|
|
COM/DCOM
Setting Default COM Security on Windows NT/2000
Default COM security affects all COM applications that do not have launch permissions of their own.
- If authentication is used, client machines that receive events from a DCOM server must include "Everyone" in the default access permissions.
- If authentication is not used, client machines must specify "None" in the default access permissions.
To set default COM security on Windows NT/2000:
From the Windows taskbar, click Start 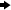 Run. Run. Type dcomcnfg and click OK. The Distributed COM Configuration Properties window appears. Select the Default Security tab.
- From the Default Security tab, you must edit the Default Access Permissions and
the Default Launch Permissions. (The Default Configuration Permissions are
adequate for a development environment). For details, see the following topics:
Global Access Permissions
To set global access policies for selected users and groups from the Default Security tab of dcomcnfg:
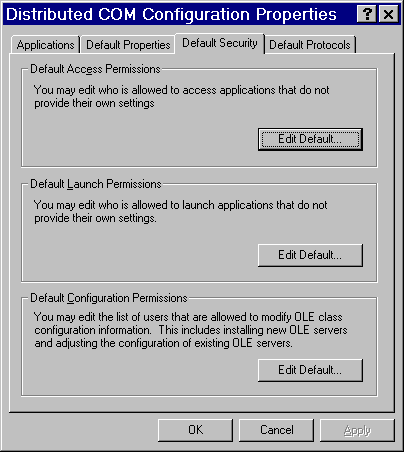
In the Default Access Permissions box, click Edit Default.
The following dialog box appears, showing current registry settings for the Default Access Permissions:
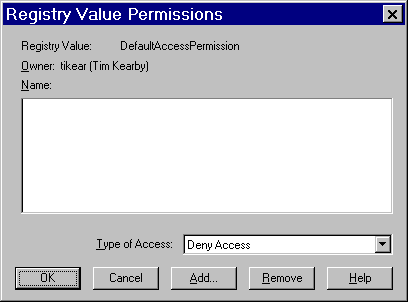
To add users and groups to the list, click Add. The Add Users and Groups dialog box appears.
Use the Add Users and Groups dialog box to identify the users and groups at your site and the type of access (allow or deny access).
You should also give access permission to System.
For field descriptions, refer to the Windows NT or Windows 2000 Help. When you are finished, click OK and then OK again to return to
the Default Security tab.
Global Launch Permissions
To set global launch permissions for selected users and groups from the Default Security tab of dcomcnfg:
In the Default Launch Permissions box, click Edit Default.
The following dialog box appears, showing the current registry settings for Default Launch Permissions.
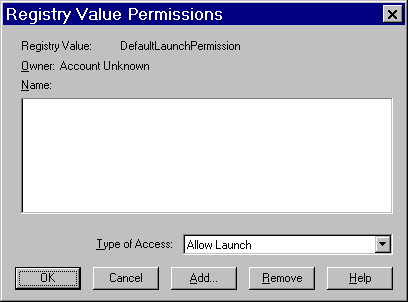
Click Add to add users and groups to the list. The following dialog box appears.
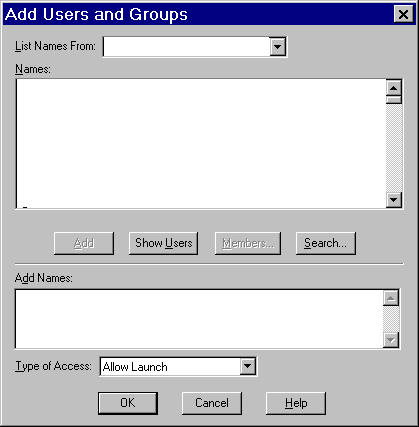
Use the Add Users and Groups dialog box to identify users and groups at your site and the type of access (allow or deny
launch access). It is recommended
that you enter the same values that you entered for the Default Access Permissions.
You should also give launch permission to System. When you are finished, click OK and then OK again to return to the Default Security tab.
Global Configuration Permissions
To set global configuration permissions for selected users and groups from the Default Security tab of dcomcnfg:
If you need to specify more restrictive configuration permissions, from the
Default Security tab of dcomcnfg, click Edit Default in the Default Configuration Permissions box. Consult the Windows NT or Windows 2000 Help for further information. When you are finished, click OK to save the new settings and exit from the dcomcnfg utility.
|




