|
|
COM/DCOM
Enabling DCOM on the Server and the Client
To establish a DCOM session, you must ensure that DCOM is enabled on the server machine and on each client machine. Perform the following steps on each machine:
From the Windows Taskbar, click Start  Run. Run. - Type
dcomcnfg, as shown in the illustration.
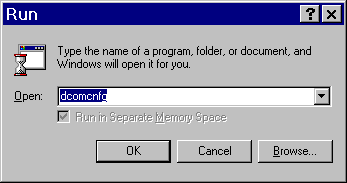
Click OK. The dialog box that appears depends on the Windows operating system you are using:
- If you are using Windows NT/2000, the Distributed COM Configuration Properties dialog box appears.
- If you are using Windows XP, the Component Services dialog box appears. Expand the Component Services folder,
expand the Computers folder, then right-click on My Computer and select Properties.
Select the Default Properties tab.
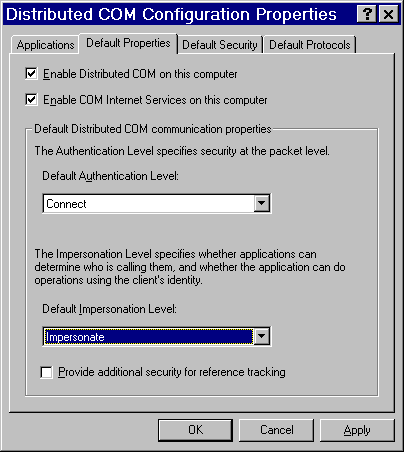
Note: The dialog box might look slightly different than the illustration, depending on the version of Windows you are running and which Service Pack you have applied.
Select Enable Distributed COM on this computer. COM uses the Default Authentication Level when a client or server does
not provide a specific value, either programmatically or on the Applications tab
(which creates an AppID-based setting in the Windows registry). For Default
Authentication Level, choose the value that is most appropriate for applications
that do not have a specific setting of their own. This value will not be used by
an IOM server if you set its authentication level individually using the
Application tab (see Setting Permissions per Application on
Windows NT/2000
and Windows XP).
Select an Authentication level of Connect to provide a good balance between security and system performance. More restrictive security levels can be required based on the needs of your site and your users. For a description of additional levels, consult the Windows NT Help.
Note: Currently, event output from the SAS server sent to client applications cannot be encrypted due to Microsoft COM restrictions. It is recommended that you select an Impersonation Level of Impersonate.
This completes the steps necessary to enable DCOM on the clients and servers.
|

