The STDRATE Procedure
- Overview
- Getting Started
-
Syntax

-
Details
 RateRiskDirect StandardizationMantel-Haenszel Effect EstimationIndirect Standardization and Standardized Morbidity/Mortality RatioAttributable Fraction and Population Attributable FractionApplicable Data Sets and Required Variables for Method SpecificationsApplicable Confidence Limits for Rate and Risk StatisticsTable OutputODS Table NamesGraphics OutputODS Graphics
RateRiskDirect StandardizationMantel-Haenszel Effect EstimationIndirect Standardization and Standardized Morbidity/Mortality RatioAttributable Fraction and Population Attributable FractionApplicable Data Sets and Required Variables for Method SpecificationsApplicable Confidence Limits for Rate and Risk StatisticsTable OutputODS Table NamesGraphics OutputODS Graphics -
Examples

- References
Example 107.3 Computing Attributable Fraction Estimates
This example computes the excess event risk fraction that is attributable to a specific chemical exposure for workers in a factory.
Suppose that the Factory data set contains the stratum-specific event information for exposure to a specific chemical agent. The variable Age is the grouping variable that forms the strata. The variables Event_E and Count_E indicate the number of events and number of workers for workers with the specific chemical exposure, respectively. The variables
Event_NE and Count_NE indicate the number of events and number of workers for workers without the specific chemical exposure, respectively.
data Factory; input Age $ Event_E Count_E Event_NE Count_NE; datalines; 20-29 31 352 143 2626 30-39 57 486 392 4124 40-49 62 538 459 4662 50-59 50 455 337 3622 60-69 38 322 199 2155 70+ 9 68 35 414 ;
The following statements invoke the STDRATE procedure and compute the attributable risk and population attributable risk for the chemical exposure:
ods graphics on;
proc stdrate data=Factory
refdata=Factory
method=indirect(af)
stat=risk
plots(stratum=horizontal)
;
population event=Event_E total=Count_E;
reference event=Event_NE total=Count_NE;
strata Age / stats;
run;
The "Standardization Information" table in Output 107.3.1 displays the standardization information.
Output 107.3.1: Standardization Information
The STATS option in the STRATA statement requests that the "Indirectly Standardized Strata Statistics" table in Output 107.3.2 display the strata information and the expected number of events at each stratum. The Expected Events column shows the expected numbers of events when the stratum-specific risks in the reference data set are applied to the corresponding numbers of workers in the study data set.
Output 107.3.2: Strata Information (Indirect Standardization)
| Indirectly Standardized Strata Statistics | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stratum Index |
Age | Study Population | Reference Population | Expected Events |
||||||||
| Observed Events |
Number of Observations | Crude Risk | Standard Error |
Number of Observations | Crude Risk |
|||||||
| Value | Proportion | 95% Normal Confidence Limits |
Value | Proportion | ||||||||
| 1 | 20-29 | 31 | 352 | 0.1585 | 0.088068 | 0.015105 | 0.058463 | 0.117673 | 2626 | 0.1492 | 0.05446 | 19.1683 |
| 2 | 30-39 | 57 | 486 | 0.2188 | 0.117284 | 0.014595 | 0.088678 | 0.145890 | 4124 | 0.2343 | 0.09505 | 46.1959 |
| 3 | 40-49 | 62 | 538 | 0.2422 | 0.115242 | 0.013767 | 0.088260 | 0.142224 | 4662 | 0.2648 | 0.09846 | 52.9691 |
| 4 | 50-59 | 50 | 455 | 0.2049 | 0.109890 | 0.014662 | 0.081153 | 0.138627 | 3622 | 0.2058 | 0.09304 | 42.3343 |
| 5 | 60-69 | 38 | 322 | 0.1450 | 0.118012 | 0.017979 | 0.082774 | 0.153251 | 2155 | 0.1224 | 0.09234 | 29.7346 |
| 6 | 70+ | 9 | 68 | 0.0306 | 0.132353 | 0.041095 | 0.051809 | 0.212897 | 414 | 0.0235 | 0.08454 | 5.7488 |
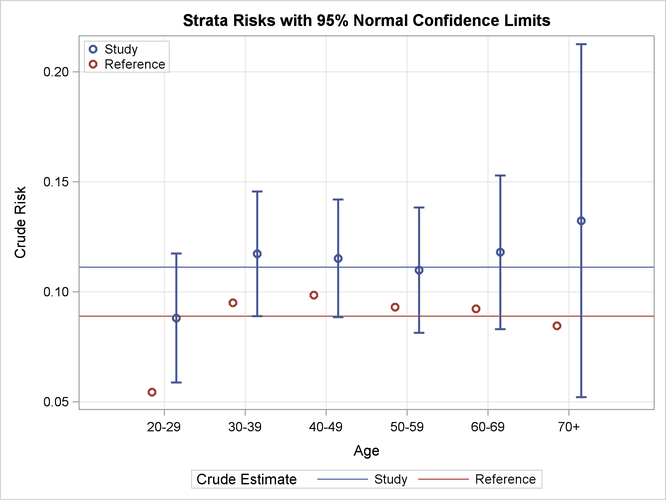
With ODS Graphics enabled and the specified STAT=RISK option, the default PLOTS=RISK option displays the stratum-specific risk estimates in the study and reference populations, as shown in Output 107.3.3. The STRATUM=HORIZONTAL global option in the PLOTS option displays the strata information on the horizontal axis. The plot displays the stratum-specific risk estimates in the "Indirect Standardized Strata Statistics" table in Output 107.3.2. In addition, confidence limits for the risk estimates in the study population and the overall crude risks for the two populations are also displayed
Output 107.3.3: Strata Risk Plot
The METHOD=INDIRECT option requests that the "Standardized Morbidity/Mortality Ratio" table in Output 107.3.4 display the SMR, its 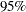 confidence limits, and the test for the null hypothesis
confidence limits, and the test for the null hypothesis 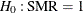 .
.
Output 107.3.4: Standardized Morbidity/Mortality Ratio
The "Standardized Morbidity/Mortality Ratio" table shows that SMR=1.259, the 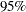 confidence limits do not contain the null value SMR=1, and the null hypothesis of SMR=1 is rejected at
confidence limits do not contain the null value SMR=1, and the null hypothesis of SMR=1 is rejected at 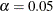 level from the normal test.
level from the normal test.
The "Indirectly Standardized Risk Estimates" table in Output 107.3.5 displays the standardized risks and related statistics.
Output 107.3.5: Standardized Risks (Indirect Standardization)
The AF suboption in the METHOD=INDIRECT option requests that the "Attributable Fraction Estimates" table display the attributable risk and population attributable risk, as shown in Output 107.3.6
Output 107.3.6: Attributable Fraction Estimates
The attributable risk fraction 0.206 indicates that 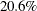 of all events in the chemical exposure group are attributed to the chemical exposure, and the population attributable risk
fraction 0.028 indicates that about
of all events in the chemical exposure group are attributed to the chemical exposure, and the population attributable risk
fraction 0.028 indicates that about 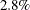 of all events in the total population are attributed to the chemical exposure.
of all events in the total population are attributed to the chemical exposure.
The Attributable fraction can also be computed by using Mantel-Haenszel method.
Suppose that the Factory1 data set contains the stratum-specific event information for exposure to a specific chemical agent. The variable Age is the grouping variable that forms the strata, and the variable Exposure identifies workers with chemical exposure. The variables Event and Count indicate the number of events and number of workers, respectively.
data Factory1; input Exposure $ Age $ Event Count; datalines; Yes 20-29 31 352 Yes 30-39 57 486 Yes 40-49 62 538 Yes 50-59 50 455 Yes 60-69 38 322 Yes 70+ 9 68 No 20-29 143 2626 No 30-39 392 4124 No 40-49 459 4662 No 50-59 337 3622 No 60-69 199 2155 No 70+ 35 414 ;
The following statements invoke the STDRATE procedure and compute the attributable risk and population attributable risk for the chemical exposure:
proc stdrate data=Factory1
method=mh(af)
stat=risk
effect
;
population group(order=data exposed='Yes')=Exposure
event=Event total=Count;
strata Age;
run;
The GROUP=EXPOSURE option specifies the variable Exposure, whose values identify the various populations. The ORDER= suboption specifies the order in which the values of Exposure are to be displayed, and the EXPOSED= option identifies the exposed group in the derivation of the attributable fraction.
The "Standardization Information" table in Output 107.3.7 displays the standardization information.
Output 107.3.7: Standardization Information
The "Mantel-Haenszel Standardized Risk Estimates" table in Output 107.3.8 displays the Mantel-Haenszel standardized risks and related statistics.
Output 107.3.8: Standardized Risk Estimates (Mantel-Haenszel Estimation)
| Mantel-Haenszel Standardized Risk Estimates | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exposure | Study Population | Mantel-Haenszel | Standardized Risk | ||||||
| Observed Events |
Number of Observations |
Crude Risk |
Expected Events |
Weight | Estimate | Standard Error |
95% Normal Confidence Limits |
||
| Yes | 247 | 2221 | 0.1112 | 219.122 | 1970.26 | 0.1112 | 0.00667 | 0.0981 | 0.1243 |
| No | 1565 | 17603 | 0.0889 | 174.134 | 1970.26 | 0.0884 | 0.00214 | 0.0842 | 0.0926 |
The EFFECT option requests that the "Risk Effect Estimates" table display the risk ratio statistic for the two directly standardized risks, as shown in Output 107.3.9.
Output 107.3.9: Mantel-Haenszel Effect Estimates
The AF suboption in the METHOD=MH option requests that the "Attributable Fraction Estimates" table display the attributable risk and population attributable risk, as shown in Output 107.3.10
Output 107.3.10: Attributable Fraction Estimates
Similar to the results of using the SMR estimates, the attributable risk fraction (0.205) indicates that 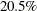 of all events in the chemical exposure group are attributed to the chemical exposure, and the population attributable risk
fraction (0.028) indicates that about
of all events in the chemical exposure group are attributed to the chemical exposure, and the population attributable risk
fraction (0.028) indicates that about 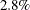 of all events in the total population are attributed to the chemical exposure.
of all events in the total population are attributed to the chemical exposure.