The HPSEVERITY Procedure
- Overview
-
Getting Started

-
Syntax

-
Details
 Predefined DistributionsCensoring and TruncationParameter Estimation MethodDetails of Optimization AlgorithmsParameter InitializationEstimating Regression EffectsEmpirical Distribution Function Estimation MethodsStatistics of FitDistributed and Multithreaded ComputationDefining a Severity Distribution Model with the FCMP ProcedurePredefined Utility FunctionsCustom Objective FunctionsInput Data SetsOutput Data SetsDisplayed Output
Predefined DistributionsCensoring and TruncationParameter Estimation MethodDetails of Optimization AlgorithmsParameter InitializationEstimating Regression EffectsEmpirical Distribution Function Estimation MethodsStatistics of FitDistributed and Multithreaded ComputationDefining a Severity Distribution Model with the FCMP ProcedurePredefined Utility FunctionsCustom Objective FunctionsInput Data SetsOutput Data SetsDisplayed Output -
Examples
 Defining a Model for Gaussian DistributionDefining a Model for the Gaussian Distribution with a Scale ParameterDefining a Model for Mixed-Tail DistributionsFitting a Scaled Tweedie Model with RegressorsFitting Distributions to Interval-Censored DataBenefits of Distributed and Multithreaded ComputingEstimating Parameters Using Cramér-von Mises Estimator
Defining a Model for Gaussian DistributionDefining a Model for the Gaussian Distribution with a Scale ParameterDefining a Model for Mixed-Tail DistributionsFitting a Scaled Tweedie Model with RegressorsFitting Distributions to Interval-Censored DataBenefits of Distributed and Multithreaded ComputingEstimating Parameters Using Cramér-von Mises Estimator - References
PROC HPSEVERITY options ;
The PROC HPSEVERITY statement invokes the procedure. You can specify two types of options in the PROC HPSEVERITY statement. One set of options controls input and output. The other set of options controls the model estimation and selection process.
The following options control the input data sets used by PROC HPSEVERITY and various forms of output generated by PROC HPSEVERITY. The options are listed in alphabetical order:
- COVOUT
-
specifies that the OUTEST= data set contain the estimate of the covariance structure of the parameters. This option has no effect if the OUTEST= option is not specified. For more information about how the covariance is reported in the OUTEST= data set, see the section OUTEST= Data Set.
- DATA=SAS-data-set
-
names the input data set. If the DATA= option is not specified, then the most recently created SAS data set is used.
- INEST=SAS-data-set
-
names the input data set that contains the initial values of the parameter estimates to start the optimization process. The initial values specified in the INIT= option in the DIST statement take precedence over any initial values specified in this data set. For more information about the variables in this data set, see the section INEST= Data Set.
-
INITSAMPLE (initsample-option)
INITSAMPLE (initsample-option …initsample-option) -
specifies that a sample of the input data be used for initializing the distribution parameters. If you specify more than one initsample-option, then separate them with spaces.
When you do not specify initial values for the distribution parameters, PROC HPSEVERITY needs to compute the empirical distribution function (EDF) estimates as part of the default method for parameter initialization. The EDF estimation process can be expensive, especially when you specify censoring or truncation effects for the loss variable. Furthermore, it is not amenable to parallelism due to the sequential nature of the algorithm for truncation effects. You can use the INITSAMPLE option to specify that only a fraction of the input data be used in order to reduce the time taken to compute the EDF estimates. PROC HPSEVERITY uses the uniform random sampling method to select the sample, the size and randomness of which is controlled by the following initsample-options:
- FRACTION=number
-
specifies the fraction, between 0 and 1, of the input data to be used for sampling.
- SEED=number
-
specifies the seed to be used for the uniform random number generator. This option enables you to select the same sample from the same input data across different runs of PROC HPSEVERITY, which can be useful for replicating the results across different runs. If you do not specify the seed value, PROC HPSEVERITY generates a seed that is based on the system clock.
- SIZE=number
-
specifies the size of the sample. If the data are distributed across different nodes, then this size applies to the sample that is prepared at each node. For example, let the input data set of size 100,000 observations be distributed across 10 nodes such that each node has 10,000 observations. If you specify SIZE=1000, then each node computes a local EDF estimate by using a sample of size 1,000 selected randomly from its 10,000 observations. If you specify both of the SIZE= and FRACTION= options, then the value specified in the SIZE= option is used and the FRACTION= option is ignored.
If you do not specify the INITSAMPLE option, then a uniform random sample of at most 10,000 observations is used for EDF estimation.
- NOPRINT
-
turns off all displayed output. If specified, any value specified for the PRINT= option is ignored.
- OUTEST=SAS-data-set
-
names the output data set to contain estimates of the parameter values and their standard errors for each model whose parameter estimation process converges. For more information about the variables in this data set, see the section OUTEST= Data Set.
- OUTMODELINFO=SAS-data-set
-
names the output data set to contain the status of each fitted model. The status information includes the convergence status of the optimization process that is used to estimate the parameters, the status of estimating the covariance matrix, and whether a model is the best according to the specified selection criterion. For more information about the variables in this data set, see the section OUTMODELINFO= Data Set.
- OUTSTAT=SAS-data-set
-
names the output data set to contain the values of statistics of fit for each model whose parameter estimation process converges. For more information about the variables in this data set, see the section OUTSTAT= Data Set.
-
PRINT <(global-display-option)> <=display-option>
PRINT <(global-display-option)> <= (display-option …display-option) > -
specifies the desired displayed output. If you specify more than one display-option, then separate them with spaces and enclose them in parentheses.
The following global-display-option is available:
The following display-options are available:
- ALL
-
displays all the output.
- ALLFITSTATS
-
displays the comparison of all the statistics of fit for all the models in one table. The table does not include the models whose parameter estimation process does not converge.
- CONVSTATUS
-
displays the convergence status of the parameter estimation process.
- DESCSTATS
-
displays the descriptive statistics for the response variable and the regressor variables, if they are specified.
- DISTINFO
-
displays the information about each specified distribution. For each distribution, the information includes the name, description, validity status, and number of distribution parameters.
-
ESTIMATES
PARMEST -
displays the final estimates of parameters. The estimates are not displayed for models whose parameter estimation process does not converge.
- ESTIMATIONDETAILS
-
displays the details of the estimation process for all the models in one table.
- INITIALVALUES
-
displays the initial values and bounds used for estimating each model.
- NLOHISTORY
-
displays the iteration history of the nonlinear optimization process used for estimating the parameters.
- NLOSUMMARY
-
displays the summary of the nonlinear optimization process used for estimating the parameters.
- NONE
-
displays none of the output. If specified, this option overrides all the other display options. The default displayed output is also suppressed.
-
SELECTION
SELECT -
displays the model selection table.
-
STATISTICS
FITSTATS -
displays the statistics of fit for each model. The statistics of fit are not displayed for models whose parameter estimation process does not converge.
If the PRINT= option is not specified or the ONLY global-display-option is not specified, then the default displayed output is equivalent to specifying PRINT=(SELECTION CONVSTATUS NLOSUMMARY STATISTICS ESTIMATES).
- VARDEF=option
-
specifies the denominator to use for computing the covariance estimates. You can specify one of the following values for option:
For more information about the covariance estimation, see the section Estimating Covariance and Standard Errors.
- VERBOSE=verbosity-level
-
specifies the amount of messages printed to the SAS log by PROC HPSEVERITY. A higher number prints messages with the same or more detail.
The following options control the model estimation and selection process:
-
CRITERION=criterion-option
CRITERIA=criterion-option
CRIT=criterion-option -
specifies the model selection criterion.
If two or more models are specified for estimation, then the one with the best value for the selection criterion is chosen as the best model. If the OUTMODELINFO= data set is specified, then the best model’s observation has a value of 1 for the _SELECTED_ variable. You can specify one of the following criterion-options:
- AD
-
specifies the Anderson-Darling (AD) statistic value, which is computed by using the empirical distribution function (EDF) estimate, as the selection criterion. A lower value is deemed better.
- AIC
-
specifies Akaike’s information criterion (AIC) as the selection criterion. A lower value is deemed better.
- AICC
-
specifies the finite-sample corrected Akaike’s information criterion (AICC) as the selection criterion. A lower value is deemed better.
- BIC
-
specifies the Schwarz Bayesian information criterion (BIC) as the selection criterion. A lower value is deemed better.
- CUSTOM
-
specifies the custom objective function as the selection criterion. You can specify this only if you also specify the OBJECTIVE= option. A lower value is deemed better.
- CVM
-
specifies the Cra
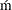
er-von Mises (CvM) statistic value, which is computed by using the empirical distribution function (EDF) estimate, as the selection criterion. A lower value is deemed better.
- KS
-
specifies the Kolmogorov-Smirnov (KS) statistic value, which is computed by using the empirical distribution function (EDF) estimate, as the selection criterion. A lower value is deemed better.
-
LOGLIKELIHOOD
LL -
specifies
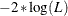 as the selection criterion, where
as the selection criterion, where 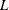 is the likelihood of the data. A lower value is deemed better. This is the default.
is the likelihood of the data. A lower value is deemed better. This is the default.
For more information about these criterion-options, see the section Statistics of Fit.
- EMPIRICALCDF | EDF=method
-
specifies the method to use for computing the nonparametric or empirical estimate of the cumulative distribution function of the data. You can specify one of the following values for method:
- AUTOMATIC | AUTO
-
specifies that the method be chosen automatically based on the data specification.
If you do not specify any censoring or truncation, then the standard empirical estimation method (STANDARD) is chosen. If you specify both right-censoring and left-censoring, then Turnbull’s estimation method (TURNBULL) is chosen. For all other combinations of censoring and truncation, the Kaplan-Meier method (KAPLANMEIER) is chosen.
- KAPLANMEIER | KM
-
specifies that the product limit estimator proposed by Kaplan and Meier (1958) be used. Specification of this method has no effect when both right-censoring and left-censoring are specified.
- MODIFIEDKM | MKM <(options)>
-
specifies that the modified product limit estimator be used. Specification of this method has no effect when both right-censoring and left-censoring are specified.
This method allows Kaplan-Meier’s product limit estimates to be more robust by ignoring the contributions to the estimate due to small risk-set sizes. The risk set is the set of observations at the risk of failing, where an observation is said to fail if it has not been processed yet and might experience censoring or truncation. The minimum risk-set size that makes it eligible to be included in the estimation can be specified either as an absolute lower bound on the size (RSLB= option) or a relative lower bound determined by the formula
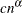 proposed by Lai and Ying (1991). Values of
proposed by Lai and Ying (1991). Values of  and
and  can be specified by using the C= and ALPHA= options, respectively. By default, the relative lower bound is used with values
of
can be specified by using the C= and ALPHA= options, respectively. By default, the relative lower bound is used with values
of 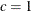 and
and 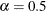 . However, you can modify the default by using the following options:
. However, you can modify the default by using the following options:
- ALPHA | A=number
-
specifies the value to use for
 when the lower bound on the risk set size is defined as
when the lower bound on the risk set size is defined as 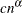 . This value must satisfy
. This value must satisfy 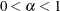 .
.
- C=number
-
specifies the value to use for
 when the lower bound on the risk set size is defined as
when the lower bound on the risk set size is defined as 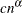 . This value must satisfy
. This value must satisfy 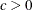 .
.
- RSLB=number
-
specifies the absolute lower bound on the risk set size to be included in the estimate.
- NOTURNBULL
-
specifies that the method be chosen automatically based on the data specification and that Turnbull’s method not be used. This is the default.
This method first replaces each left-censored or interval-censored observation with an uncensored observation. If the resulting set of observations has any truncated or right-censored observations, then the Kaplan-Meier method (KAPLANMEIER) is chosen. Otherwise, the standard empirical estimation method (STANDARD) is chosen. The observations are modified only for the purpose of computing the EDF estimates; the modification does not affect the parameter estimation process.
- STANDARD | STD
-
specifies that the standard empirical estimation method be used. This ignores any censoring or truncation information even if specified, and can thus result in estimates that are more biased than those obtained with other methods more suitable for such data. Specification of this method has no effect when both right-censoring and left-censoring are specified.
- TURNBULL | EM <(options)>
-
specifies that the Turnbull’s method be used. An iterative expectation-maximization (EM) algorithm proposed by Turnbull (1976) is used to compute the empirical estimates. If truncation is also specified, then the modification suggested by Frydman (1994) is used.
This method is used if both right-censoring and left-censoring are specified and if you have explicitly specified the EMPIRICALCDF=TURNBULL option.
You can modify the default behavior of the EM algorithm by using the following options:
- ENSUREMLE
-
specifies that the final EDF estimates be maximum likelihood estimates. The Kuhn-Tucker conditions are computed for the likelihood maximization problem and checked to ensure that EM algorithm converges to maximum likelihood estimates. The method generalizes the method proposed by Gentleman and Geyer (1994) by taking into account the truncation information, if specified.
- EPS=number
-
specifies the maximum relative error to be allowed between estimates of two consecutive iterations. This criterion is used to check the convergence of the algorithm. If you do not specify this option, then PROC HPSEVERITY uses a default value of 1.0E–8.
- MAXITER=number
-
specifies the maximum number of iterations to attempt to find the empirical estimates. If you do not specify this option, then PROC HPSEVERITY uses a default value of 500.
- ZEROPROB=number
-
specifies the threshold below which an empirical estimate of the probability is considered zero. This option is used to decide if the final estimate is a maximum likelihood estimate. This option does not have an effect if you do not specify the ENSUREMLE option. If you specify the ENSUREMLE option, but do not specify this option, then PROC HPSEVERITY uses a default value of 1.0E–8.
For more information about each of the methods, see the section Empirical Distribution Function Estimation Methods.
- OBJECTIVE=symbol-name
-
names the symbol that represents the objective function in the specified SAS programming statements. For each model to be estimated, PROC HPSEVERITY executes the programming statements to compute the value of this symbol for each observation. The values are added across all observations to obtain the value of the objective function. The optimization algorithm estimates the model parameters such that the objective function value is minimized. A separate optimization problem is solved for each candidate distribution.
For more information about writing SAS programming statements to define your own objective function, see the section Custom Objective Functions.