About Aggregation Tables
What Is an Aggregation Table?
Aggregation tables contain
data that is collected and accumulated according to rules that are
defined to an Aggregation transformation. These rules pertain to
columns from the source table and are used to classify, organize,
and calculate columns such as statistics, percentiles, and moving
statistics about IT data. The target table that is produced by an
Aggregation transformation is used for further data management, analysis,
or report processes.
With SAS IT Resource
Management, you can perform the following actions:
-
generate a simple or a summarized aggregation tableTo generate a summarized or simple aggregation table, you must first set up the Aggregation transformation. For information about setting up the Aggregation transformation, see Preparing to Create an Aggregation Table .You can then invoke one of the three wizards that enable you to specify the aggregation table.
-
For information about creating simple aggregation tables, see Creating an Aggregation Table with the Simple Aggregation Table Wizard.
-
For information about creating a summarized aggregation table, see Creating Aggregation Tables with the Summarized Aggregation Table Wizard.
-
For information about creating an aggregation table using a template, see Creating Aggregation Tables with the Aggregation through the Template Wizard.
-
-
add a column to an aggregation table
-
clone an aggregation table
-
delete an aggregation table
-
edit (or modify) an aggregation table
-
publish an aggregation table as a template
-
purge an aggregation table
-
rename an aggregation table
The tables in SAS IT
Resource Management 3.2 and later are sorted in this order: <Alphabetic
List of Class Columns> <Aging Column>.)
Note: If you want to perform BY-group
processing on the data in any other order, sort it into a work table.
Then perform the task using the work table or a view that accesses
that work table.
How Is the Metadata for an Aggregation Table Created?
Methods for Creating Metadata for an Aggregation Table
The metadata for an
aggregation table can be created in these ways:
-
automatically, by means of the Adapter Setup wizard
-
automatically, by means of the Add Domain Category wizard
-
directly, by invoking one of the three aggregation wizards from an Aggregation transformation
-
Summarized Aggregation Table wizard
-
Simple Aggregation Table wizard
-
Aggregations through Template wizard
-
Creating Metadata with the Adapter Setup Wizard
Using the Adapter
Setup wizard, you can specify the adapter, domain category,
and time periods for which you want to generate reports. The Adapter
Setup wizard creates the metadata for the appropriate
Staging and Aggregation transformations, according to your specifications.
To invoke the wizard,
from the menu bar, select New IT Resource Management
IT Resource Management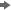 Adapter Setup.
Adapter Setup.
Note: The Adapter Setup wizard
prompts for other input, such as the IT data mart where the job is
to be stored, the location of the formulas that should be used when
creating computed columns, and information about where the reports
are to be stored. For more information about the Adapter Setup wizard
and the other objects that it creates, see About the Adapter Setup Wizard.
The following display
shows the Disk Aggregation job that was generated by the Adapter
Setup wizard for the SAR adapter. It contains a SAR Disk
Aggregation transformation that specifies the creation of five aggregation
tables.
SAR Disk Job That Generates Multiple Aggregation Tables
Note: The Adapter Setup wizard
can generate multiple aggregation tables from a single Aggregation
transformation.
Creating Metadata with the Add Domain Category Wizard
The Add
Domain Category wizard enables you to add domain categories
to an existing staging transformation that was generated by the Adapter
Setup wizard. For each new domain category, the wizard
creates metadata for the appropriate Aggregation transformations according
to your specifications. The wizard prompts you for information such
as the domain category, time period, the location of the formulas
that should be used when creating computed columns, and information
about where the reports are to be stored. For more information
about the Add Domain Category wizard and
the other objects that it creates, see About the Add Domain Category Wizard.
Creating Metadata with the Aggregation Wizard
To create an aggregation
table with an aggregation wizard from an Aggregation transformation,
you must first open a job in the Diagram tab
of the Job Editor window. Then drag and drop
the Aggregation transformation onto the process flow diagram. For information about
how to perform these steps, see Set Up the Aggregation Transformation in the Process Flow Diagram.
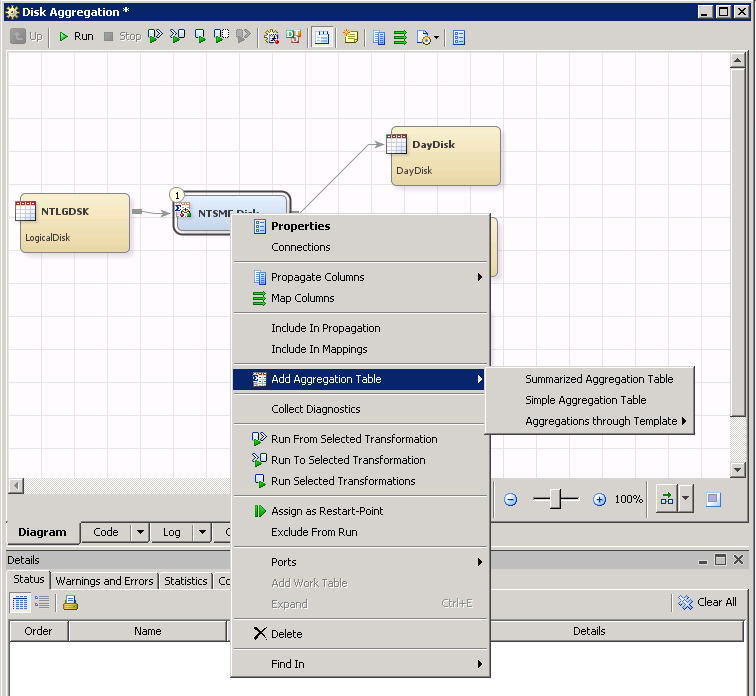
To invoke an aggregation
wizard, right-click the Aggregation transformation and select Add
Aggregation Table from the drop-down list. You can then
choose to create one of the following wizards:
-
Summarized Aggregation Table
-
Simple Aggregation Table
-
Aggregations through TemplateNote: From this option, you can choose to create an aggregation table from either a supplied table template or a user-defined table template.
Respond to the prompts
of the selected wizard in order to specify how the aggregation table
is to be generated. When the wizard is successfully completed, the
metadata for the aggregation table is generated and stored in the
folder of the IT data mart in which the job resides.) The Diagram tab
of the Job Editor window is updated to display
the job that, when run, generates the aggregation table that you specified.
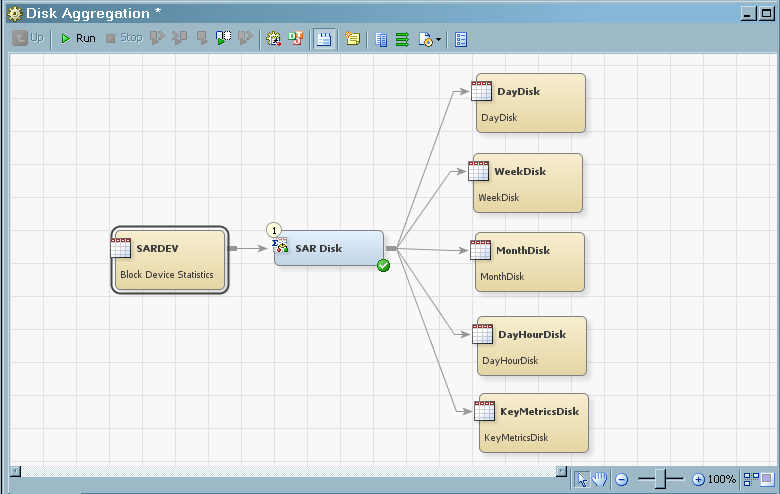
The following display
shows a job called MyJob that was generated by directly invoking the Summarized
Aggregation Table wizard. It contains an Aggregation
transformation that is specified to create a single aggregation table.
Table Generated by the Summarized Aggregation Table Wizard
Note: An aggregation wizard that
is directly invoked can generate only one aggregation table for each
invocation of the wizard. However, you can invoke the wizard multiple
times on the same Aggregation transformation, each time generating
another aggregation table
How Is the Physical Aggregation Table Generated?
Aggregation transformations
are contained in jobs that generate physical aggregation tables when
the jobs are successfully run. For information about
how to run a job immediately, see Running Jobs. For
information about how to deploy a job for batch scheduling, see Run a Job Immediately.
What Are the Properties of an Aggregation Table?
CAUTION:
Except
for defining an index, do not make changes to an aggregation table
from the Properties dialog box.
For all changes other
than index definition, use the Edit wizard
to make changes to an aggregation table. This ensures that all metadata
is properly updated.
To open the Properties dialog
box of an aggregation table, right-click the aggregation table in
the process flow diagram. The following menu appears:
From the drop-down menu
that is displayed, select Properties.
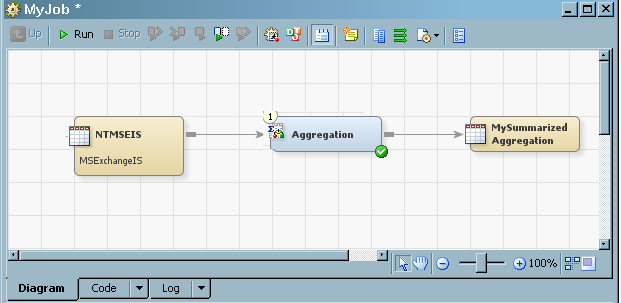
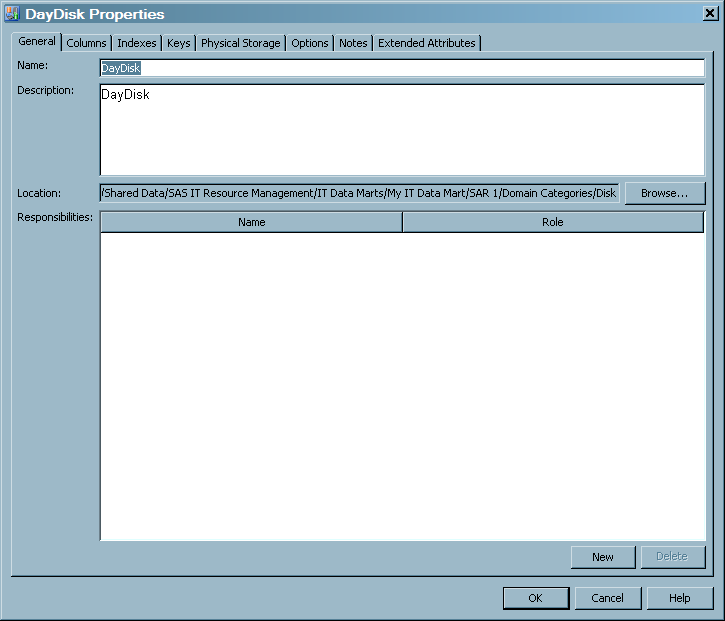
The following display
shows the Property dialog box for the DayDisk
aggregation table, which was displayed by right-clicking the DayDisk
aggregation table image on the process flow diagram. (The metadata
for this table is one of many tables that are generated by the Disk
Aggregation transformation of the SAR adapter.)
Properties for the DayDisk Aggregation Table
Note: Unlike other SAS Data Integration
Studio transformations, there is no Mapping tab.
The aggregation wizards manage this function.
The Properties
dialog box consists of the following tabs:
-
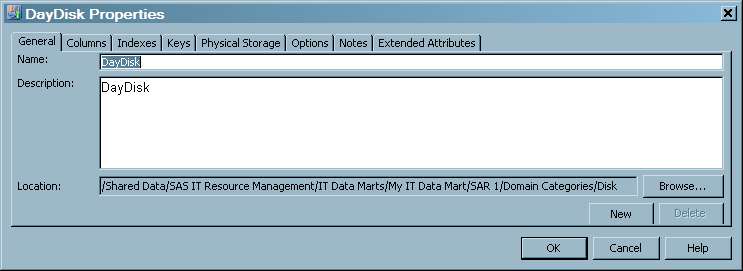
The General tab contains the identifying information about the table.The following display shows the General tab of an aggregation table.For items in the preceding display, the following definitions apply.Nameidentifies the name of the aggregation table.Descriptiondescribes the aggregation table.Locationspecifies the location of the aggregation table in the metadata folder hierarchy. Click Browse to select a path to the table from the Select a Location dialog box that displays the metadata directory structure.
-
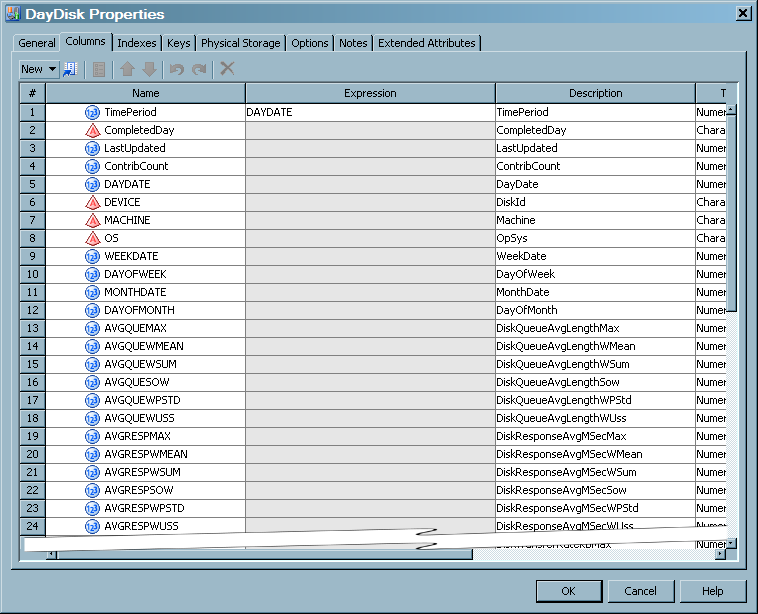
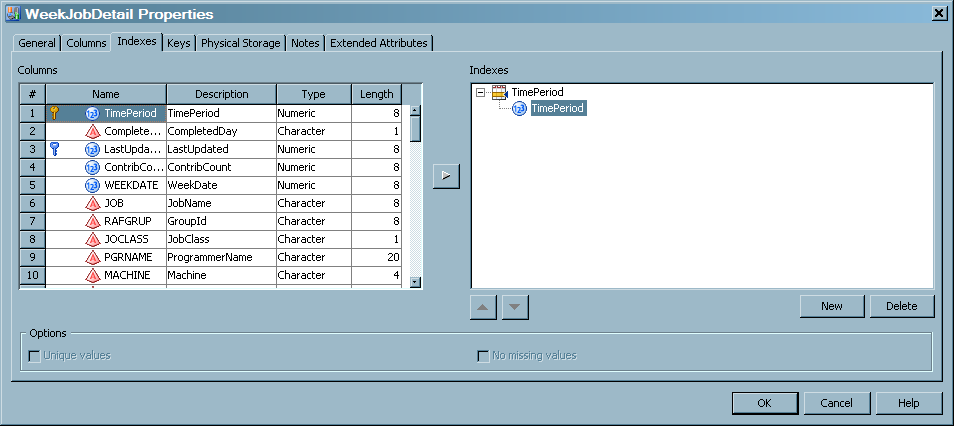
The Columns tab contains a grid that provides information about each column of the table. For each aggregation table, the aggregation wizards supply the following three columns:
-
ContribCountis a numeric column in summarized aggregation tables. The value of ContribCount is the number of input observations (rows of data) that were used in computing this summarized row of data -
LastUpdatedis the system datetime of when this row of data was last updated. This column is in simple and summarized aggregation tables. -
CompletedDayis a single character, set to 'Y', 'N', or blank. If the Completed Day processing is not enabled, it is always set to blank. If the Completed Day processing is enabled, this column is set to 'Y' if the value of DATETIME indicates that this row of data represents a completed day. Otherwise, this column is set to 'N', which indicates an incomplete day. A day is considered complete if any input row of data has a time portion of the datetime value that is greater than the specified cutoff time.
For items in the preceding display, the following definitions apply.#specifies the column's ordinal position in the grid on the Columns tab.Namespecifies the name of the column.If the Key icon appears next to the name, then that column is used
as a primary, unique, or foreign key.
Expressionspecifies the combination of functions and mathematical operations that are used to derive a value for the column. This field is blank unless the column is a computed column.Descriptiondescribes the column.Typespecifies the data type of the column. Valid types are character and numeric. You can also identify column types by looking at the Name column. A round
appears next to the name, then that column is used
as a primary, unique, or foreign key.
Expressionspecifies the combination of functions and mathematical operations that are used to derive a value for the column. This field is blank unless the column is a computed column.Descriptiondescribes the column.Typespecifies the data type of the column. Valid types are character and numeric. You can also identify column types by looking at the Name column. A round icon to the left of the name indicates that the column
is numeric. A pyramid
icon to the left of the name indicates that the column
is numeric. A pyramid  icon to the left of the name indicates that the column
contains character data.
Lengthspecifies the length of the column. The length of numeric columns is from 2 through 8. The length of character columns is from 1 through 32,767.Informatspecifies the SAS informat that is used (if needed) to read values for the selected column. Informats are not used by the Aggregation transformation.Formatspecifies the SAS format that is used to write or display values for the selected column.Summary Rolespecifies the type of the column. It is not used by SAS IT Resource Management.CAUTION:The New, Import, and Delete buttons at the top of the grid should not be used.The preferred method of adding, deleting, or modifying a column is to do so from the appropriate aggregation wizard. Using the wizard ensures that the metadata is properly updated.
icon to the left of the name indicates that the column
contains character data.
Lengthspecifies the length of the column. The length of numeric columns is from 2 through 8. The length of character columns is from 1 through 32,767.Informatspecifies the SAS informat that is used (if needed) to read values for the selected column. Informats are not used by the Aggregation transformation.Formatspecifies the SAS format that is used to write or display values for the selected column.Summary Rolespecifies the type of the column. It is not used by SAS IT Resource Management.CAUTION:The New, Import, and Delete buttons at the top of the grid should not be used.The preferred method of adding, deleting, or modifying a column is to do so from the appropriate aggregation wizard. Using the wizard ensures that the metadata is properly updated. -
-
The Indexes tab contains a list of the columns (and their descriptions, types, and lengths) that can be selected to use as indexes. Indexes can improve queries that use the aggregation table.For more information about indexes, see Indexing an Aggregation Table.
-
The Keys tab is not used by SAS IT Resource Management, and its values are ignored.
-
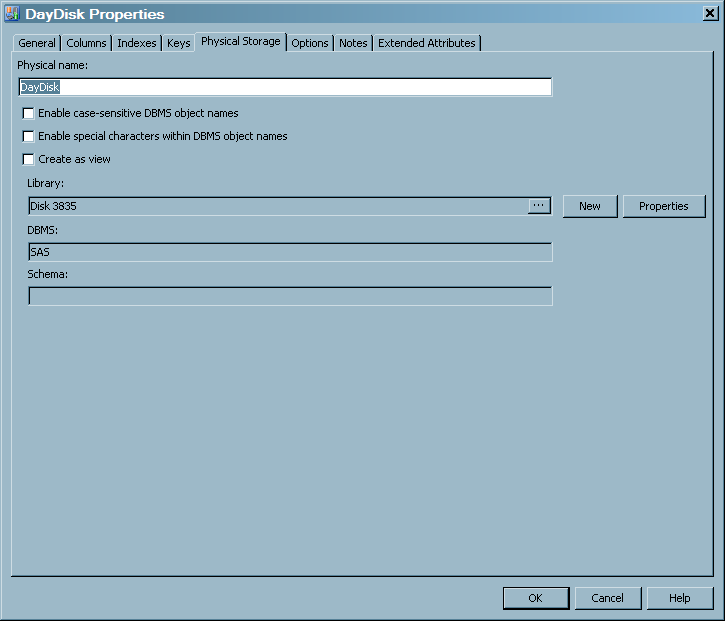
The Physical Storage tab contains information about where the table is stored.For items in the preceding display, the following definitions apply.Physical namespecifies the name of the physical table. The name must follow the rules for table names in the DBMS that is selected in the DBMS field. For example, if SAS is the selected DBMS, the name must follow the rules for SAS data sets. If you select another DBMS, the name must follow the rules for tables in that DBMS. Note the check boxes for DBMS names below.Note: SAS IT Resource Management does not use this field.Enable case-sensitive DBMS object namesspecifies whether case-sensitive names for tables and columns are to be supported in the metadata for the current table. If the check box is deselected, no support is provided. If the check box is selected, support is provided.Note: Do not select or modify this field.Enable special characters within DBMS object namesspecifies whether special characters in names for tables and columns are to be supported in the metadata for the current table.Note: Do not select or modify this field.Create as viewis valid only if the table is specified as an output in a SAS IT Resource Management job. If this option is selected, the table is created as a view, if that is possible. If it is not possible to create a view, a physical table is created even when the Create as view option is selected. Deselect this option to specify that the table should be created as physical table instead of a view.Note: SAS IT Resource Management does not use this field.Libraryspecifies a library that can be used to access the table. To create a new library, click New, which opens the New Library wizard. To edit the properties of the existing library, click Properties, which opens the properties window for the data library.DBMSdisplays the database management system (DBMS) format of the library that is selected in the Library field.Note: Do not select or modify this field.Schemais for DBMS software other than SAS. It specifies the database schema that is associated with the table that is specified in the Name field.Note: Do not select or modify this field.
-
The Notes tab contains areas where you can annotate the table.
-
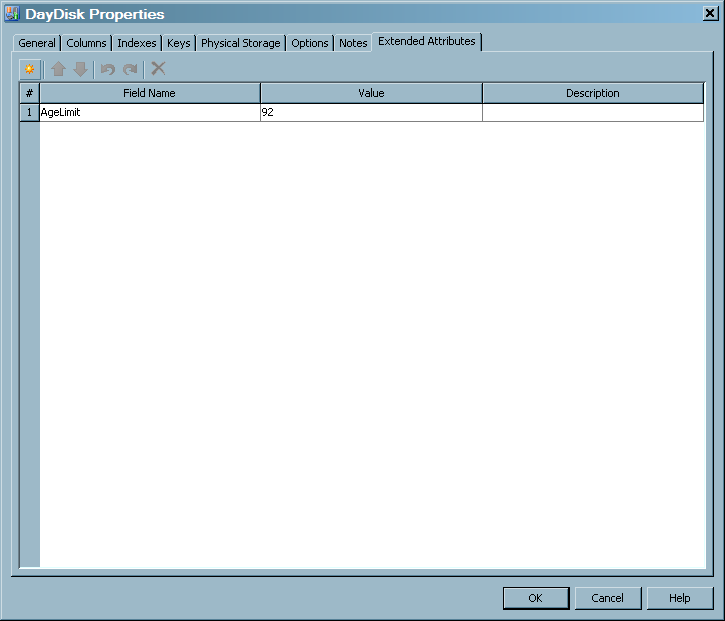
The Extended Attributes tab contains a custom property that is not part of the metadata for the table.For items in the preceding display, the following definitions apply.
 adds a row to the attribute table. A number and a default name are provided, but you must enter the value and description.
adds a row to the attribute table. A number and a default name are provided, but you must enter the value and description. deletes a selected attribute from the list.
deletes a selected attribute from the list. If present, enables you to reorder rows by moving a selected row up in the table.
If present, enables you to reorder rows by moving a selected row up in the table. if present, enables you to reorder rows by moving a selected row down in the table.#specifies the number of the extended attribute.Field Namespecifies the attribute name to be defined.Valuespecifies the value for the attribute that is specified in the Field Name column.Descriptiondescribes the attribute and value.
if present, enables you to reorder rows by moving a selected row down in the table.#specifies the number of the extended attribute.Field Namespecifies the attribute name to be defined.Valuespecifies the value for the attribute that is specified in the Field Name column.Descriptiondescribes the attribute and value.
CAUTION:
Do not
delete or modify the AgeLimit field from the Extended Attributes tab.
In addition, do not delete the Filter from the Extended Attributes
tab.
Modifying or deleting
these fields can cause processing errors.
Copyright © SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved.