The Network Solver
- Overview
- Getting Started
-
Syntax

-
Details
 Input Data for the Network SolverSolving over Subsets of Nodes and Links (Filters)Numeric LimitationsBiconnected Components and Articulation PointsCliqueConnected ComponentsCycleLinear Assignment (Matching)Minimum-Cost Network FlowMinimum CutMinimum Spanning TreeShortest PathTransitive ClosureTraveling Salesman ProblemMacro Variable _OROPTMODEL_
Input Data for the Network SolverSolving over Subsets of Nodes and Links (Filters)Numeric LimitationsBiconnected Components and Articulation PointsCliqueConnected ComponentsCycleLinear Assignment (Matching)Minimum-Cost Network FlowMinimum CutMinimum Spanning TreeShortest PathTransitive ClosureTraveling Salesman ProblemMacro Variable _OROPTMODEL_ -
Examples
 Articulation Points in a Terrorist NetworkCycle Detection for Kidney Donor ExchangeLinear Assignment Problem for Minimizing Swim TimesLinear Assignment Problem, Sparse Format versus Dense FormatMinimum Spanning Tree for Computer Network TopologyTransitive Closure for Identification of Circular Dependencies in a Bug Tracking SystemTraveling Salesman Tour through US Capital Cities
Articulation Points in a Terrorist NetworkCycle Detection for Kidney Donor ExchangeLinear Assignment Problem for Minimizing Swim TimesLinear Assignment Problem, Sparse Format versus Dense FormatMinimum Spanning Tree for Computer Network TopologyTransitive Closure for Identification of Circular Dependencies in a Bug Tracking SystemTraveling Salesman Tour through US Capital Cities - References
Input Data for the Network Solver
This section describes how you can import and export node, link, and problem data from and to SAS data sets and how you can solve problems over a subgraph without changing your original sets. The section Graph Input Data describes how to load node and link data in some common formats. The section Solving over Subsets of Nodes and Links (Filters) describes subgraphs and how to access the objective value of a network problem.
Graph Input Data
This section describes how to input a graph for analysis by the network solver. Because PROC OPTMODEL uses node and link attributes
that are indexed over the sets of nodes and links, you need to provide only node and link attributes. PROC OPTMODEL infers
the graph from the attributes you provide. When a documented default value exists for the attribute of a link or a node, you
need to provide only the values that differ from the default. For example, the section Minimum-Cost Network Flow assumes that the link flow upper bound is 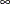 . You need to specify only the finite upper bounds.
. You need to specify only the finite upper bounds.
Consider the directed graph shown in Figure 9.5.
Figure 9.5: A Simple Directed Graph
Each node and link has associated attributes: a node label and a link weight.
None of the algorithms in PROC OPTMODEL support Null Graphs, i.e., graphs with 0 nodes. PROC OPTMODEL will usually raise a semantic error and stop processing any remaining statements in a block if after processing its inputs it determines that the graph is null. If the graph definition itself is not null, but the graph to be passed to the solver after applying the SUBGRAPH= option is null, then the predeclared parameter _SOLUTION_STATUS_ will be set to NULL_GRAPH. For more information, see Solving over Subsets of Nodes and Links (Filters).
Data Indexed by Nodes or Links
Nodes often represent entities, and links represent relationships between these entities. Therefore, it is common to store a graph as a link-indexed table. When nodes have attributes beyond their name (label), these attributes are stored in a node-indexed table. This section covers the more complex link-indexed case. The node-indexed case is essentially identical to this one, except that the PROC OPTMODEL set has tuple length of one when node-indexed data are read, whereas the PROC OPTMODEL set has tuple length two when link-indexed data are read.
Let  define a graph with a set N of nodes and a set A of links. A link is an ordered pair of nodes. Each node is defined by using either numeric or string labels.
define a graph with a set N of nodes and a set A of links. A link is an ordered pair of nodes. Each node is defined by using either numeric or string labels.
The directed graph G shown in Figure 9.5 can be represented by the following links data set LinkSetIn:
data LinkSetIn; input from $ to $ weight @@; datalines; A B 1 A C 2 A D 4 B C 1 B E 2 B F 5 C E 1 D E 1 E D 1 E F 2 F G 6 G H 1 G I 1 H G 2 H I 3 ;
The following statements read in this graph and print the resulting links and nodes sets. These statements do not run any algorithms, so the resulting output contains only the input graph.
proc optmodel;
set<str,str> LINKS;
set NODES = union{<ni,nj> in LINKS} {ni,nj};
num weight{LINKS};
read data LinkSetIn into LINKS=[from to] weight;
print weight;
put NODES=; /* computed automatically by OPTMODEL */
quit;
The network solver preserves the node order of each link that you provide, even in cases where the link is traversed in the
opposite order, such as in paths or tours. For an example, see the tour 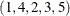 in Figure 9.8.
in Figure 9.8.
The log output in Figure 9.6 shows the nodes that are read from the input link data set. In this example PROC OPTMODEL computed the node set N (NODES) from its definition when it was needed. The ODS output in Figure 9.7 shows the weights that are read from the input link data set, which is indexed by link. PUT is used for NODES because PROC OPTMODEL sets are basic types such as number and string. Thus, you use PUT to quickly inspect a set value. In contrast, you use PRINT to inspect an array, such as weight.
Figure 9.6: Node Set Printout of a Simple Directed Graph
Figure 9.7: Link Set of a Simple Directed Graph That Includes Weights
As described in the GRAPH_DIRECTION=
option, if the graph is undirected, the from and to labels are interchangeable. If you define this graph as undirected, then reciprocal links (for example, 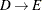 and
and 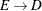 ) are treated as the same link, and duplicates are removed. The network solver takes the first occurrence of the link and
ignores the others. By default, GRAPH_DIRECTION=UNDIRECTED, so to declare the graph as undirected you can just omit this option.
) are treated as the same link, and duplicates are removed. The network solver takes the first occurrence of the link and
ignores the others. By default, GRAPH_DIRECTION=UNDIRECTED, so to declare the graph as undirected you can just omit this option.
After you read the data into PROC OPTMODEL sets, you pass link information to the solver by using the LINKS=
option. Node input is analogous to link input. You pass node information to the solver by using the NODES=
option.
The INCLUDE= suboption is especially useful for algorithms that depend only on the graph topology, (such as the connected components algorithm). If an algorithm requires a node or link property and that property is not defined for a node or link that is added by the INCLUDE= suboption, the algorithm will not run.
Matrix Input Data
The contents of a table can be represented as a graph. The relationships between two sets of nodes, 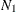 and
and 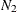 , can be represented by a
, can be represented by a 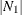 by
by 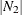 incidence matrix A, in which
incidence matrix A, in which 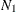 is the set of rows and
is the set of rows and 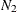 is the set of columns.
is the set of columns.
To read a matrix that is stored in a data set into PROC OPTMODEL, you need to take two extra steps:
-
Determine the name of each numeric variable that you want to use. PROC CONTENTS can be useful for this task.
-
Use an iterated READ DATA statement.
For more information, see Example 9.3: Linear Assignment Problem for Minimizing Swim Times.