The ICPHREG Procedure
Example 63.1 Fitting Cubic Spline Models
This example illustrates how to use a cubic spline baseline hazard to fit a proportional hazards model.
Consider the HIV data set in the section Getting Started: ICPHREG Procedure. The following statements request a cubic spline proportional hazards model and the hazard ratio between the two levels of
the Stage variable.
proc icphreg data=hiv; class Stage / desc; model (Left, Right) = Stage / basehaz=splines; hazardratio Stage; run;
Output 63.1.1 displays information about the fitted spline model.
Output 63.1.1: Model Information
If no suboption is specified for the spline model, PROC ICPHREG uses three knots, generating three spline coefficients. Output 63.1.2 shows the selected knots.
Output 63.1.2: Cubic Spline Coefficients
The table of parameter estimates for the spline model is displayed in Output 63.1.3.
Output 63.1.3: Parameter Estimates for the Spline Model
| Analysis of Maximum Likelihood Parameter Estimates | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Effect | Stage | DF | Estimate | Standard Error |
95% Confidence Limits | Chi-Square | Pr > ChiSq | |
| Coef1 | 1 | -6.0630 | 3.2263 | -12.3865 | 0.2605 | |||
| Coef2 | 1 | 1.4921 | 2.2568 | -2.9311 | 5.9152 | |||
| Coef3 | 1 | -0.3086 | 0.6708 | -1.6233 | 1.0060 | |||
| Stage | 1 | 1 | 1.9016 | 0.6662 | 0.5959 | 3.2072 | 8.15 | 0.0043 |
| Stage | 0 | 0 | 0.0000 | |||||
Output 63.1.4 shows the estimated hazard ratio between the two stages and the 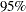 confidence limits.
confidence limits.
Output 63.1.4: Hazard Ratio Estimate for Stage Values 1 and 0
The cubic spline model can be considered a generalization of the Weibull proportional hazards model. It reduces to the Weibull model when there are only two knots, in which case the degrees of freedom is one (DF=1). The Weibull model assumes that the cumulative hazard function is a straight line in the log time scale whereas cubic splines offer a richer set of shapes that have more knots. The following statements fit the spline model with DF=1:
proc icphreg data=hiv; class Stage / desc; model (Left, Right) = Stage / basehaz=splines(df=1); hazardratio Stage; run;
The "Fit Statistics" table is displayed in Output 63.1.5.
Output 63.1.5: Fit Statistics for the Spline Model When DF=1
The table of parameter estimates for the fitted spline model is displayed in Output 63.1.6.
Output 63.1.6: Parameter Estimates for the Spline Model When DF=1
You can request that PROC LIFEREG fit an accelerated failure lifetime model by using the default distribution (Weibull). This would be equivalent to fitting the proportional hazards model by using a Weibull baseline hazard (Klein and Moeschberger 1997). The following statements fit the Weibull model:
proc lifereg data=hiv; class Stage; model (Left, Right) = Stage; run;
The table of fit statistics is displayed in Output 63.1.7.
Output 63.1.7: Fit Statistics That Are Produced by PROC LIFEREG
The table of parameter estimates for the Weibull model is displayed in Output 63.1.8.
Output 63.1.8: Parameter Estimates That Are Produced PROC LIFEREG
| Analysis of Maximum Likelihood Parameter Estimates | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | DF | Estimate | Standard Error |
95% Confidence Limits | Chi-Square | Pr > ChiSq | ||
| Intercept | 1 | 2.1722 | 0.1791 | 1.8211 | 2.5233 | 147.06 | <.0001 | |
| Stage | 0 | 1 | 0.7185 | 0.2711 | 0.1871 | 1.2499 | 7.02 | 0.0080 |
| Stage | 1 | 0 | 0.0000 | . | . | . | . | . |
| Scale | 1 | 0.3934 | 0.1389 | 0.1969 | 0.7858 | |||
| Weibull Shape | 1 | 2.5420 | 0.8974 | 1.2726 | 5.0776 | |||
Comparing Output 63.1.7 with Output 63.1.5, you can see that the two model fits produce identical likelihood values.
The Weibull shape estimate is equal to the second spline coefficient, but the rest of the parameter estimates are different. This is because PROC LIFEREG fits the Weibull model under the configuration of accelerated failure time models. The estimates of regression coefficients from PROC LIFEREG and PROC ICPHREG are proportional; their ratio equals the negative of the Weibull shape parameter. For example, the estimate –0.7185 from PROC LIFEREG can also be obtained by dividing the estimate 1.8265 from PROC ICPHREG by –2.5420.
