GPROJECT Procedure
Overview: GPROJECT Procedure
The GPROJECT procedure
processes GfK and traditionalmap
data sets by converting spherical coordinates (longitude and latitude)
into Cartesian coordinates for use by the GMAP procedure. The process
of converting coordinates from spherical to Cartesian is called projecting.
All of the GfK and many of the traditional map data sets that are
available with SAS/GRAPH
contain unprojected longitude and latitude coordinates. When these
coordinates are plotted by the GMAP procedure, which is designed to
plot points on a two-dimensional plane, the resulting map is often
reversed and distorted as a result of forcing the spherical map coordinates
onto a flat plane.
The GPROJECT procedure
enables you to use one of several map projection techniques to project
the latitude and longitude coordinates onto a two-dimensional plane
while attempting to minimize the distortion of area, distance, direction,
and shape properties of the original sphere. The output map data set
that is produced by the GPROJECT procedure contains Cartesian coordinates
that can be displayed correctly using the GMAP procedure.
The GPROJECT procedure
can also create a rectangular subset of the input map data set by
excluding all points with longitude and latitude values that fall
outside of a specified range. This provides a simple way to reduce
the size of the map data set if you need only a portion of a larger
map.
The GPROJECT procedure
does not produce any graphics output. Instead, it produces an output
map data set, which can be used as the input map data set for the
GMAP procedure (see GMAP Procedure).
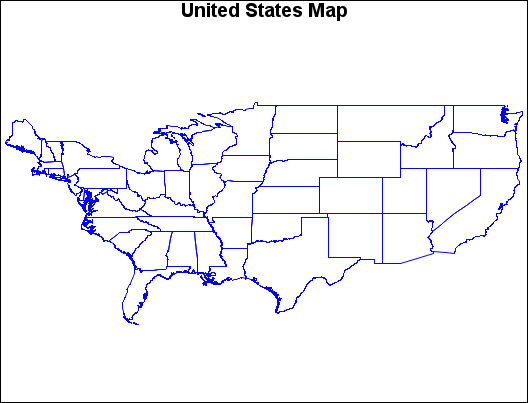
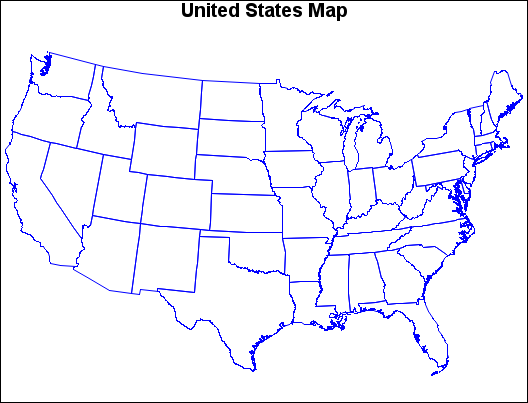
Map before Projection (GPJDEFLT(a)) and Map after Projection (GPJDEFLT(b)) illustrate the effect of using GPROJECT defaults (Albers
projection with standard parallels that are calculated by the procedure)
to project a typical map data set with coordinates that are stored
as longitude and latitude.
The program for the
following maps can be seen in Using Default Projection Specifications.