|
|
Getting Started
Planning for Metadata Definitions
To plan your server metadata, you must first plan for your SAS application server and logical server definitions. This page describes the SAS application server and logical server concepts.
Understanding SAS Application Servers and Logical Server Definitions
At a minimum, the metadata for a SAS server consists of three definitions: a SAS application server, a logical server, and a server. The following diagram shows how the SAS application server, logical server, and servers are related.
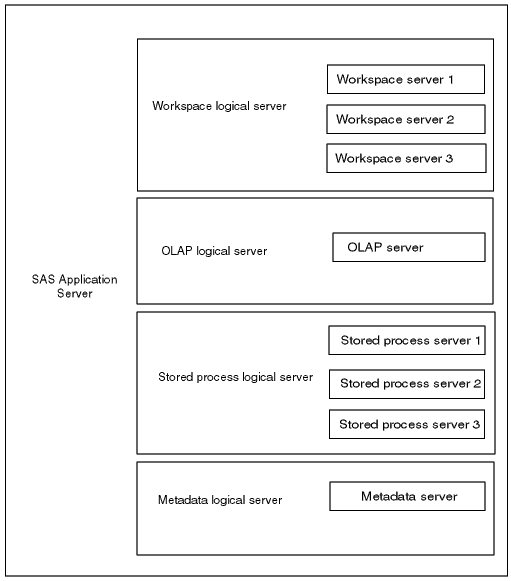
SAS application server.
A SAS application server is a metadata definition that contains one or more logical servers. A SAS application server enables you to specify resource metadata that applies to all of the logical servers and servers that it contains. A SAS application server is a container to which you can assign libraries, schemas, directories and other resources that are available to SAS servers, regardless of the type of server. For example, when you define a SAS library in the Data Library Manager, you assign the library to a SAS application server; all of the servers within the SAS application server will have access to the library.
The SAS application server definition and logical servers are not actual server definitions.
In SAS Management Console, when you define the first server of a SAS application server, three definitions are created:
- the SAS application server definition
- a logical server definition
- a server definition
The SAS application server definition contains the logical server definition and its corresponding server definition.
A SAS application server can contain one or more logical server definitions. However, each SAS application server can contain only one of each type of logical server. The types of logical
servers correspond to the four types of IOM servers: SAS Metadata Server (COM connection is experimental), SAS Workspace Server, SAS Stored Process Server (IOM Bridge connection only), and SAS OLAP Server. For example, in one SAS application server definition, you can have up to 4 logical servers: one logical metadata server (COM connection is experimental), one logical workspace server, one logical stored process server (IOM Bridge connection only), and one logical OLAP server.
Logical servers.
For SAS Stored Process Servers (IOM Bridge connection only) and SAS Workspace Servers, a logical server definition contains one or more server definitions. For SAS OLAP Servers and SAS Metadata Servers (COM connection is experimental), a logical server contains one server definition. However, each logical server can contain only one type of IOM server. For example, a logical workspace server can only contain workspace servers.
After you have created a particular type of logical server within the SAS application server definition,
you can then add servers to this logical server and do one of the following:
- Leave the servers as standard servers that do not pool or load balance within the logical server group. In this case, the multiple standard servers are used as redundant servers to provide fail-over capability. Clients that cannot connect to the first server will try subsequent servers within the logical server.
- For workspace servers (IOM Bridge or COM connection), convert the logical server to a pooled logical server and set pooling parameters on the servers that are contained within the logical server group.
- For workspace or stored process servers (IOM Bridge connection only), convert the logical server to a load-balancing logical server and set load-balancing parameters on the servers that are contained within the logical server group.
- Servers. A server definition contains the actual server metadata required to connect to a SAS server on a particular machine.
The following diagram shows the SAS application server, logical server, and servers defined
in SAS Management Console:

After you have planned for your metadata, you can set up a server with a COM or IOM Bridge connection:
|

