The HPLOGISTIC Procedure
-
Overview

-
Getting Started

-
Syntax

-
Details
 Missing ValuesResponse DistributionsLog-Likelihood FunctionsExistence of Maximum Likelihood EstimatesUsing Validation and Test DataModel Fit and Assessment StatisticsThe Hosmer-Lemeshow Goodness-of-Fit TestComputational Method: MultithreadingChoosing an Optimization AlgorithmDisplayed OutputODS Table Names
Missing ValuesResponse DistributionsLog-Likelihood FunctionsExistence of Maximum Likelihood EstimatesUsing Validation and Test DataModel Fit and Assessment StatisticsThe Hosmer-Lemeshow Goodness-of-Fit TestComputational Method: MultithreadingChoosing an Optimization AlgorithmDisplayed OutputODS Table Names -
Examples

- References
References
-
Akaike, H. (1974). “A New Look at the Statistical Model Identification.” IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control AC-19:716–723.
-
Albert, A., and Anderson, J. A. (1984). “On the Existence of Maximum Likelihood Estimates in Logistic Regression Models.” Biometrika 71:1–10.
-
Asuncion, A., and Newman, D. J. (2007). “UCI Machine Learning Repository.” http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/.
-
Brier, G. W. (1950). “Verification of Forecasts Expressed in Terms of Probability.” Monthly Weather Review 78:1–3.
-
Burnham, K. P., and Anderson, D. R. (1998). Model Selection and Inference: A Practical Information-Theoretic Approach. New York: Springer-Verlag.
-
Cox, D. R., and Snell, E. J. (1989). The Analysis of Binary Data. 2nd ed. London: Chapman & Hall.
-
Dennis, J. E., Gay, D. M., and Welsch, R. E. (1981). “An Adaptive Nonlinear Least-Squares Algorithm.” ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software 7:348–368.
-
Dennis, J. E., and Mei, H. H. W. (1979). “Two New Unconstrained Optimization Algorithms Which Use Function and Gradient Values.” Journal of Optimization Theory and Applications 28:453–482.
-
Eskow, E., and Schnabel, R. B. (1991). “Algorithm 695: Software for a New Modified Cholesky Factorization.” ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software 17:306–312.
-
Fleiss, J. L. (1981). Statistical Methods for Rates and Proportions. 2nd ed. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Fletcher, R. (1987). Practical Methods of Optimization. 2nd ed. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Gay, D. M. (1983). “Subroutines for Unconstrained Minimization.” ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software 9:503–524.
-
Hastie, T. J., Tibshirani, R. J., and Friedman, J. H. (2001). The Elements of Statistical Learning: Data Mining, Inference, and Prediction. New York: Springer-Verlag.
-
Hosmer, D. W., Jr., and Lemeshow, S. (2000). Applied Logistic Regression. 2nd ed. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Hurvich, C. M., and Tsai, C.-L. (1989). “Regression and Time Series Model Selection in Small Samples.” Biometrika 76:297–307.
-
Lawless, J. F., and Singhal, K. (1978). “Efficient Screening of Nonnormal Regression Models.” Biometrics 34:318–327.
-
Magee, L. (1990). “
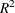 Measures Based on Wald and Likelihood Ratio Joint Significant Tests.” American Statistician 44:250–253.
Measures Based on Wald and Likelihood Ratio Joint Significant Tests.” American Statistician 44:250–253.
-
McCullagh, P., and Nelder, J. A. (1989). Generalized Linear Models. 2nd ed. London: Chapman & Hall.
-
McFadden, D. (1974). “Conditional Logit Analysis of Qualitative Choice Behavior.” In Frontiers in Econometrics, edited by P. Zarembka, 105–142. New York: Academic Press.
-
McNicol, D. (2005). A Primer of Signal Detection Theory. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
-
Moré, J. J., and Sorensen, D. C. (1983). “Computing a Trust-Region Step.” SIAM Journal on Scientific and Statistical Computing 4:553–572.
-
Murphy, A. H. (1973). “A New Vector Partition of the Probability Score.” Journal of Applied Meteorology 12:595–600.
-
Nagelkerke, N. J. D. (1991). “A Note on a General Definition of the Coefficient of Determination.” Biometrika 78:691–692.
-
Pepe, M. S. (2003). The Statistical Evaluation of Medical Tests for Classification and Prediction. New York: Oxford University Press.
-
Santner, T. J., and Duffy, D. E. (1986). “A Note on A. Albert and J. A. Anderson’s Conditions for the Existence of Maximum Likelihood Estimates in Logistic Regression Models.” Biometrika 73:755–758.
-
Schwarz, G. (1978). “Estimating the Dimension of a Model.” Annals of Statistics 6:461–464.
-
Tjur, T. (2009). “Coefficients of Determination in Logistic Regression Models—a New Proposal: The Coefficient of Discrimination.” American Statistician 63:366–372.