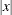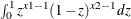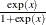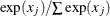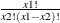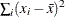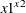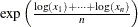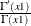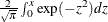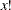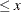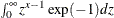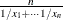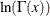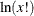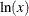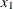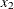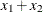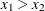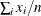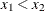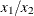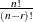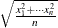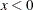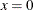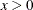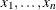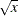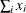The MCMC Procedure
-
Overview

-
Getting Started

-
Syntax

-
Details
 How PROC MCMC WorksBlocking of ParametersSampling MethodsTuning the Proposal DistributionDirect SamplingConjugate SamplingInitial Values of the Markov ChainsAssignments of ParametersStandard DistributionsUsage of Multivariate DistributionsSpecifying a New DistributionUsing Density Functions in the Programming StatementsTruncation and CensoringSome Useful SAS FunctionsMatrix Functions in PROC MCMCCreate Design MatrixModeling Joint LikelihoodAccess Lag and Lead VariablesCALL ODE and CALL QUAD SubroutinesRegenerating Diagnostics PlotsCaterpillar PlotAutocall Macros for PostprocessingGamma and Inverse-Gamma DistributionsPosterior Predictive DistributionHandling of Missing DataFunctions of Random-Effects ParametersFloating Point Errors and OverflowsHandling Error MessagesComputational ResourcesDisplayed OutputODS Table NamesODS Graphics
How PROC MCMC WorksBlocking of ParametersSampling MethodsTuning the Proposal DistributionDirect SamplingConjugate SamplingInitial Values of the Markov ChainsAssignments of ParametersStandard DistributionsUsage of Multivariate DistributionsSpecifying a New DistributionUsing Density Functions in the Programming StatementsTruncation and CensoringSome Useful SAS FunctionsMatrix Functions in PROC MCMCCreate Design MatrixModeling Joint LikelihoodAccess Lag and Lead VariablesCALL ODE and CALL QUAD SubroutinesRegenerating Diagnostics PlotsCaterpillar PlotAutocall Macros for PostprocessingGamma and Inverse-Gamma DistributionsPosterior Predictive DistributionHandling of Missing DataFunctions of Random-Effects ParametersFloating Point Errors and OverflowsHandling Error MessagesComputational ResourcesDisplayed OutputODS Table NamesODS Graphics -
Examples
 Simulating Samples From a Known DensityBox-Cox TransformationLogistic Regression Model with a Diffuse PriorLogistic Regression Model with Jeffreys’ PriorPoisson RegressionNonlinear Poisson Regression ModelsLogistic Regression Random-Effects ModelNonlinear Poisson Regression Multilevel Random-Effects ModelMultivariate Normal Random-Effects ModelMissing at Random AnalysisNonignorably Missing Data (MNAR) AnalysisChange Point ModelsExponential and Weibull Survival AnalysisTime Independent Cox ModelTime Dependent Cox ModelPiecewise Exponential Frailty ModelNormal Regression with Interval CensoringConstrained AnalysisImplement a New Sampling AlgorithmUsing a Transformation to Improve MixingGelman-Rubin DiagnosticsOne-Compartment Model with Pharmacokinetic Data
Simulating Samples From a Known DensityBox-Cox TransformationLogistic Regression Model with a Diffuse PriorLogistic Regression Model with Jeffreys’ PriorPoisson RegressionNonlinear Poisson Regression ModelsLogistic Regression Random-Effects ModelNonlinear Poisson Regression Multilevel Random-Effects ModelMultivariate Normal Random-Effects ModelMissing at Random AnalysisNonignorably Missing Data (MNAR) AnalysisChange Point ModelsExponential and Weibull Survival AnalysisTime Independent Cox ModelTime Dependent Cox ModelPiecewise Exponential Frailty ModelNormal Regression with Interval CensoringConstrained AnalysisImplement a New Sampling AlgorithmUsing a Transformation to Improve MixingGelman-Rubin DiagnosticsOne-Compartment Model with Pharmacokinetic Data - References
Some Useful SAS Functions
Table 73.43: Some Useful SAS Functions
|
SAS Function |
Definition |
|---|---|
|
abs (x); |
|
|
airy (x); |
Returns the value of the AIRY function. |
|
beta (x1, x2); |
|
|
call logistic (x); |
|
|
call softmax (x1, …, xn); |
Each element is replaced by |
|
call stdize (x1, …, xn); |
Standardize values |
|
cdf (); |
Cumulative distribution function |
|
cdf (’normal’, x, 0, 1); |
Standard normal cumulative distribution function |
|
comb (x1, x2); |
|
|
constant (’.’); |
Calculate commonly used constants |
|
cos (x); |
cosine(x) |
|
css (x1, …, xn); |
|
|
cv (x1, …, xn); |
std(x) / mean(x) * 100 |
|
dairy (x); |
Derivative of the AIRY function |
|
dimN (m); |
Returns the numbers of elements in the Nth dim of array m |
|
x1 eq x2 |
Returns 1 if x1 = x2; 0 otherwise |
|
x1**x2 |
|
|
geomean (x1, …, xn); |
|
|
difN (x); |
Returns differences between the argument and its Nth lag |
|
digamma (x1); |
|
|
erf (x); |
|
|
erfc (x); |
1 – erf(x) |
|
fact (x); |
|
|
floor (x); |
Greatest integer |
|
gamma (x); |
|
|
harmean (x1, …, xn); |
|
|
ibessel (nu, x, kode); |
Modified Bessel function of order nu evaluated at x |
|
jbessel (nu, x); |
Bessel function of order nu evaluated at x |
|
lagN (x); |
Returns values from a queue |
|
largest (k, x1, …, xn); |
Returns the kth largest element |
|
lgamma (x); |
|
|
lgamma (x+1); |
|
|
log (x, logN(x)); |
|
|
logbeta (x1, x2); |
lgamma( |
|
logcdf (); |
Log of a left cumulative distribution function |
|
logpdf (); |
Log of a probability density (mass) function |
|
logsdf (); |
Log of a survival function |
|
max (x1, x2); |
Returns |
|
mean (of x1–xn); |
|
|
median (of x1–xn); |
Returns the median of nonmissing values |
|
min (x1, x2); |
Returns |
|
missing (x); |
Returns 1 if x is missing; 0 otherwise |
|
mod (x1, x2); |
Returns the remainder from |
|
n (x1, …, xn); |
Returns number of nonmissing values |
|
nmiss (of y1–yn); |
Number of missing values |
|
quantile (); |
Computes the quantile from a specific distribution |
|
pdf (); |
Probability density (mass) functions |
|
perm (n, r); |
|
|
put (); |
Returns a value that uses a specified format |
|
round (x); |
Rounds x |
|
rms (of x1–xn); |
|
|
sdf (); |
Survival function |
|
sign (x); |
Returns –1 if |
|
sin (x); |
sine(x) |
|
smallest (s, x1, …, en ); |
Returns the sth smallest component of |
|
sortn (of x1-xn); |
Sorts the values of the variables |
|
sqrt (x); |
|
|
std (x1, …, xn) ); |
Standard deviation of |
|
sum (of x:); |
|
|
trigamma (x); |
Derivative of the DIGAMMA(x) function |
|
uss (of x1–xn); |
Uncorrected sum of squares |
Here are examples of some commonly used transformations: