The MCMC Procedure
-
Overview

-
Getting Started

-
Syntax

-
Details
 How PROC MCMC Works Blocking of Parameters Sampling Methods Tuning the Proposal Distribution Conjugate Sampling Initial Values of the Markov Chains Assignments of Parameters Standard Distributions Usage of Multivariate Distributions Specifying a New Distribution Using Density Functions in the Programming Statements Truncation and Censoring Some Useful SAS Functions Matrix Functions in PROC MCMC Create Design Matrix Modeling Joint Likelihood Regenerating Diagnostics Plots Caterpillar Plot Posterior Predictive Distribution Handling of Missing Data Floating Point Errors and Overflows Handling Error Messages Computational Resources Displayed Output ODS Table Names ODS Graphics
How PROC MCMC Works Blocking of Parameters Sampling Methods Tuning the Proposal Distribution Conjugate Sampling Initial Values of the Markov Chains Assignments of Parameters Standard Distributions Usage of Multivariate Distributions Specifying a New Distribution Using Density Functions in the Programming Statements Truncation and Censoring Some Useful SAS Functions Matrix Functions in PROC MCMC Create Design Matrix Modeling Joint Likelihood Regenerating Diagnostics Plots Caterpillar Plot Posterior Predictive Distribution Handling of Missing Data Floating Point Errors and Overflows Handling Error Messages Computational Resources Displayed Output ODS Table Names ODS Graphics -
Examples
 Simulating Samples From a Known Density Box-Cox Transformation Logistic Regression Model with a Diffuse Prior Logistic Regression Model with Jeffreys’ Prior Poisson Regression Nonlinear Poisson Regression Models Logistic Regression Random-Effects Model Nonlinear Poisson Regression Random-Effects Model Multivariate Normal Random-Effects Model Change Point Models Exponential and Weibull Survival Analysis Time Independent Cox Model Time Dependent Cox Model Piecewise Exponential Frailty Model Normal Regression with Interval Censoring Constrained Analysis Implement a New Sampling Algorithm Using a Transformation to Improve Mixing Gelman-Rubin Diagnostics
Simulating Samples From a Known Density Box-Cox Transformation Logistic Regression Model with a Diffuse Prior Logistic Regression Model with Jeffreys’ Prior Poisson Regression Nonlinear Poisson Regression Models Logistic Regression Random-Effects Model Nonlinear Poisson Regression Random-Effects Model Multivariate Normal Random-Effects Model Change Point Models Exponential and Weibull Survival Analysis Time Independent Cox Model Time Dependent Cox Model Piecewise Exponential Frailty Model Normal Regression with Interval Censoring Constrained Analysis Implement a New Sampling Algorithm Using a Transformation to Improve Mixing Gelman-Rubin Diagnostics - References
Example 54.18 Using a Transformation to Improve Mixing
Proper transformations of parameters can often improve the mixing in PROC MCMC. You already saw this in Nonlinear Poisson Regression Models, which sampled using the 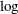 scale of parameters that priors that are strictly positive, such as the gamma priors. This example shows another useful transformation: the logit transformation on parameters that take a uniform prior on [0, 1].
scale of parameters that priors that are strictly positive, such as the gamma priors. This example shows another useful transformation: the logit transformation on parameters that take a uniform prior on [0, 1].
The data set is taken from Sharples (1990). It is used in Chaloner and Brant (1988) and Chaloner (1994) to identify outliers in the data set in a two-level hierarchical model. Congdon (2003) also uses this data set to demonstrates the same technique. This example uses the data set to illustrate how mixing can be improved using transformation and does not address the question of outlier detection as in those papers. The following statements create the data set:
data inputdata; input nobs grp y @@; ind = _n_; datalines; 1 1 24.80 2 1 26.90 3 1 26.65 4 1 30.93 5 1 33.77 6 1 63.31 1 2 23.96 2 2 28.92 3 2 28.19 4 2 26.16 5 2 21.34 6 2 29.46 1 3 18.30 2 3 23.67 3 3 14.47 4 3 24.45 5 3 24.89 6 3 28.95 1 4 51.42 2 4 27.97 3 4 24.76 4 4 26.67 5 4 17.58 6 4 24.29 1 5 34.12 2 5 46.87 3 5 58.59 4 5 38.11 5 5 47.59 6 5 44.67 ;
There are five groups (grp,  ) with six observations (nobs,
) with six observations (nobs, 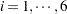 ) in each. The two-level hierarchical model is specified as follows:
) in each. The two-level hierarchical model is specified as follows:
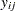 |
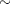 |
 |
|||
 |
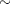 |
 |
|||
 |
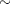 |
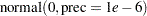 |
|||
 |
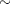 |
 |
|||
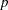 |
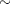 |
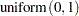 |
with the precision parameters related to each other in the following way:
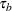 |
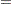 |
 |
|||
 |
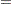 |
 |
The total number of parameters in this model is eight: 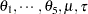 , and
, and 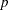 .
.
The following statements fit the model:
ods graphics on;
proc mcmc data=inputdata nmc=50000 thin=10 outpost=m1 seed=17
plot=trace;
ods select ess tracepanel;
parms p;
parms tau;
parms mu;
prior p ~ uniform(0,1);
prior tau ~ gamma(shape=0.001,iscale=0.001);
prior mu ~ normal(0,prec=0.00000001);
beginnodata;
taub = tau/p;
tauw = taub-tau;
endnodata;
random theta ~ normal(mu, prec=taub) subject=grp monitor=(theta);
model y ~ normal(theta,prec=tauw);
run;
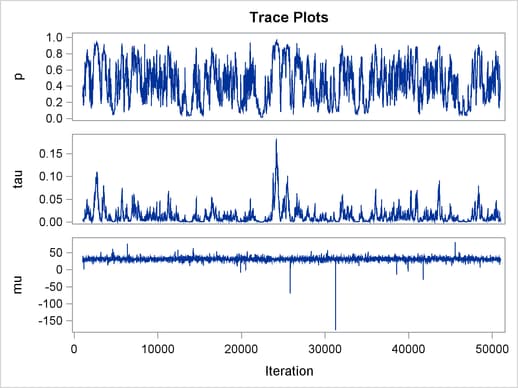
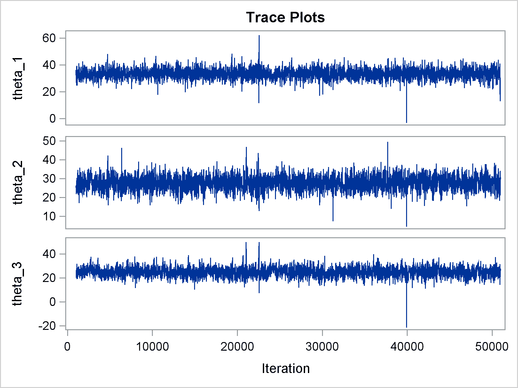
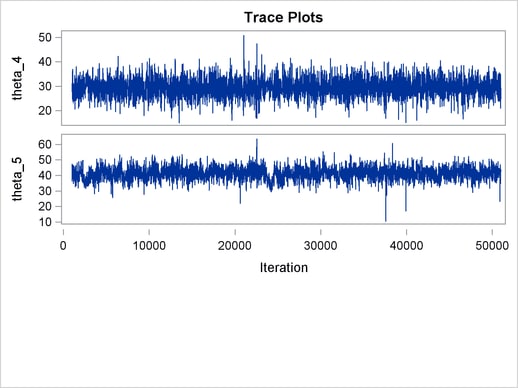
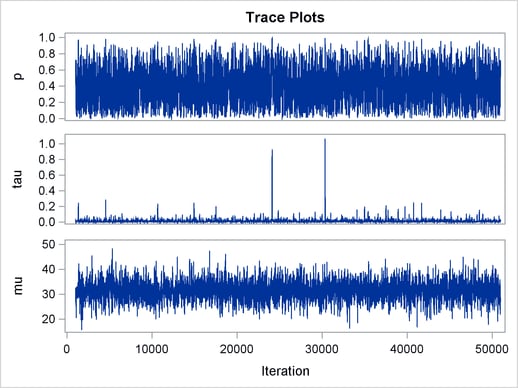
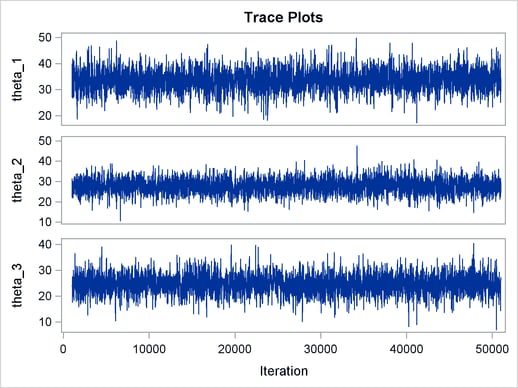
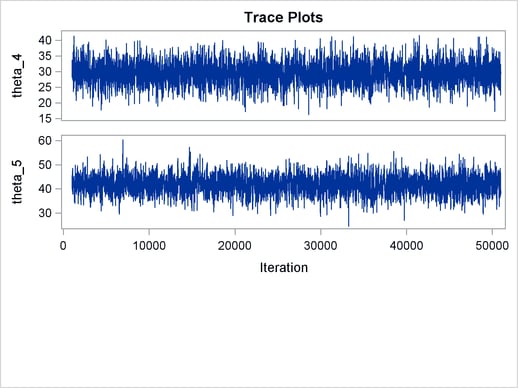
The ODS SELECT statement displays the effective sample size table and the trace plots. The ODS GRAPHICS ON statement enables ODS Graphics. The PROC MCMC statement specifies the usual options for the procedure run and produces trace plots (PLOTS=TRACE). The three PARMS statements put three model parameters, p, tau, and mu, in three different blocks. The PRIOR statements specify the prior distributions, and the programming statements enclosed with the BEGINNODATA and ENDNODATA statements calculate the transformation to taub and tauw. The RANDOM statement specifies the random effect, its prior distribution, and the subject variable. The resulting trace plots are shown in Output 54.18.1, and the effective sample size table is shown in Output 54.18.2.
| Implement a New Sampling Algorithm |
| Effective Sample Sizes | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | ESS | Autocorrelation Time |
Efficiency |
| p | 90.3 | 55.3525 | 0.0181 |
| tau | 84.1 | 59.4546 | 0.0168 |
| mu | 4175.9 | 1.1973 | 0.8352 |
| theta_1 | 3574.2 | 1.3989 | 0.7148 |
| theta_2 | 3341.0 | 1.4966 | 0.6682 |
| theta_3 | 1879.8 | 2.6598 | 0.3760 |
| theta_4 | 3417.1 | 1.4632 | 0.6834 |
| theta_5 | 784.8 | 6.3708 | 0.1570 |
The trace plots show that most parameters have relatively good mixing. Two exceptions appear to be 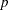 and
and  . The trace plot of
. The trace plot of 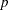 shows a slow periodic movement. The
shows a slow periodic movement. The  parameter does not have good mixing either. When the values are close to zero, the chain stays there for periods of time. An inspection of the effective sample sizes table reveals the same conclusion:
parameter does not have good mixing either. When the values are close to zero, the chain stays there for periods of time. An inspection of the effective sample sizes table reveals the same conclusion: 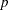 and
and  have much smaller ESSs than the rest of the parameters.
have much smaller ESSs than the rest of the parameters.
A scatter plot of the posterior samples of 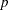 and
and  reveals why mixing is bad in these two dimensions. The following statements generate the scatter plot in Output 54.18.3:
reveals why mixing is bad in these two dimensions. The following statements generate the scatter plot in Output 54.18.3:
title 'Scatter Plot of Parameters on Original Scales'; proc sgplot data=m1; yaxis label = 'p'; xaxis label = 'tau' values=(0 to 0.4 by 0.1); scatter x = tau y = p; run;
 versus
versus 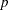
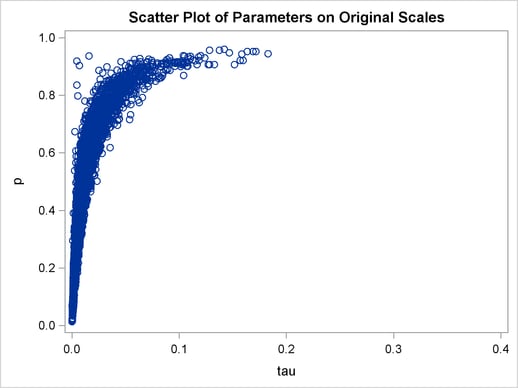
The two parameters clearly have a nonlinear relationship. It is not surprising that the Metropolis algorithm does not work well here. The algorithm is designed for cases where the parameters are linearly related with each other.
To improve on mixing, you can sample on the log of  , instead of sampling on
, instead of sampling on  . The formulation is:
. The formulation is:
 |
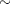 |
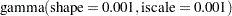 |
|||
 |
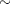 |
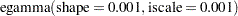 |
See the section Standard Distributions for the definitions of the gamma and egamma distributions. In addition, you can sample on the logit of 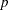 . Note that
. Note that
 |
is equivalent to
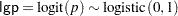 |
The following statements fit the same model by using transformed parameters:
proc mcmc data=inputdata nmc=50000 thin=10 outpost=m2 seed=17
monitor=(p tau mu) plot=trace;
ods select ess tracepanel;
parms ltau lgp mu ;
prior ltau ~ egamma(shape=0.001,iscale=0.001);
prior lgp ~ logistic(0,1);
prior mu ~ normal(0,prec=0.00000001);
beginnodata;
tau = exp(ltau);
p = logistic(lgp);
taub = tau/p;
tauw = taub-tau;
endnodata;
random theta ~ normal(mu, prec=taub) subject=grp monitor=(theta);
model y ~ normal(theta,prec=tauw);
run;
The variable lgp is the logit transformation of 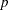 , and ltau is the log transformation of
, and ltau is the log transformation of  . The prior for ltau is egamma, and the prior for lgp is logistic. The tau and p assignment statements transform the parameters back to their original scales. The rest of the programs remain unchanged. Trace plots (Output 54.18.4) and effective sample size (Output 54.18.5) both show significant improvements in the mixing for both
. The prior for ltau is egamma, and the prior for lgp is logistic. The tau and p assignment statements transform the parameters back to their original scales. The rest of the programs remain unchanged. Trace plots (Output 54.18.4) and effective sample size (Output 54.18.5) both show significant improvements in the mixing for both 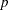 and
and  .
.
| Effective Sample Sizes | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | ESS | Autocorrelation Time |
Efficiency |
| p | 3120.9 | 1.6021 | 0.6242 |
| tau | 2304.1 | 2.1700 | 0.4608 |
| mu | 3989.1 | 1.2534 | 0.7978 |
| theta_1 | 3725.2 | 1.3422 | 0.7450 |
| theta_2 | 4007.3 | 1.2477 | 0.8015 |
| theta_3 | 3736.7 | 1.3381 | 0.7473 |
| theta_4 | 3900.2 | 1.2820 | 0.7800 |
| theta_5 | 3116.3 | 1.6044 | 0.6233 |
The following statements generate Output 54.18.6 and Output 54.18.7:
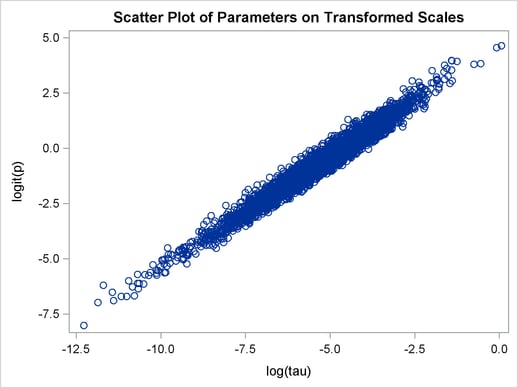
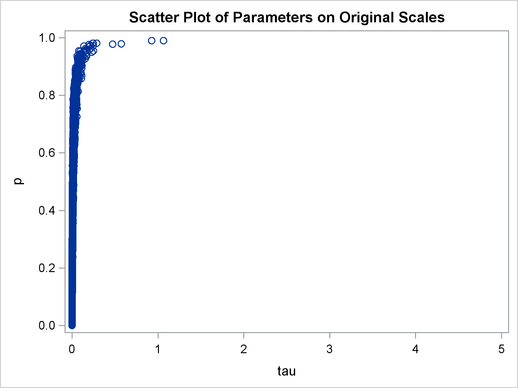
title 'Scatter Plot of Parameters on Transformed Scales'; proc sgplot data=m2; yaxis label = 'logit(p)'; xaxis label = 'log(tau)'; scatter x = ltau y = lgp; run; title 'Scatter Plot of Parameters on Original Scales'; proc sgplot data=m2; yaxis label = 'p'; xaxis label = 'tau' values=(0 to 5.0 by 1); scatter x = tau y = p; run; ods graphics off;
 versus
versus 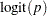 , After Transformation
, After Transformation
 versus
versus 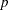 , After Transformation
, After Transformation
The scatter plot of  versus
versus 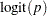 shows a linear relationship between the two transformed parameters, and this explains the improvement in mixing. In addition, the transformations also help the Markov chain better explore in the original parameter space. Output 54.18.7 shows a scatter plot of
shows a linear relationship between the two transformed parameters, and this explains the improvement in mixing. In addition, the transformations also help the Markov chain better explore in the original parameter space. Output 54.18.7 shows a scatter plot of  versus
versus 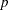 . The plot is similar to Output 54.18.3. However, note that tau has a far longer tail in Output 54.18.7, extending all the way to 5 as opposed to 0.15 in Output 54.18.3. This means that the second Markov chain can explore this dimension of the parameter more efficiently, and as a result, you are able to draw more precise inference with an equal number of simulations.
. The plot is similar to Output 54.18.3. However, note that tau has a far longer tail in Output 54.18.7, extending all the way to 5 as opposed to 0.15 in Output 54.18.3. This means that the second Markov chain can explore this dimension of the parameter more efficiently, and as a result, you are able to draw more precise inference with an equal number of simulations.