The OPTNET Procedure
- Overview
-
Getting Started

-
Syntax
 Functional SummaryPROC OPTNET StatementBICONCOMP StatementCLIQUE StatementCONCOMP StatementCYCLE StatementDATA_LINKS_VAR StatementDATA_MATRIX_VAR StatementDATA_NODES_VAR StatementLINEAR_ASSIGNMENT StatementMINCOSTFLOW StatementMINCUT StatementMINSPANTREE StatementPERFORMANCE StatementSHORTPATH StatementTRANSITIVE_CLOSURE StatementTSP Statement
Functional SummaryPROC OPTNET StatementBICONCOMP StatementCLIQUE StatementCONCOMP StatementCYCLE StatementDATA_LINKS_VAR StatementDATA_MATRIX_VAR StatementDATA_NODES_VAR StatementLINEAR_ASSIGNMENT StatementMINCOSTFLOW StatementMINCUT StatementMINSPANTREE StatementPERFORMANCE StatementSHORTPATH StatementTRANSITIVE_CLOSURE StatementTSP Statement -
Details
 Graph Input DataMatrix Input DataData Input OrderParallel ProcessingNumeric LimitationsSize LimitationsBiconnected Components and Articulation PointsCliqueConnected ComponentsCycleLinear Assignment (Matching)Minimum-Cost Network FlowMinimum CutMinimum Spanning TreeShortest PathTransitive ClosureTraveling Salesman ProblemMacro VariablesODS Table Names
Graph Input DataMatrix Input DataData Input OrderParallel ProcessingNumeric LimitationsSize LimitationsBiconnected Components and Articulation PointsCliqueConnected ComponentsCycleLinear Assignment (Matching)Minimum-Cost Network FlowMinimum CutMinimum Spanning TreeShortest PathTransitive ClosureTraveling Salesman ProblemMacro VariablesODS Table Names -
Examples
 Articulation Points in a Terrorist NetworkCycle Detection for Kidney Donor ExchangeLinear Assignment Problem for Minimizing Swim TimesLinear Assignment Problem, Sparse Format versus Dense FormatMinimum Spanning Tree for Computer Network TopologyTransitive Closure for Identification of Circular Dependencies in a Bug Tracking SystemTraveling Salesman Tour through US Capital Cities
Articulation Points in a Terrorist NetworkCycle Detection for Kidney Donor ExchangeLinear Assignment Problem for Minimizing Swim TimesLinear Assignment Problem, Sparse Format versus Dense FormatMinimum Spanning Tree for Computer Network TopologyTransitive Closure for Identification of Circular Dependencies in a Bug Tracking SystemTraveling Salesman Tour through US Capital Cities - References
Overview: OPTNET Procedure
The OPTNET procedure includes a number of graph theory, combinatorial optimization, and network analysis algorithms. The algorithm classes are listed in Table 2.1.
Table 2.1: Algorithm Classes in PROC OPTNET
|
Algorithm Class |
PROC OPTNET Statement |
|
Biconnected components |
|
|
Maximal cliques |
|
|
Connected components |
|
|
Cycle detection |
|
|
Weighted matching |
|
|
Minimum-cost network flow |
|
|
Minimum cut |
|
|
Minimum spanning tree |
|
|
Shortest path |
|
|
Transitive closure |
|
|
Traveling salesman |
You can use the OPTNET procedure to analyze relationships between entities. These relationships are typically defined by using
a graph. A graph 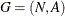 is defined over a set N of nodes and a set A of arcs. A node is an abstract representation of some entity (or object), and an arc defines some relationship (or connection) between two nodes. The terms node and vertex are often interchanged in describing an entity. The term arc is often interchanged with the term edge or link when describing a connection.
is defined over a set N of nodes and a set A of arcs. A node is an abstract representation of some entity (or object), and an arc defines some relationship (or connection) between two nodes. The terms node and vertex are often interchanged in describing an entity. The term arc is often interchanged with the term edge or link when describing a connection.
You can also access these network algorithms via the network solver in PROC OPTMODEL. For more information, see the network solver chapter in SAS/OR User's Guide: Mathematical Programming.