The AUTOREG Procedure
- Overview
-
Getting Started

-
Syntax

-
Details
 Missing ValuesAutoregressive Error ModelAlternative Autocorrelation Correction MethodsGARCH ModelsHeteroscedasticity- and Autocorrelation-Consistent Covariance Matrix EstimatorGoodness-of-Fit Measures and Information CriteriaTestingPredicted ValuesOUT= Data SetOUTEST= Data SetPrinted OutputODS Table NamesODS Graphics
Missing ValuesAutoregressive Error ModelAlternative Autocorrelation Correction MethodsGARCH ModelsHeteroscedasticity- and Autocorrelation-Consistent Covariance Matrix EstimatorGoodness-of-Fit Measures and Information CriteriaTestingPredicted ValuesOUT= Data SetOUTEST= Data SetPrinted OutputODS Table NamesODS Graphics -
Examples

- References
Printed Output
The AUTOREG procedure prints the following items:
-
the name of the dependent variable
-
the ordinary least squares estimates
-
Estimates of autocorrelations, which include the estimates of the autocovariances, the autocorrelations, and (if there is sufficient space) a graph of the autocorrelation at each LAG
-
if the PARTIAL option is specified, the partial autocorrelations
-
the preliminary MSE, which results from solving the Yule-Walker equations. This is an estimate of the final MSE.
-
the estimates of the autoregressive parameters (Coefficient), their standard errors (Standard Error), and the ratio of estimate to standard error (t Value)
-
the statistics of fit for the final model. These include the error sum of squares (SSE), the degrees of freedom for error (DFE), the mean square error (MSE), the mean absolute error (MAE), the mean absolute percentage error (MAPE), the root mean square error (Root MSE), the Schwarz information criterion (SBC), the Hannan-Quinn information criterion (HQC), the Akaike information criterion (AIC), the corrected Akaike information criterion (AICC), the Durbin-Watson statistic (Durbin-Watson), the transformed regression
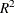 (Transformed Regress R-Square), and the total
(Transformed Regress R-Square), and the total 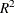 (Total R-Square). For GARCH models, the following additional items are printed:
(Total R-Square). For GARCH models, the following additional items are printed:
-
the value of the log-likelihood function (Log Likelihood)
-
the number of observations that are used in estimation (Observations)
-
the unconditional variance (Uncond Var)
-
the normality test statistic and its p-value (Normality Test and Pr > ChiSq)
-
-
the parameter estimates for the structural model (Estimate), a standard error estimate (Standard Error), the ratio of estimate to standard error (t Value), and an approximation to the significance probability for the parameter being 0 (Approx Pr > |t|)
-
If the NLAG= option is specified with METHOD=ULS or METHOD=ML, the regression parameter estimates are printed again, assuming that the autoregressive parameter estimates are known. In this case, the Standard Error and related statistics for the regression estimates will, in general, be different from the case when they are estimated. Note that from a standpoint of estimation, Yule-Walker and iterated Yule-Walker methods (NLAG= with METHOD=YW, ITYW) generate only one table, assuming AR parameters are given.
-
If you specify the NORMAL option, the Bera-Jarque normality test statistics are printed. If you specify the LAGDEP option, Durbin’s h or Durbin’s t is printed.