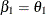The SEQDESIGN Procedure
-
Overview

- Getting Started
-
Syntax

-
Details
 Fixed-Sample Clinical TrialsOne-Sided Fixed-Sample Tests in Clinical TrialsTwo-Sided Fixed-Sample Tests in Clinical TrialsGroup Sequential MethodsStatistical Assumptions for Group Sequential DesignsBoundary ScalesBoundary VariablesType I and Type II ErrorsUnified Family MethodsHaybittle-Peto MethodWhitehead MethodsError Spending MethodsAcceptance (beta) BoundaryBoundary Adjustments for Overlapping Lower and Upper beta BoundariesSpecified and Derived ParametersApplicable Boundary KeysSample Size ComputationApplicable One-Sample Tests and Sample Size ComputationApplicable Two-Sample Tests and Sample Size ComputationApplicable Regression Parameter Tests and Sample Size ComputationAspects of Group Sequential DesignsSummary of Methods in Group Sequential DesignsTable OutputODS Table NamesGraphics OutputODS Graphics
Fixed-Sample Clinical TrialsOne-Sided Fixed-Sample Tests in Clinical TrialsTwo-Sided Fixed-Sample Tests in Clinical TrialsGroup Sequential MethodsStatistical Assumptions for Group Sequential DesignsBoundary ScalesBoundary VariablesType I and Type II ErrorsUnified Family MethodsHaybittle-Peto MethodWhitehead MethodsError Spending MethodsAcceptance (beta) BoundaryBoundary Adjustments for Overlapping Lower and Upper beta BoundariesSpecified and Derived ParametersApplicable Boundary KeysSample Size ComputationApplicable One-Sample Tests and Sample Size ComputationApplicable Two-Sample Tests and Sample Size ComputationApplicable Regression Parameter Tests and Sample Size ComputationAspects of Group Sequential DesignsSummary of Methods in Group Sequential DesignsTable OutputODS Table NamesGraphics OutputODS Graphics -
Examples
 Creating Fixed-Sample DesignsCreating a One-Sided O’Brien-Fleming DesignCreating Two-Sided Pocock and O’Brien-Fleming DesignsGenerating Graphics Display for Sequential DesignsCreating Designs Using Haybittle-Peto MethodsCreating Designs with Various Stopping CriteriaCreating Whitehead’s Triangular DesignsCreating a One-Sided Error Spending DesignCreating Designs with Various Number of StagesCreating Two-Sided Error Spending Designs with and without Overlapping Lower and Upper beta BoundariesCreating a Two-Sided Asymmetric Error Spending Design with Early Stopping to Reject H0Creating a Two-Sided Asymmetric Error Spending Design with Early Stopping to Reject or Accept H0Creating a Design with a Nonbinding Beta BoundaryComputing Sample Size for Survival Data That Have Uniform AccrualComputing Sample Size for Survival Data with Truncated Exponential Accrual
Creating Fixed-Sample DesignsCreating a One-Sided O’Brien-Fleming DesignCreating Two-Sided Pocock and O’Brien-Fleming DesignsGenerating Graphics Display for Sequential DesignsCreating Designs Using Haybittle-Peto MethodsCreating Designs with Various Stopping CriteriaCreating Whitehead’s Triangular DesignsCreating a One-Sided Error Spending DesignCreating Designs with Various Number of StagesCreating Two-Sided Error Spending Designs with and without Overlapping Lower and Upper beta BoundariesCreating a Two-Sided Asymmetric Error Spending Design with Early Stopping to Reject H0Creating a Two-Sided Asymmetric Error Spending Design with Early Stopping to Reject or Accept H0Creating a Design with a Nonbinding Beta BoundaryComputing Sample Size for Survival Data That Have Uniform AccrualComputing Sample Size for Survival Data with Truncated Exponential Accrual - References
SAMPLESIZE Statement
-
SAMPLESIZE <option>;
If each observation in the data set provides one unit of information in a hypothesis testing (such as a one-sample test for the mean), the SAMPLESIZE statement computes the required sample sizes for each sequential design that is specified in a DESIGN statement. However, for a survival analysis, an individual in the survival time data might provide only partial information because of censoring. For this hypothesis, the SAMPLESIZE statement computes the required numbers of events. With additional accrual information in a survival analysis, the sample sizes can also be computed.
Only one SAMPLESIZE statement can be specified. For each specified group sequential design, the SAMPLESIZE statement computes the required sample sizes or numbers of events. The SAMPLESIZE statement is not required if the SEQDESIGN procedure is used only to compare features among different designs.
You can specify the following option:
Table 101.4 summarizes the types of model-request that you can specify.
Table 101.4: MODEL= Option
|
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Fixed-Sample Models |
|
|
Specifies the sample size for a fixed-sample design |
|
|
Specifies the number of events for a fixed-sample design |
|
|
One-Sample Models |
|
|
Specifies the one-sample Z test for the mean |
|
|
Specifies the one-sample test for the binomial proportion |
|
|
Two-Sample Models |
|
|
Specifies the two-sample Z test for the mean difference |
|
|
Specifies the two-sample test for binomial proportions |
|
|
Specifies the log-rank test for two survival distributions |
|
|
Regression Models |
|
|
Specifies the test for a regression parameter |
|
|
Specifies the test for a logistic regression parameter |
|
|
Specifies the test for a proportional hazards regression parameter |
|
The MODEL=INPUTNOBS option specifies the input sample size from a fixed-sample study of nonsurvival data, and the MODEL=INPUTNEVENTS option specifies the number of events from a fixed-sample study of survival data. The remaining MODEL= options specify the statistical models that are used to compute the required sample size. The default is MODEL=TWOSAMPLEMEAN, the two-sample Z test for the mean difference.
When MODEL=INPUTNOBS or MODEL=INPUTNEVENTS, the required sample size or number of events for the group sequential trial is computed by multiplying the input sample size or number of events by the ratio of the design information level to its corresponding fixed-sample information level. This ratio can be obtained by dividing the Max Information (Percent Fixed-Sample) in the "Design Information" table by 100. For a description of the "Design Information" table, see the section Design Information.
Fixed-Sample Models
The following two options compute the required sample size or number of events for a group sequential trial by using the sample size or number of events for the fixed-sample design:
One-Sample Models
The following two options compute the required sample size for a one-sample group sequential test:
Two-Sample Models
The following three options compute the required sample size or number of events for a two-sample group sequential trial.
Regression Models
The following three options compute the required sample size or number of events for group sequential tests on a regression parameter.
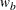
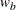
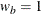
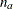
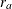
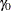
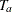
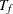
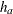
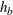

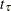
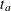
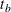
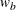
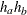
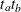
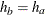
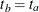
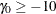
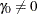
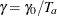
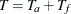
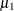

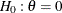
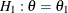
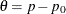
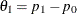
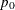
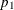
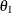
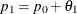
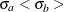
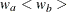
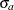
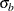
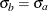
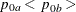
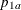
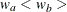
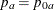
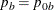
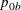
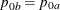
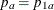
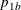
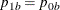
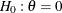
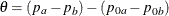
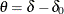
![\[ \delta = \mr{log} \left( \frac{p_{a} (1-p_{b})}{p_{b} (1-p_{a})} \right) \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \delta _{0} = \mr{log} \left( \frac{p_{0a} (1-p_{0b})}{p_{0b} (1-p_{0a})} \right) \]](images/statug_seqdesign0150.png)
![\[ \delta = \mr{log} \left( \frac{p_{a}}{p_{b}} \right) \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \, \delta _{0} = \mr{log} \left( \frac{p_{0a}}{p_{0b}} \right) \]](images/statug_seqdesign0151.png)
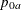
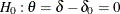
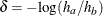
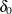
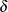
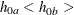
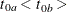
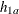
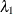
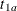
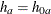
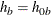
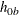
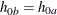
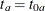
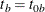
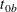
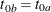
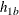
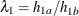
![\[ \theta _1= -\mr{log} \left( \frac{h_{1a}}{h_{1b}} \right) - \left( -\mr{log} \left( \frac{h_{0a}}{h_{0b}} \right) \right) = -\mr{log} \left( \frac{h_{1a}}{h_{0a}} \right) \]](images/statug_seqdesign0172.png)