionsSpecifying a New DistributionUsing Density Functions in the Programming StatementsTruncation and CensoringSome Useful SAS FunctionsMatrix Functions in PROC MCMCCreate Design MatrixModeling Joint LikelihoodAccess Lag and Lead VariablesCALL ODE and CALL QUAD SubroutinesRegenerating Diagnostics PlotsCaterpillar PlotAutocall Macros for PostprocessingGamma and Inverse-Gamma DistributionsPosterior Predictive DistributionHandling of Missing DataFunctions of Random-Effects ParametersFloating Point Errors and OverflowsHandling Error MessagesComputational ResourcesDisplayed OutputODS Table NamesODS Graphics -
Examples
 Simulating Samples From a Known DensityBox-Cox TransformationLogistic Regression Model with a Diffuse PriorLogistic Regression Model with Jeffreys’ PriorPoisson RegressionNonlinear Poisson Regression ModelsLogistic Regression Random-Effects ModelNonlinear Poisson Regression Multilevel Random-Effects ModelMultivariate Normal Random-Effects ModelMissing at Random AnalysisNonignorably Missing Data (MNAR) AnalysisChange Point ModelsExponential and Weibull Survival AnalysisTime Independent Cox ModelTime Dependent Cox ModelPiecewise Exponential Frailty ModelNormal Regression with Interval CensoringConstrained AnalysisImplement a New Sampling AlgorithmUsing a Transformation to Improve MixingGelman-Rubin DiagnosticsOne-Compartment Model with Pharmacokinetic Data
Simulating Samples From a Known DensityBox-Cox TransformationLogistic Regression Model with a Diffuse PriorLogistic Regression Model with Jeffreys’ PriorPoisson RegressionNonlinear Poisson Regression ModelsLogistic Regression Random-Effects ModelNonlinear Poisson Regression Multilevel Random-Effects ModelMultivariate Normal Random-Effects ModelMissing at Random AnalysisNonignorably Missing Data (MNAR) AnalysisChange Point ModelsExponential and Weibull Survival AnalysisTime Independent Cox ModelTime Dependent Cox ModelPiecewise Exponential Frailty ModelNormal Regression with Interval CensoringConstrained AnalysisImplement a New Sampling AlgorithmUsing a Transformation to Improve MixingGelman-Rubin DiagnosticsOne-Compartment Model with Pharmacokinetic Data - References
References
-
Aitkin, M., Anderson, D. A., Francis, B., and Hinde, J. (1989). Statistical Modelling in GLIM. Oxford: Oxford Science Publications.
-
Atkinson, A. C. (1979). “The Computer Generation of Poisson Random Variables.” Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series C 28:29–35.
-
Atkinson, A. C., and Whittaker, J. (1976). “A Switching Algorithm for the Generation of Beta Random Variables with at Least One Parameter Less Than One.” Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series A 139:462–467.
-
Bacon, D. W., and Watts, D. G. (1971). “Estimating the Transition between Two Intersecting Straight Lines.” Biometrika 58:525–534.
-
Berger, J. O. (1985). Statistical Decision Theory and Bayesian Analysis. 2nd ed. New York: Springer-Verlag.
-
Box, G. E. P., and Cox, D. R. (1964). “An Analysis of Transformations.” Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B 26:211–234.
-
Byrne, G. D., and Hindmarsh, A. C. (1975). “A Polyalgorithm for the Numerical Solution of ODEs.” ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software 1:71–96.
-
Carlin, B. P., Gelfand, A. E., and Smith, A. F. M. (1992). “Hierarchical Bayesian Analysis of Changepoint Problems.” Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series C 41:389–405.
-
Chaloner, K. (1994). “Residual Analysis and Outliers in Bayesian Hierarchical Models.” In Aspects of Uncertainty: A Tribute to D. V. Lindley, 149–157. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Chaloner, K., and Brant, R. (1988). “A Bayesian Approach to Outlier Detection and Residual Analysis.” Biometrika 75:651–659.
-
Cheng, R. C. H. (1978). “Generating Beta Variates with Non-integral Shape Parameters.” Communications ACM 28:290–295.
-
Clayton, D. G. (1991). “A Monte Carlo Method for Bayesian Inference in Frailty Models.” Biometrics 47:467–485.
-
Congdon, P. (2003). Applied Bayesian Modeling. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Crowder, M. J. (1978). “Beta-Binomial Anova for Proportions.” Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series C 27:34–37.
-
Draper, D. (1996). “Discussion of the Paper by Lee and Nelder.” Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B 58:662–663.
-
Eilers, P. H. C., and Marx, B. D. (1996). “Flexible Smoothing with B-Splines and Penalties.” Statistical Science 11:89–121. With discussion.
-
Finney, D. J. (1947). “The Estimation from Individual Records of the Relationship between Dose and Quantal Response.” Biometrika 34:320–334.
-
Fisher, R. A. (1935). “The Fiducial Argument in Statistical Inference.” Annals of Eugenics 6:391–398.
-
Fishman, G. S. (1996). Monte Carlo: Concepts, Algorithms, and Applications. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Gaver, D. P., and O’Muircheartaigh, I. G. (1987). “Robust Empirical Bayes Analysis of Event Rates.” Technometrics 29:1–15.
-
Gelfand, A. E., Hills, S. E., Racine-Poon, A., and Smith, A. F. M. (1990). “Illustration of Bayesian Inference in Normal Data Models Using Gibbs Sampling.” Journal of the American Statistical Association 85:972–985.
-
Gelman, A., Carlin, J. B., Stern, H. S., and Rubin, D. B. (2004). Bayesian Data Analysis. 2nd ed. London: Chapman & Hall.
-
Gentleman, R., and Geyer, C. J. (1994). “Maximum Likelihood for Interval Censored Data: Consistency and Computation.” Biometrika 81:618–623.
-
Gilks, W. R. (2003). “Adaptive Metropolis Rejection Sampling (ARMS).” Software from MRC Biostatistics Unit, Cambridge, UK. http://www.maths.leeds.ac.uk/~wally.gilks/adaptive.rejection/web_page/Welcome.html.
-
Gilks, W. R., and Wild, P. (1992). “Adaptive Rejection Sampling for Gibbs Sampling.” Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series C 41:337–348.
-
Holmes, C. C., and Held, L. (2006). “Bayesian Auxiliary Variable Models for Binary and Multinomial Regression.” Bayesian Analysis 1:145–168. http://ba.stat.cmu.edu/journal/2006/vol01/issue01/held.pdf.
-
Ibrahim, J. G., Chen, M.-H., and Lipsitz, S. R. (2001). “Missing Responses in Generalised Linear Mixed Models When the Missing Data Mechanism Is Nonignorable.” Biometrika 88:551–564.
-
Kass, R. E., Carlin, B. P., Gelman, A., and Neal, R. M. (1998). “Markov Chain Monte Carlo in Practice: A Roundtable Discussion.” American Statistician 52:93–100.
-
Krall, J. M., Uthoff, V. A., and Harley, J. B. (1975). “A Step-Up Procedure for Selecting Variables Associated with Survival.” Biometrics 31:49–57.
-
Kuhfeld, W. F. (2010). Conjoint Analysis. Technical report, SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC. http://support.sas.com/resources/papers/tnote/tnote_marketresearch.html.
-
Lin, D. Y. (1994). “Cox Regression Analysis of Multivariate Failure Time Data: The Marginal Approach.” Statistics in Medicine 13:2233–2247.
-
Little, R. J. A., and Rubin, D. B. (2002). Statistical Analysis with Missing Data. 2nd ed. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Matsumoto, M., and Kurita, Y. (1992). “Twisted GFSR Generators.” ACM Transactions on Modeling and Computer Simulation 2:179–194.
-
Matsumoto, M., and Kurita, Y. (1994). “Twisted GFSR Generators II.” ACM Transactions on Modeling and Computer Simulation 4:254–266.
-
Matsumoto, M., and Nishimura, T. (1998). “Mersenne Twister: A 623-Dimensionally Equidistributed Uniform Pseudo-random Number Generator.” ACM Transactions on Modeling and Computer Simulation 8:3–30.
-
McGrath, E. J., and Irving, D. C. (1973). Techniques for Efficient Monte Carlo Simulation, Vol. 2: Random Number Generation for Selected Probability Distributions. Technical report, Science Applications Inc., La Jolla, CA.
-
Michael, J. R., Schucany, W. R., and Haas, R. W. (1976). “Generating Random Variates Using Transformations with Multiple Roots.” American Statistician 30:88–90.
-
Pinheiro, J. C., and Bates, D. M. (1995). “Approximations to the Log-Likelihood Function in the Nonlinear Mixed-Effects Model.” Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics 4:12–35.
-
Pregibon, D. (1981). “Logistic Regression Diagnostics.” Annals of Statistics 9:705–724.
-
Ralston, A., and Rabinowitz, P. (1978). A First Course in Numerical Analysis. New York: McGraw-Hill.
-
Rice, S. O. (1973). “Efficient Evaluation of Integrals of Analytic Functions by the Trapezoidal Rule.” Bell System Technical Journal 52:707–722.
-
Ripley, B. D. (1987). Stochastic Simulation. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Robert, C. P. (1995). “Simulation of Truncated Normal Variables.” Statistics and Computing 5:121–125.
-
Roberts, G. O., Gelman, A., and Gilks, W. R. (1997). “Weak Convergence and Optimal Scaling of Random Walk Metropolis Algorithms.” Annals of Applied Probability 7:110–120.
-
Roberts, G. O., and Rosenthal, J. S. (2001). “Optimal Scaling for Various Metropolis-Hastings Algorithms.” Statistical Science 16:351–367.
-
Rubin, D. B. (1976). “Inference and Missing Data.” Biometrika 63:581–592.
-
Rubin, D. B. (1981). “Estimation in Parallel Randomized Experiments.” Journal of Educational Statistics 6:377–411.
-
Schervish, M. J. (1995). Theory of Statistics. New York: Springer-Verlag.
-
Sharples, L. (1990). “Identification and Accommodation of Outliers in General Hierarchical Models.” Biometrika 77:445–453.
-
Sikorsky, K. (1982). “Optimal Quadrature Algorithms in
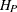 Spaces.” Numerische Mathematik 39:405–410.
Spaces.” Numerische Mathematik 39:405–410.
-
Sikorsky, K., and Stenger, F. (1984). “Optimal Quadratures in
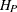 Spaces.” ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software 3:140–151.
Spaces.” ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software 3:140–151.
-
Spiegelhalter, D. J., Thomas, A., Best, N. G., and Gilks, W. R. (1996a). “BUGS Examples, Volume 1.” Version 0.5 (version ii).
-
Spiegelhalter, D. J., Thomas, A., Best, N. G., and Gilks, W. R. (1996b). “BUGS Examples, Volume 2.” Version 0.5 (version ii).
-
Squire, W. (1987). “Comparison of Gauss-Hermite and Midpoint Quadrature with Application to the Voigt Function.” In Numerical Integration: Recent Developments, edited by P. Keast, and G. Fairweather, 111–112. Dordrecht, Netherlands: D. Reidel Publishing.
-
Stenger, F. (1973a). “Integration Formulas Based on the Trapezoidal Formula.” Journal of the Institute of Mathematics and Its Applications 12:103–114.
-
Stenger, F. (1973b). “Remarks on Integration Formulas Based on the Trapezoidal Formula.” Journal of the Institute of Mathematics and Its Applications 19:145–147.