The POWER Procedure
- Overview
-
Getting Started

-
Syntax

-
Details

-
Examples
 One-Way ANOVAThe Sawtooth Power Function in Proportion AnalysesSimple AB/BA Crossover DesignsNoninferiority Test with Lognormal DataMultiple Regression and CorrelationComparing Two Survival CurvesConfidence Interval PrecisionCustomizing PlotsBinary Logistic Regression with Independent PredictorsWilcoxon-Mann-Whitney Test
One-Way ANOVAThe Sawtooth Power Function in Proportion AnalysesSimple AB/BA Crossover DesignsNoninferiority Test with Lognormal DataMultiple Regression and CorrelationComparing Two Survival CurvesConfidence Interval PrecisionCustomizing PlotsBinary Logistic Regression with Independent PredictorsWilcoxon-Mann-Whitney Test - References
Analyses in the ONEWAYANOVA Statement
One-Degree-of-Freedom Contrast (TEST=CONTRAST)
The hypotheses are
|
|
|
|
|
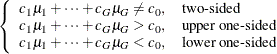 |
where G is the number of groups, ![]() are the contrast coefficients, and
are the contrast coefficients, and ![]() is the null contrast value.
is the null contrast value.
The test is the usual F test for a contrast in one-way ANOVA. It assumes normal data with common group variances and requires ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
O’Brien and Muller (1993, Section 8.2.3.2) give the exact power as
![\[ \mr {power} = \left\{ \begin{array}{ll} P\left(F(1, N-G, \delta ^2) \ge F_{1-\alpha }(1, N-G)\right), & \mbox{two-sided} \\ P\left(t(N-G, \delta ) \ge t_{1-\alpha }(N-G)\right), & \mbox{upper one-sided} \\ P\left(t(N-G, \delta ) \le t_{\alpha }(N-G)\right), & \mbox{lower one-sided} \\ \end{array} \right. \]](images/statug_power0583.png) |
where
![\[ \delta = N^\frac {1}{2} \left( \frac{\sum _{i=1}^{G} c_ i \mu _ i - c_0}{\sigma \left( \sum _{i=1}^{G} \frac{c_ i^2}{w_ i} \right)^\frac {1}{2}} \right) \]](images/statug_power0584.png) |
Overall F Test (TEST=OVERALL)
The hypotheses are
|
|
|
|
|
|
where G is the number of groups.
The test is the usual overall F test for equality of means in one-way ANOVA. It assumes normal data with common group variances and requires ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
O’Brien and Muller (1993, Section 8.2.3.1) give the exact power as
|
|
where the noncentrality is
|
|
and
|
|