| The ROBUSTREG Procedure |
Example 74.3 Growth Study of De Long and Summers
Robust regression and outlier detection techniques have considerable applications to econometrics. The following example from Zaman, Rousseeuw, and Orhan (2001) shows how these techniques substantially improve the ordinary least squares (OLS) results for the growth study of De Long and Summers.
De Long and Summers (1991) studied the national growth of 61 countries from 1960 to 1985 by using OLS with the following data set growth.
data growth;
input country$ GDP LFG EQP NEQ GAP @@;
datalines;
Argentin 0.0089 0.0118 0.0214 0.2286 0.6079
Austria 0.0332 0.0014 0.0991 0.1349 0.5809
Belgium 0.0256 0.0061 0.0684 0.1653 0.4109
Bolivia 0.0124 0.0209 0.0167 0.1133 0.8634
Botswana 0.0676 0.0239 0.1310 0.1490 0.9474
Brazil 0.0437 0.0306 0.0646 0.1588 0.8498
Cameroon 0.0458 0.0169 0.0415 0.0885 0.9333
Canada 0.0169 0.0261 0.0771 0.1529 0.1783
Chile 0.0021 0.0216 0.0154 0.2846 0.5402
Colombia 0.0239 0.0266 0.0229 0.1553 0.7695
CostaRic 0.0121 0.0354 0.0433 0.1067 0.7043
Denmark 0.0187 0.0115 0.0688 0.1834 0.4079
Dominica 0.0199 0.0280 0.0321 0.1379 0.8293
Ecuador 0.0283 0.0274 0.0303 0.2097 0.8205
ElSalvad 0.0046 0.0316 0.0223 0.0577 0.8414
Ethiopia 0.0094 0.0206 0.0212 0.0288 0.9805
Finland 0.0301 0.0083 0.1206 0.2494 0.5589
France 0.0292 0.0089 0.0879 0.1767 0.4708
Germany 0.0259 0.0047 0.0890 0.1885 0.4585
Greece 0.0446 0.0044 0.0655 0.2245 0.7924
Guatemal 0.0149 0.0242 0.0384 0.0516 0.7885
Honduras 0.0148 0.0303 0.0446 0.0954 0.8850
HongKong 0.0484 0.0359 0.0767 0.1233 0.7471
India 0.0115 0.0170 0.0278 0.1448 0.9356
Indonesi 0.0345 0.0213 0.0221 0.1179 0.9243
Ireland 0.0288 0.0081 0.0814 0.1879 0.6457
Israel 0.0452 0.0305 0.1112 0.1788 0.6816
Italy 0.0362 0.0038 0.0683 0.1790 0.5441
IvoryCoa 0.0278 0.0274 0.0243 0.0957 0.9207
Jamaica 0.0055 0.0201 0.0609 0.1455 0.8229
Japan 0.0535 0.0117 0.1223 0.2464 0.7484
Kenya 0.0146 0.0346 0.0462 0.1268 0.9415
Korea 0.0479 0.0282 0.0557 0.1842 0.8807
Luxembou 0.0236 0.0064 0.0711 0.1944 0.2863
Madagasc -0.0102 0.0203 0.0219 0.0481 0.9217
Malawi 0.0153 0.0226 0.0361 0.0935 0.9628
Malaysia 0.0332 0.0316 0.0446 0.1878 0.7853
Mali 0.0044 0.0184 0.0433 0.0267 0.9478
Mexico 0.0198 0.0349 0.0273 0.1687 0.5921
Morocco 0.0243 0.0281 0.0260 0.0540 0.8405
Netherla 0.0231 0.0146 0.0778 0.1781 0.3605
Nigeria -0.0047 0.0283 0.0358 0.0842 0.8579
Norway 0.0260 0.0150 0.0701 0.2199 0.3755
Pakistan 0.0295 0.0258 0.0263 0.0880 0.9180
Panama 0.0295 0.0279 0.0388 0.2212 0.8015
Paraguay 0.0261 0.0299 0.0189 0.1011 0.8458
Peru 0.0107 0.0271 0.0267 0.0933 0.7406
Philippi 0.0179 0.0253 0.0445 0.0974 0.8747
Portugal 0.0318 0.0118 0.0729 0.1571 0.8033
Senegal -0.0011 0.0274 0.0193 0.0807 0.8884
Spain 0.0373 0.0069 0.0397 0.1305 0.6613
SriLanka 0.0137 0.0207 0.0138 0.1352 0.8555
Tanzania 0.0184 0.0276 0.0860 0.0940 0.9762
Thailand 0.0341 0.0278 0.0395 0.1412 0.9174
Tunisia 0.0279 0.0256 0.0428 0.0972 0.7838
U.K. 0.0189 0.0048 0.0694 0.1132 0.4307
U.S. 0.0133 0.0189 0.0762 0.1356 0.0000
Uruguay 0.0041 0.0052 0.0155 0.1154 0.5782
Venezuel 0.0120 0.0378 0.0340 0.0760 0.4974
Zambia -0.0110 0.0275 0.0702 0.2012 0.8695
Zimbabwe 0.0110 0.0309 0.0843 0.1257 0.8875
;
The regression equation they used is
 |
where the response variable is the growth in gross domestic product per worker (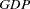 ) and the regressors are labor force growth (
) and the regressors are labor force growth (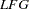 ), relative GDP gap (
), relative GDP gap (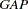 ), equipment investment (
), equipment investment (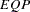 ), and nonequipment investment (
), and nonequipment investment (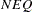 ).
).
The following statements invoke the REG procedure ( Chapter 73, The REG Procedure ) for the OLS analysis:
proc reg data=growth;
model GDP = LFG GAP EQP NEQ ;
run;
| Parameter Estimates | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | DF | Parameter Estimate |
Standard Error |
t Value | Pr > |t| |
| Intercept | 1 | -0.01430 | 0.01028 | -1.39 | 0.1697 |
| LFG | 1 | -0.02981 | 0.19838 | -0.15 | 0.8811 |
| GAP | 1 | 0.02026 | 0.00917 | 2.21 | 0.0313 |
| EQP | 1 | 0.26538 | 0.06529 | 4.06 | 0.0002 |
| NEQ | 1 | 0.06236 | 0.03482 | 1.79 | 0.0787 |
The OLS analysis shown in Output 74.3.1 indicates that 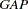 and
and 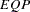 have a significant influence on
have a significant influence on 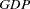 at the
at the 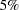 level.
level.
The following statements invoke the ROBUSTREG procedure with the default M estimation.
ods graphics on;
proc robustreg data=growth plots=all;
model GDP = LFG GAP EQP NEQ / diagnostics leverage;
id country;
run;
ods graphics off;
Output 74.3.2 displays model information and summary statistics for variables in the model.
| Model Information | |
|---|---|
| Data Set | WORK.GROWTH |
| Dependent Variable | GDP |
| Number of Independent Variables | 4 |
| Number of Observations | 61 |
| Method | M Estimation |
| Summary Statistics | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Q1 | Median | Q3 | Mean | Standard Deviation |
MAD |
| LFG | 0.0118 | 0.0239 | 0.0281 | 0.0211 | 0.00979 | 0.00949 |
| GAP | 0.5796 | 0.8015 | 0.8863 | 0.7258 | 0.2181 | 0.1778 |
| EQP | 0.0265 | 0.0433 | 0.0720 | 0.0523 | 0.0296 | 0.0325 |
| NEQ | 0.0956 | 0.1356 | 0.1812 | 0.1399 | 0.0570 | 0.0624 |
| GDP | 0.0121 | 0.0231 | 0.0310 | 0.0224 | 0.0155 | 0.0150 |
Output 74.3.3 displays the M estimates. Besides 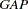 and
and 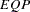 , the robust analysis also indicates that
, the robust analysis also indicates that 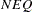 is significant. This new finding is explained by Output 74.3.4, which shows that Zambia, the 60th country in the data, is an outlier. Output 74.3.4 also identifies leverage points based on the robust MCD distances; however, there are no serious high-leverage points in this data set.
is significant. This new finding is explained by Output 74.3.4, which shows that Zambia, the 60th country in the data, is an outlier. Output 74.3.4 also identifies leverage points based on the robust MCD distances; however, there are no serious high-leverage points in this data set.
| Parameter Estimates | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | DF | Estimate | Standard Error | 95% Confidence Limits | Chi-Square | Pr > ChiSq | |
| Intercept | 1 | -0.0247 | 0.0097 | -0.0437 | -0.0058 | 6.53 | 0.0106 |
| LFG | 1 | 0.1040 | 0.1867 | -0.2619 | 0.4699 | 0.31 | 0.5775 |
| GAP | 1 | 0.0250 | 0.0086 | 0.0080 | 0.0419 | 8.36 | 0.0038 |
| EQP | 1 | 0.2968 | 0.0614 | 0.1764 | 0.4172 | 23.33 | <.0001 |
| NEQ | 1 | 0.0885 | 0.0328 | 0.0242 | 0.1527 | 7.29 | 0.0069 |
| Scale | 1 | 0.0099 | |||||
| Diagnostics | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Obs | country | Mahalanobis Distance | Robust MCD Distance | Leverage | Standardized Robust Residual |
Outlier |
| 1 | Argentin | 2.6083 | 4.0639 | * | -0.9424 | |
| 5 | Botswana | 3.4351 | 6.7391 | * | 1.4200 | |
| 8 | Canada | 3.1876 | 4.6843 | * | -0.1972 | |
| 9 | Chile | 3.6752 | 5.0599 | * | -1.8784 | |
| 17 | Finland | 2.6024 | 3.8186 | * | -1.7971 | |
| 23 | HongKong | 2.1225 | 3.8238 | * | 1.7161 | |
| 27 | Israel | 2.6461 | 5.0336 | * | 0.0909 | |
| 31 | Japan | 2.9179 | 4.7140 | * | 0.0216 | |
| 53 | Tanzania | 2.2600 | 4.3193 | * | -1.8082 | |
| 57 | U.S. | 3.8701 | 5.4874 | * | 0.1448 | |
| 58 | Uruguay | 2.5953 | 3.9671 | * | -0.0978 | |
| 59 | Venezuel | 2.9239 | 4.1663 | * | 0.3573 | |
| 60 | Zambia | 1.8562 | 2.7135 | -4.9798 | * | |
| 61 | Zimbabwe | 1.9634 | 3.9128 | * | -2.5959 | |
Figure 74.3.5 displays robust versions of goodness-of-fit statistics for the model.
The PLOTS=ALL option generates four diagnostic plots. Figure 74.3.6 and Figure 74.3.7 are for outlier and leverage-point diagnostics. Figure 74.3.8 and Figure 74.3.9 are a histogram and a Q-Q plot of the standardized robust residuals, respectively.
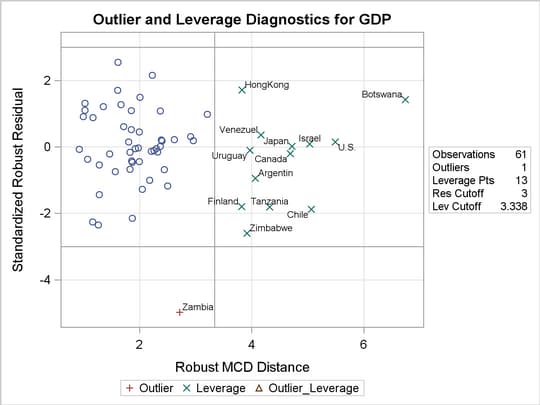
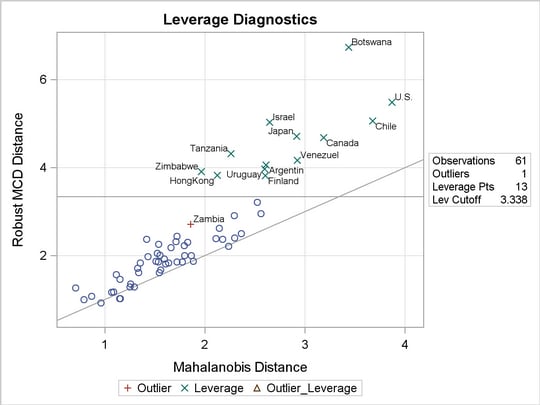
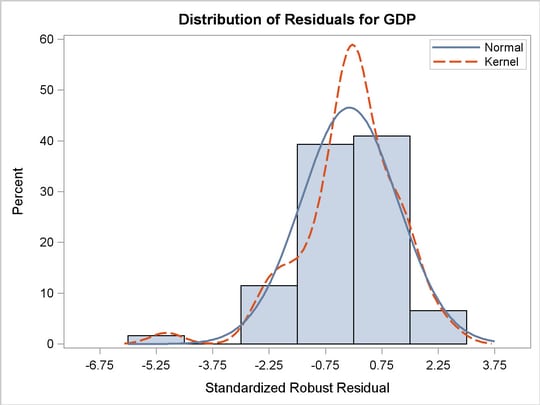
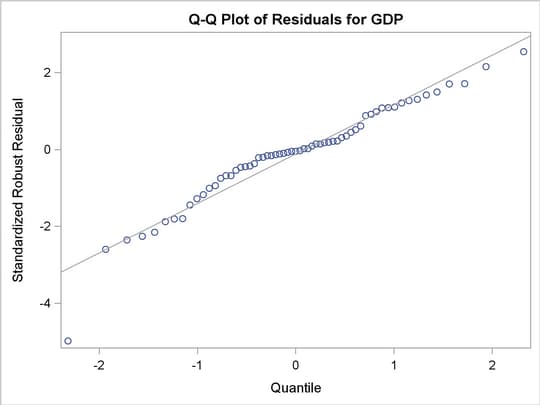
The following statements invoke the ROBUSTREG procedure with LTS estimation, which was used by Zaman, Rousseeuw, and Orhan (2001). The results are consistent with those of M estimation.
proc robustreg method=lts(h=33) fwls data=growth;
model GDP = LFG GAP EQP NEQ / diagnostics leverage ;
id country;
run;
| LTS Parameter Estimates | ||
|---|---|---|
| Parameter | DF | Estimate |
| Intercept | 1 | -0.0249 |
| LFG | 1 | 0.1123 |
| GAP | 1 | 0.0214 |
| EQP | 1 | 0.2669 |
| NEQ | 1 | 0.1110 |
| Scale (sLTS) | 0 | 0.0076 |
| Scale (Wscale) | 0 | 0.0109 |
Output 74.3.10 displays the LTS estimates.
| Diagnostics | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Obs | country | Mahalanobis Distance | Robust MCD Distance | Leverage | Standardized Robust Residual |
Outlier |
| 1 | Argentin | 2.6083 | 4.0639 | * | -1.0715 | |
| 5 | Botswana | 3.4351 | 6.7391 | * | 1.6574 | |
| 8 | Canada | 3.1876 | 4.6843 | * | -0.2324 | |
| 9 | Chile | 3.6752 | 5.0599 | * | -2.0896 | |
| 17 | Finland | 2.6024 | 3.8186 | * | -1.6367 | |
| 23 | HongKong | 2.1225 | 3.8238 | * | 1.7570 | |
| 27 | Israel | 2.6461 | 5.0336 | * | 0.2334 | |
| 31 | Japan | 2.9179 | 4.7140 | * | 0.0971 | |
| 53 | Tanzania | 2.2600 | 4.3193 | * | -1.2978 | |
| 57 | U.S. | 3.8701 | 5.4874 | * | 0.0605 | |
| 58 | Uruguay | 2.5953 | 3.9671 | * | -0.0857 | |
| 59 | Venezuel | 2.9239 | 4.1663 | * | 0.4113 | |
| 60 | Zambia | 1.8562 | 2.7135 | -4.4984 | * | |
| 61 | Zimbabwe | 1.9634 | 3.9128 | * | -2.1201 | |
Output 74.3.11 displays outlier and leverage-point diagnostics based on the LTS estimates.
| Parameter Estimates for Final Weighted Least Squares Fit | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | DF | Estimate | Standard Error | 95% Confidence Limits | Chi-Square | Pr > ChiSq | |
| Intercept | 1 | -0.0222 | 0.0093 | -0.0405 | -0.0039 | 5.65 | 0.0175 |
| LFG | 1 | 0.0446 | 0.1771 | -0.3026 | 0.3917 | 0.06 | 0.8013 |
| GAP | 1 | 0.0245 | 0.0082 | 0.0084 | 0.0406 | 8.89 | 0.0029 |
| EQP | 1 | 0.2824 | 0.0581 | 0.1685 | 0.3964 | 23.60 | <.0001 |
| NEQ | 1 | 0.0849 | 0.0314 | 0.0233 | 0.1465 | 7.30 | 0.0069 |
| Scale | 0 | 0.0116 | |||||
Output 74.3.12 displays the final weighted least squares estimates, which are identical to those reported in Zaman, Rousseeuw, and Orhan (2001).
Copyright © 2009 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.