The VARMAX Procedure
- Overview
-
Getting Started

-
Syntax

-
Details
 Missing ValuesVARMAX ModelDynamic Simultaneous Equations ModelingImpulse Response FunctionForecastingTentative Order SelectionVAR and VARX ModelingBayesian VAR and VARX ModelingVARMA and VARMAX ModelingModel Diagnostic ChecksCointegrationVector Error Correction ModelingI(2) ModelMultivariate GARCH ModelingOutput Data SetsOUT= Data SetOUTEST= Data SetOUTHT= Data SetOUTSTAT= Data SetPrinted OutputODS Table NamesODS GraphicsComputational Issues
Missing ValuesVARMAX ModelDynamic Simultaneous Equations ModelingImpulse Response FunctionForecastingTentative Order SelectionVAR and VARX ModelingBayesian VAR and VARX ModelingVARMA and VARMAX ModelingModel Diagnostic ChecksCointegrationVector Error Correction ModelingI(2) ModelMultivariate GARCH ModelingOutput Data SetsOUT= Data SetOUTEST= Data SetOUTHT= Data SetOUTSTAT= Data SetPrinted OutputODS Table NamesODS GraphicsComputational Issues -
Examples

- References
In the previous example, the VARX(1,0) model is written as
with
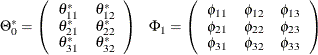
In Figure 35.20 of the preceding section, you can see several insignificant parameters. For example, the coefficients XL0_1_2, AR1_1_2, and AR1_3_2 are insignificant.
The following statements restrict the coefficients of ![]() for the VARX(1,0) model.
for the VARX(1,0) model.
/*--- Models with Restrictions and Tests ---*/ proc varmax data=grunfeld; model y1-y3 = x1 x2 / p=1 print=(estimates); restrict XL(0,1,2)=0, AR(1,1,2)=0, AR(1,3,2)=0; run;
The output in Figure 35.21 shows that three parameters ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() are replaced by the restricted values, zeros. In the schematic representation of parameter estimates, the three restricted
parameters
are replaced by the restricted values, zeros. In the schematic representation of parameter estimates, the three restricted
parameters ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() are replaced by
are replaced by ![]() .
.
Figure 35.21: Parameter Estimation with Restrictions
| XLag | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Lag | Variable | x1 | x2 |
| 0 | y1 | 1.67592 | 0.00000 |
| y2 | -6.30880 | 2.65308 | |
| y3 | -0.03576 | -0.00919 | |
| AR | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lag | Variable | y1 | y2 | y3 |
| 1 | y1 | 0.27671 | 0.00000 | 0.01747 |
| y2 | -2.16968 | 0.10945 | -0.93053 | |
| y3 | 0.96398 | 0.00000 | 0.93412 | |
| Schematic Representation | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Variable/Lag | C | XL0 | AR1 |
| y1 | . | +* | ... |
| y2 | + | .+ | ..- |
| y3 | - | .. | +*+ |
| + is > 2*std error, - is < -2*std error, . is between, * is N/A | |||
The output in Figure 35.22 shows the estimates of the Lagrangian parameters and their significance. Based on the p-values associated with the Lagrangian parameters, you cannot reject the null hypotheses ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() with the 0.05 significance level.
with the 0.05 significance level.
The TEST statement in the following example tests ![]() and
and ![]() for the VARX(1,0) model:
for the VARX(1,0) model:
proc varmax data=grunfeld; model y1-y3 = x1 x2 / p=1; test AR(1,3,1)=0; test XL(0,1,2)=0, AR(1,1,2)=0, AR(1,3,2)=0; run;
The output in Figure 35.23 shows that the first column in the output is the index corresponding to each TEST statement. You can reject the hypothesis
test ![]() at the 0.05 significance level, but you cannot reject the joint hypothesis test
at the 0.05 significance level, but you cannot reject the joint hypothesis test ![]() at the 0.05 significance level.
at the 0.05 significance level.