The REG Procedure
- Overview
-
Getting Started

-
Syntax

-
Details
 Missing Values Input Data Sets Output Data Sets Interactive Analysis Model-Selection Methods Criteria Used in Model-Selection Methods Limitations in Model-Selection Methods Parameter Estimates and Associated Statistics Predicted and Residual Values Models of Less Than Full Rank Collinearity Diagnostics Model Fit and Diagnostic Statistics Influence Statistics Reweighting Observations in an Analysis Testing for Heteroscedasticity Testing for Lack of Fit Multivariate Tests Autocorrelation in Time Series Data Computations for Ridge Regression and IPC Analysis Construction of Q-Q and P-P Plots Computational Methods Computer Resources in Regression Analysis Displayed Output ODS Table Names ODS Graphics
Missing Values Input Data Sets Output Data Sets Interactive Analysis Model-Selection Methods Criteria Used in Model-Selection Methods Limitations in Model-Selection Methods Parameter Estimates and Associated Statistics Predicted and Residual Values Models of Less Than Full Rank Collinearity Diagnostics Model Fit and Diagnostic Statistics Influence Statistics Reweighting Observations in an Analysis Testing for Heteroscedasticity Testing for Lack of Fit Multivariate Tests Autocorrelation in Time Series Data Computations for Ridge Regression and IPC Analysis Construction of Q-Q and P-P Plots Computational Methods Computer Resources in Regression Analysis Displayed Output ODS Table Names ODS Graphics -
Examples

- References
| Parameter Estimates and Associated Statistics |
The following example uses the fitness data from Example 76.2. Figure 76.30 shows the parameter estimates and the tables from the SS1, SS2, STB, CLB, COVB, and CORRB options:
proc reg data=fitness;
model Oxygen=RunTime Age Weight RunPulse MaxPulse RestPulse
/ ss1 ss2 stb clb covb corrb;
run;
The procedure first displays an analysis of variance table (Figure 76.29). The 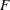 statistic for the overall model is significant, indicating that the model explains a significant portion of the variation in the data.
statistic for the overall model is significant, indicating that the model explains a significant portion of the variation in the data.
| Analysis of Variance | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source | DF | Sum of Squares |
Mean Square |
F Value | Pr > F |
| Model | 6 | 722.54361 | 120.42393 | 22.43 | <.0001 |
| Error | 24 | 128.83794 | 5.36825 | ||
| Corrected Total | 30 | 851.38154 | |||
| Root MSE | 2.31695 | R-Square | 0.8487 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent Mean | 47.37581 | Adj R-Sq | 0.8108 |
| Coeff Var | 4.89057 |
The procedure next displays parameter estimates and some associated statistics (Figure 76.30). First, the estimates are shown, followed by their standard errors. The next two columns of the table contain the  statistics and the corresponding probabilities for testing the null hypothesis that the parameter is not significantly different from zero. These probabilities are usually referred to as
statistics and the corresponding probabilities for testing the null hypothesis that the parameter is not significantly different from zero. These probabilities are usually referred to as 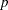 -values. For example, the Intercept term in the model is estimated to be 102.9 and is significantly different from zero. The next two columns of the table are the result of requesting the SS1 and SS2 options, and they show sequential and partial sums of squares (SS) associated with each variable. The standardized estimates (produced by the STB option) are the parameter estimates that result when all variables are standardized to a mean of 0 and a variance of 1. These estimates are computed by multiplying the original estimates by the standard deviation of the regressor (independent) variable and then dividing by the standard deviation of the dependent variable. The CLB option adds the upper and lower
-values. For example, the Intercept term in the model is estimated to be 102.9 and is significantly different from zero. The next two columns of the table are the result of requesting the SS1 and SS2 options, and they show sequential and partial sums of squares (SS) associated with each variable. The standardized estimates (produced by the STB option) are the parameter estimates that result when all variables are standardized to a mean of 0 and a variance of 1. These estimates are computed by multiplying the original estimates by the standard deviation of the regressor (independent) variable and then dividing by the standard deviation of the dependent variable. The CLB option adds the upper and lower 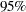 confidence limits for the parameter estimates; the
confidence limits for the parameter estimates; the  level can be changed by specifying the ALPHA= option in the PROC REG or MODEL statement.
level can be changed by specifying the ALPHA= option in the PROC REG or MODEL statement.
| Parameter Estimates | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | DF | Parameter Estimate |
Standard Error |
t Value | Pr > |t| | Type I SS | Type II SS | Standardized Estimate |
95% Confidence Limits | |
| Intercept | 1 | 102.93448 | 12.40326 | 8.30 | <.0001 | 69578 | 369.72831 | 0 | 77.33541 | 128.53355 |
| RunTime | 1 | -2.62865 | 0.38456 | -6.84 | <.0001 | 632.90010 | 250.82210 | -0.68460 | -3.42235 | -1.83496 |
| Age | 1 | -0.22697 | 0.09984 | -2.27 | 0.0322 | 17.76563 | 27.74577 | -0.22204 | -0.43303 | -0.02092 |
| Weight | 1 | -0.07418 | 0.05459 | -1.36 | 0.1869 | 5.60522 | 9.91059 | -0.11597 | -0.18685 | 0.03850 |
| RunPulse | 1 | -0.36963 | 0.11985 | -3.08 | 0.0051 | 38.87574 | 51.05806 | -0.71133 | -0.61699 | -0.12226 |
| MaxPulse | 1 | 0.30322 | 0.13650 | 2.22 | 0.0360 | 26.82640 | 26.49142 | 0.52161 | 0.02150 | 0.58493 |
| RestPulse | 1 | -0.02153 | 0.06605 | -0.33 | 0.7473 | 0.57051 | 0.57051 | -0.03080 | -0.15786 | 0.11480 |
The final two tables are produced as a result of requesting the COVB and CORRB options (Figure 76.31). These tables show the estimated covariance matrix of the parameter estimates, and the estimated correlation matrix of the estimates.
| Covariance of Estimates | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Intercept | RunTime | Age | Weight | RunPulse | MaxPulse | RestPulse |
| Intercept | 153.84081152 | 0.7678373769 | -0.902049478 | -0.178237818 | 0.280796516 | -0.832761667 | -0.147954715 |
| RunTime | 0.7678373769 | 0.1478880839 | -0.014191688 | -0.004417672 | -0.009047784 | 0.0046249498 | -0.010915224 |
| Age | -0.902049478 | -0.014191688 | 0.009967521 | 0.0010219105 | -0.001203914 | 0.0035823843 | 0.0014897532 |
| Weight | -0.178237818 | -0.004417672 | 0.0010219105 | 0.0029804131 | 0.0009644683 | -0.001372241 | 0.0003799295 |
| RunPulse | 0.280796516 | -0.009047784 | -0.001203914 | 0.0009644683 | 0.0143647273 | -0.014952457 | -0.000764507 |
| MaxPulse | -0.832761667 | 0.0046249498 | 0.0035823843 | -0.001372241 | -0.014952457 | 0.0186309364 | 0.0003425724 |
| RestPulse | -0.147954715 | -0.010915224 | 0.0014897532 | 0.0003799295 | -0.000764507 | 0.0003425724 | 0.0043631674 |
| Correlation of Estimates | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Intercept | RunTime | Age | Weight | RunPulse | MaxPulse | RestPulse |
| Intercept | 1.0000 | 0.1610 | -0.7285 | -0.2632 | 0.1889 | -0.4919 | -0.1806 |
| RunTime | 0.1610 | 1.0000 | -0.3696 | -0.2104 | -0.1963 | 0.0881 | -0.4297 |
| Age | -0.7285 | -0.3696 | 1.0000 | 0.1875 | -0.1006 | 0.2629 | 0.2259 |
| Weight | -0.2632 | -0.2104 | 0.1875 | 1.0000 | 0.1474 | -0.1842 | 0.1054 |
| RunPulse | 0.1889 | -0.1963 | -0.1006 | 0.1474 | 1.0000 | -0.9140 | -0.0966 |
| MaxPulse | -0.4919 | 0.0881 | 0.2629 | -0.1842 | -0.9140 | 1.0000 | 0.0380 |
| RestPulse | -0.1806 | -0.4297 | 0.2259 | 0.1054 | -0.0966 | 0.0380 | 1.0000 |
For further discussion of the parameters and statistics, see the section Displayed Output, and Chapter 4, Introduction to Regression Procedures.