The UNIVARIATE Procedure
- Overview
-
Getting Started

-
Syntax

-
Details
 Missing ValuesRoundingDescriptive StatisticsCalculating the ModeCalculating PercentilesTests for LocationConfidence Limits for Parameters of the Normal DistributionRobust EstimatorsCreating Line Printer PlotsCreating High-Resolution GraphicsUsing the CLASS Statement to Create Comparative PlotsPositioning InsetsFormulas for Fitted Continuous DistributionsGoodness-of-Fit TestsKernel Density EstimatesConstruction of Quantile-Quantile and Probability PlotsInterpretation of Quantile-Quantile and Probability PlotsDistributions for Probability and Q-Q PlotsEstimating Shape Parameters Using Q-Q PlotsEstimating Location and Scale Parameters Using Q-Q PlotsEstimating Percentiles Using Q-Q PlotsInput Data SetsOUT= Output Data Set in the OUTPUT StatementOUTHISTOGRAM= Output Data SetOUTKERNEL= Output Data SetOUTTABLE= Output Data SetTables for Summary StatisticsODS Table NamesODS Tables for Fitted DistributionsODS GraphicsComputational Resources
Missing ValuesRoundingDescriptive StatisticsCalculating the ModeCalculating PercentilesTests for LocationConfidence Limits for Parameters of the Normal DistributionRobust EstimatorsCreating Line Printer PlotsCreating High-Resolution GraphicsUsing the CLASS Statement to Create Comparative PlotsPositioning InsetsFormulas for Fitted Continuous DistributionsGoodness-of-Fit TestsKernel Density EstimatesConstruction of Quantile-Quantile and Probability PlotsInterpretation of Quantile-Quantile and Probability PlotsDistributions for Probability and Q-Q PlotsEstimating Shape Parameters Using Q-Q PlotsEstimating Location and Scale Parameters Using Q-Q PlotsEstimating Percentiles Using Q-Q PlotsInput Data SetsOUT= Output Data Set in the OUTPUT StatementOUTHISTOGRAM= Output Data SetOUTKERNEL= Output Data SetOUTTABLE= Output Data SetTables for Summary StatisticsODS Table NamesODS Tables for Fitted DistributionsODS GraphicsComputational Resources -
Examples
 Computing Descriptive Statistics for Multiple VariablesCalculating ModesIdentifying Extreme Observations and Extreme ValuesCreating a Frequency TableCreating Plots for Line Printer OutputAnalyzing a Data Set With a FREQ VariableSaving Summary Statistics in an OUT= Output Data SetSaving Percentiles in an Output Data SetComputing Confidence Limits for the Mean, Standard Deviation, and VarianceComputing Confidence Limits for Quantiles and PercentilesComputing Robust EstimatesTesting for LocationPerforming a Sign Test Using Paired DataCreating a HistogramCreating a One-Way Comparative HistogramCreating a Two-Way Comparative HistogramAdding Insets with Descriptive StatisticsBinning a HistogramAdding a Normal Curve to a HistogramAdding Fitted Normal Curves to a Comparative HistogramFitting a Beta CurveFitting Lognormal, Weibull, and Gamma CurvesComputing Kernel Density EstimatesFitting a Three-Parameter Lognormal CurveAnnotating a Folded Normal CurveCreating Lognormal Probability PlotsCreating a Histogram to Display Lognormal FitCreating a Normal Quantile PlotAdding a Distribution Reference LineInterpreting a Normal Quantile PlotEstimating Three Parameters from Lognormal Quantile PlotsEstimating Percentiles from Lognormal Quantile PlotsEstimating Parameters from Lognormal Quantile PlotsComparing Weibull Quantile PlotsCreating a Cumulative Distribution PlotCreating a P-P Plot
Computing Descriptive Statistics for Multiple VariablesCalculating ModesIdentifying Extreme Observations and Extreme ValuesCreating a Frequency TableCreating Plots for Line Printer OutputAnalyzing a Data Set With a FREQ VariableSaving Summary Statistics in an OUT= Output Data SetSaving Percentiles in an Output Data SetComputing Confidence Limits for the Mean, Standard Deviation, and VarianceComputing Confidence Limits for Quantiles and PercentilesComputing Robust EstimatesTesting for LocationPerforming a Sign Test Using Paired DataCreating a HistogramCreating a One-Way Comparative HistogramCreating a Two-Way Comparative HistogramAdding Insets with Descriptive StatisticsBinning a HistogramAdding a Normal Curve to a HistogramAdding Fitted Normal Curves to a Comparative HistogramFitting a Beta CurveFitting Lognormal, Weibull, and Gamma CurvesComputing Kernel Density EstimatesFitting a Three-Parameter Lognormal CurveAnnotating a Folded Normal CurveCreating Lognormal Probability PlotsCreating a Histogram to Display Lognormal FitCreating a Normal Quantile PlotAdding a Distribution Reference LineInterpreting a Normal Quantile PlotEstimating Three Parameters from Lognormal Quantile PlotsEstimating Percentiles from Lognormal Quantile PlotsEstimating Parameters from Lognormal Quantile PlotsComparing Weibull Quantile PlotsCreating a Cumulative Distribution PlotCreating a P-P Plot - References
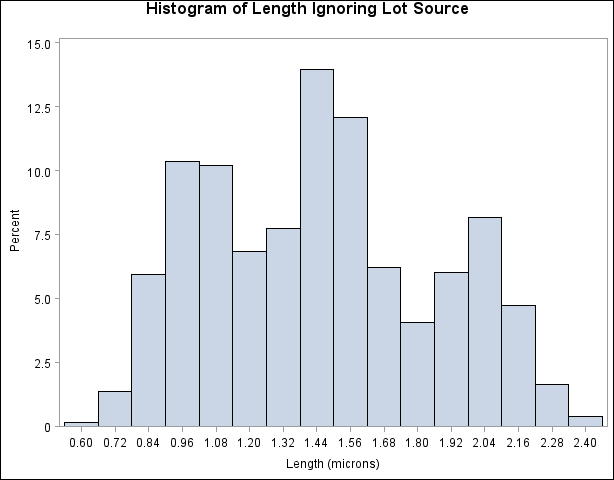
This example illustrates how to create a comparative histogram. The effective channel length (in microns) is measured for
1225 field effect transistors. The channel lengths (Length) are stored in a data set named Channel, which is partially listed in Output 4.15.1:
Output 4.15.1: Partial Listing of Data Set Channel
| The Data Set Channel |
| Lot | Length |
|---|---|
| Lot 1 | 0.91 |
| . | . |
| Lot 1 | 1.17 |
| Lot 2 | 1.47 |
| . | . |
| Lot 2 | 1.39 |
| Lot 3 | 2.04 |
| . | . |
| Lot 3 | 1.91 |
The following statements request a histogram of Length ignoring the lot source:
title 'Histogram of Length Ignoring Lot Source'; ods graphics off; proc univariate data=Channel noprint; histogram Length; run;
The resulting histogram is shown in Output 4.15.2.
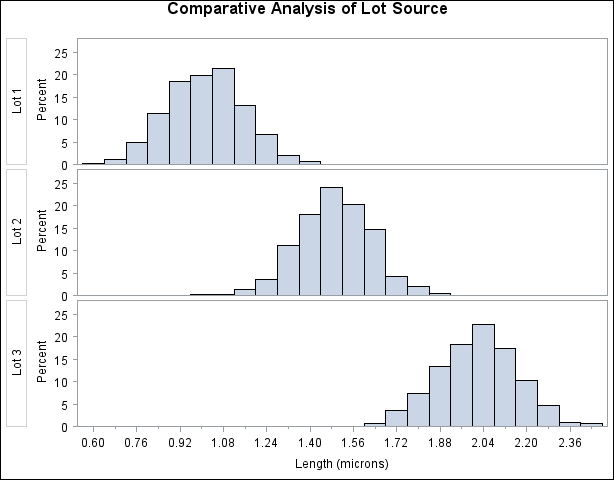
To investigate whether the peaks (modes) in Output 4.15.2 are related to the lot source, you can create a comparative histogram by using Lot as a classification variable. The following statements create the histogram shown in Output 4.15.3:
title 'Comparative Analysis of Lot Source'; ods graphics off; proc univariate data=Channel noprint; class Lot; histogram Length / nrows = 3; run;
The CLASS statement requests comparisons for each level (distinct value) of the classification variable Lot. The HISTOGRAM statement requests a comparative histogram for the variable Length. The NROWS= option specifies the number of rows per panel in the comparative histogram. By default, comparative histograms
are displayed in two rows per panel.
Output 4.15.3 reveals that the distributions of Length are similarly distributed except for shifts in mean.
A sample program for this example, uniex09.sas, is available in the SAS Sample Library for Base SAS software.