SAS 9.1.3 Integration Technologies » Administrator's Guide
|
Foundation Services
Understanding How Applications Deploy Foundation ServicesApplications can access service deployments from a SAS Metadata Repository or an XML file (that contains exported metadata). Applications deploy services as follows:
Note: A foundation service-enabled application can be either a standard client application or a Web client application that runs in a servlet container. Your application must install the appropriate JAR files (for example, sas.svc.core.jar) in a location that is only accessible to its own classloader. This installation restriction is due to the inheritance hierarchy of classloaders. This inheritance hierarchy enables multiple applications to access classes that are available to higher level class loaders. Therefore, each foundation service-enabled application should NOT install the required JAR files in a location that is accessible to a class loader that might be shared amongst multiple applications. For details about coding client applications for service deployment, see the SAS Foundation Services class documentation for com.sas.services.deployment and com.sas.services.discovery and the SAS Integration Technologies: Developer's Guide. The following diagram shows these components and how they work together. 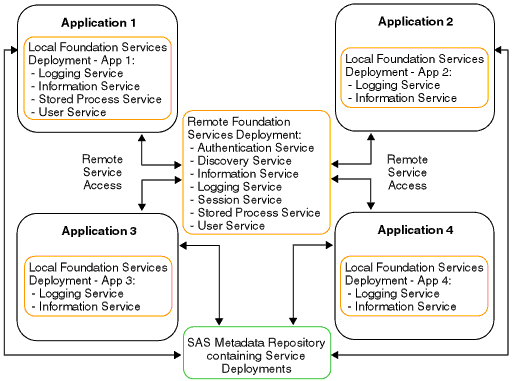 In the diagram, Applications 1 through 4 all access their local and remote service deployment configurations from a SAS Metadata Repository. If Application 1 deploys the remote service deployment, the services are registered with a local Discovery Service and a remote Discovery Service. Applications 2, 3, and 4 can then use the remote Discovery Service to locate and access the deployed remote services. All of the applications share the same remote service deployment. In addition, each application has exclusive access to its own local service deployment. For information about how applications locate and access services, see Understanding How Applications Locate Services. The different components in the diagram might exist on the same Web server, or on different Web servers. You can install your applications and deploy your services on separate machines as required by the needs of your implementation. For information about distributing service deployments, see Redistributing Service Deployments. |