HISTOGRAM Statement: CAPABILITY Procedure
Example 5.14 Annotating a Folded Normal Curve
Note: See Cpk for Folded Normal Distribution in the SAS/QC Sample Library.
This example shows how to display a fitted curve that is not supported by the HISTOGRAM statement.
The offset of an attachment point is measured (in mm) for a number of manufactured assemblies, and the measurements are saved
in a data set named Assembly.
data Assembly; label Offset = 'Offset (in mm)'; input Offset @@; datalines; 11.11 13.07 11.42 3.92 11.08 5.40 11.22 14.69 6.27 9.76 9.18 5.07 3.51 16.65 14.10 9.69 16.61 5.67 2.89 8.13 9.97 3.28 13.03 13.78 3.13 9.53 4.58 7.94 13.51 11.43 11.98 3.90 7.67 4.32 12.69 6.17 11.48 2.82 20.42 1.01 3.18 6.02 6.63 1.72 2.42 11.32 16.49 1.22 9.13 3.34 1.29 1.70 0.65 2.62 2.04 11.08 18.85 11.94 8.34 2.07 0.31 8.91 13.62 14.94 4.83 16.84 7.09 3.37 0.49 15.19 5.16 4.14 1.92 12.70 1.97 2.10 9.38 3.18 4.18 7.22 15.84 10.85 2.35 1.93 9.19 1.39 11.40 12.20 16.07 9.23 0.05 2.15 1.95 4.39 0.48 10.16 4.81 8.28 5.68 22.81 0.23 0.38 12.71 0.06 10.11 18.38 5.53 9.36 9.32 3.63 12.93 10.39 2.05 15.49 8.12 9.52 7.77 10.70 6.37 1.91 8.60 22.22 1.74 5.84 12.90 13.06 5.08 2.09 6.41 1.40 15.60 2.36 3.97 6.17 0.62 8.56 9.36 10.19 7.16 2.37 12.91 0.95 0.89 3.82 7.86 5.33 12.92 2.64 7.92 14.06 ;
The assembly process is in statistical control, and it is decided to fit a folded normal distribution to the offset measurements. A variable X has a folded normal distribution if 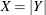 , where Y is distributed as
, where Y is distributed as 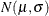 . The fitted density is
. The fitted density is
![\[ h(x) = \frac{1}{\sqrt {2\pi } \sigma } \left[ \exp \left( -\frac{(x-\mu )^2}{2\sigma ^2} \right) + \exp \left( -\frac{(x+\mu )^2}{2\sigma ^2} \right) \right] \; \; \; \; \; , \; x \geq 0 \]](images/qcug_capability0493.png)
You can use SAS/IML software to compute preliminary estimates of 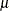 and
and  based on a method of moments given by Elandt (1961). These estimates are computed by solving equation (19) of Elandt (1961), which is given by
based on a method of moments given by Elandt (1961). These estimates are computed by solving equation (19) of Elandt (1961), which is given by
![\[ f(\theta ) = \frac{\left( \frac{2}{\sqrt {2\pi }} e^{-\theta ^2/2 } - \theta \left[ 1-2\Phi (\theta ) \right] \right)^2}{1+\theta ^2} = A \]](images/qcug_capability0494.png)
where 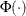 is the standard normal distribution function, and
is the standard normal distribution function, and
![\[ A = \frac{ \bar{x}^2 }{ \frac{1}{n} \sum _{i=1}^ n x_ i^2 } \]](images/qcug_capability0495.png)
Then the estimates of  and
and 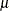 are given by
are given by
![\[ \begin{array}{lll} \hat{\sigma }_0 & = \sqrt { \frac{ \frac{1}{n} \sum _{i=1}^ n x_ i^2}{1 + \hat{\theta }^2 } } \\[.1in] \hat{\mu }_0 & = \hat{\theta } \cdot \hat{\sigma }_0 \end{array} \]](images/qcug_capability0496.png)
Begin by using the MEANS procedure to compute the first and second moments and using the DATA step to compute the constant A.
proc means data = Assembly noprint; var Offset; output out=Stat mean=m1 var=var n=n min = min; run; * Compute constant A from equation (19) of Elandt (1961) ; data Stat; keep m2 a min; set Stat; a = (m1*m1); m2 = ((n-1)/n)*var + a; a = a/m2; run;
Next, use the SAS/IML subroutine NLPDD to solve equation (19) by minimizing 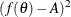 , and compute
, and compute 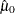 and
and 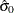 .
.
proc iml;
use Stat;
read all var {m2} into m2;
read all var {a} into a;
read all var {min} into min;
* f(t) is the function in equation (19) of Elandt (1961) ;
start f(t) global(a);
y = .39894*exp(-0.5*t*t);
y = (2*y-(t*(1-2*probnorm(t))))**2/(1+t*t);
y = (y-a)**2;
return(y);
finish;
* Minimize (f(t)-A)**2 and estimate mu and sigma ;
if ( min < 0 ) then do;
print "Warning: Observations are not all nonnegative.";
print " The folded normal is inappropriate.";
stop;
end;
if ( a < 0.637 ) then do;
print "Warning: the folded normal may be inappropriate";
end;
opt = { 0 0 };
con = { 1e-6 };
x0 = { 2.0 };
tc = { . . . . . 1e-12 . . . . . . .};
call nlpdd(rc,etheta0,"f",x0,opt,con,tc);
esig0 = sqrt(m2/(1+etheta0*etheta0));
emu0 = etheta0*esig0;
create Prelim var {emu0 esig0 etheta0};
append;
close Prelim;
* Define the log likelihood of the folded normal ;
start g(p) global(x);
y = 0.0;
do i = 1 to nrow(x);
z = exp( (-0.5/p[2])*(x[i]-p[1])*(x[i]-p[1]) );
z = z + exp( (-0.5/p[2])*(x[i]+p[1])*(x[i]+p[1]) );
y = y + log(z);
end;
y = y - nrow(x)*log( sqrt( p[2] ) );
return(y);
finish;
* Maximize the log likelihood with subroutine NLPDD ;
use Assembly;
read all var {Offset} into x;
esig0sq = esig0*esig0;
x0 = emu0||esig0sq;
opt = { 1 0 };
con = { . 0.0, . . };
call nlpdd(rc,xr,"g",x0,opt,con);
emu = xr[1];
esig = sqrt(xr[2]);
etheta = emu/esig;
create Parmest var{emu esig etheta};
append;
close Parmest;
quit;
title 'The Data Set Prelim'; proc print data=Prelim noobs; run;
The preliminary estimates are saved in the data set Prelim, as shown in Output 5.14.1.
Output 5.14.1: Preliminary Estimates of 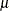 ,
,  , and
, and 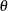
Now, using 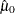 and
and 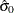 as initial estimates, call the NLPDD subroutine to maximize the log likelihood,
as initial estimates, call the NLPDD subroutine to maximize the log likelihood, 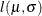 , of the folded normal distribution, where, up to a constant,
, of the folded normal distribution, where, up to a constant,
![\[ l(\mu ,\sigma ) = -n \log \sigma + \sum _{i=1}^ n \log \left[ \exp \left( -\frac{(x_ i-\mu )^2}{2\sigma ^2} \right) + \exp \left( -\frac{(x_ i+\mu )^2}{2\sigma ^2} \right) \right] \]](images/qcug_capability0501.png)
* Define the log likelihood of the folded normal ;
start g(p) global(x);
y = 0.0;
do i = 1 to nrow(x);
z = exp( (-0.5/p[2])*(x[i]-p[1])*(x[i]-p[1]) );
z = z + exp( (-0.5/p[2])*(x[i]+p[1])*(x[i]+p[1]) );
y = y + log(z);
end;
y = y - nrow(x)*log( sqrt( p[2] ) );
return(y);
finish;
* Maximize the log likelihood with subroutine NLPDD ;
use assembly;
read all var {offset} into x;
esig0sq = esig0*esig0;
x0 = emu0||esig0sq;
opt = { 1 0 };
con = { . 0.0, . . };
call nlpdd(rc,xr,"g",x0,opt,con);
emu = xr[1];
esig = sqrt(xr[2]);
etheta = emu/esig;
create parmest var{emu esig etheta};
append;
close parmest;
quit;
title 'The Data Set PARMEST'; proc print data=Parmest noobs; var emu esig etheta; run;
The data set Parmest saves the maximum likelihood estimates 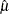 and
and 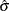 (as well as
(as well as 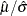 ), as shown in Output 5.14.2.
), as shown in Output 5.14.2.
Output 5.14.2: Final Estimates of 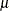 ,
,  , and
, and 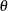
To annotate the curve on a histogram, begin by computing the width and endpoints of the histogram intervals. The following statements save these values in an OUTFIT= data set called OUT. Note that a plot is not produced at this point.
ods graphics off; proc capability data = Assembly noprint; histogram Offset / outfit = Out normal(noprint) noplot; run;
title 'OUTFIT= Data Set Out';
proc print data=Out noobs round;
var _var_ _curve_ _locatn_ _scale_ _chisq_ _df_ _pchisq_
_midpt1_ _width_ _midptn_ _expect_ _eststd_ _adasq_
_adp_ _cvmwsq_ _cvmp_ _ksd_ _ksp_;
run;
Output 5.14.3 provides a partial listing of the data set Out. The width and endpoints of the histogram bars are saved as values of the variables _WIDTH_, _MIDPT1_, and _MIDPTN_. See Output Data Sets.
Output 5.14.3: The OUTFIT= Data Set Out
The following statements create an annotate data set named Anno, which contains the coordinates of the fitted curve:
data Anno;
merge Parmest Out;
length function color $ 8;
function = 'point';
color = 'black';
size = 2;
xsys = '2';
ysys = '2';
when = 'a';
constant = 39.894*_width_;;
left = _midpt1_ - .5*_width_;
right = _midptn_ + .5*_width_;
inc = (right-left)/100;
do x = left to right by inc;
z1 = (x-emu)/esig;
z2 = (x+emu)/esig;
y = (constant/esig)*(exp(-0.5*z1*z1)+exp(-0.5*z2*z2));
output;
function = 'draw';
end;
run;
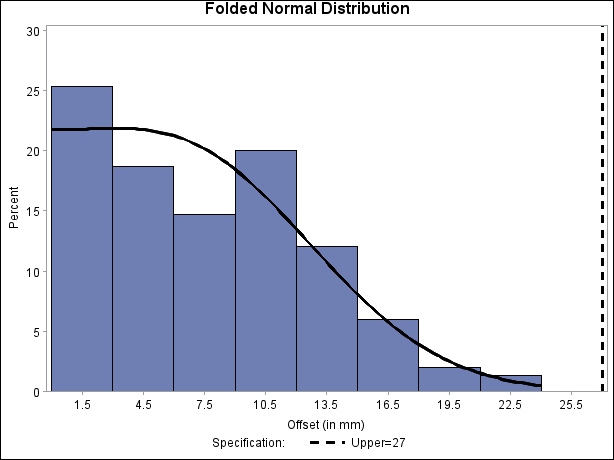
The following statements read the ANNOTATE= data set and display the histogram and fitted curve, as shown in Output 5.14.4:
ods graphics off; title "Folded Normal Distribution"; proc capability data=Assembly noprint; spec usl=27 cusl=black lusl=2 wusl=2; histogram Offset / annotate = Anno; run;
Output 5.14.4: Histogram with Annotated Folded Normal Curve