XCHART Statement: ANOM Procedure
| Syntax: XCHART Statement |
The basic syntax for the XCHART statement is as follows:
- XCHART response * group-variable ;
The general form of this syntax is as follows:
- XCHART responses * group-variable <(block-variables)> <
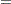 symbol-variable |
symbol-variable | 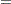 'character'> <options> ;
'character'> <options> ;
You can use any number of XCHART statements in the ANOM procedure. The components of the XCHART statement are described as follows.
- response
- responses
-
identify one or more responses to be analyzed. The specification of response depends on the input data set specified in the PROC ANOM statement.
If response values (raw data) are read from a DATA= data set, response must be the name of the variable containing the values. For an example, see the section Creating ANOM Charts for Means from Response Values.
If summary data are read from a SUMMARY= data set, response must be the common prefix of the summary variables in the SUMMARY= data set. For an example, see the section Creating ANOM Charts for Means from Group Summary Data.
If summary data and decision limits are read from a TABLE= data set, response must be the value of the variable _VAR_ in the TABLE= data set. For an example, see the section Saving Decision Limits.
A response is required. If you specify more than one response, enclose the list in parentheses. For example, the following statements request distinct ANOM charts for the means of Weight, Length, and Width:
proc anom data=Measures; xchart (Weight Length Width)*Day; run;
- group-variable
is the variable that identifies groups in the data. The group-variable is required. In the preceding XCHART statement, Day is the group variable.
- block-variables
are optional variables that group the data into blocks of consecutive groups. The blocks are labeled in a legend, and each block-variable provides one level of labels in the legend.
- symbol-variable
is an optional variable whose levels (unique values) determine the symbol marker used to plot the means. Distinct symbol markers are displayed for points corresponding to the various levels of the symbol-variable. You can specify the symbol markers with SYMBOL
 statements.
statements. - options
enhance the appearance of the chart, request additional analyses, save results in data sets, and so on. The section Summary of Options, which follows, lists all options by function.
