Range Map
Definition
Usage Information
|
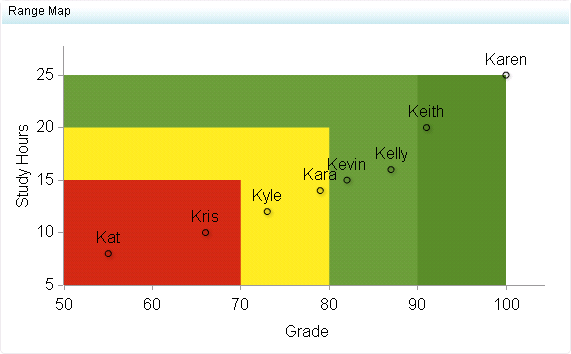
Range maps can be used
when comparing data points in terms of position and range. Use range
maps when there are many data points in different ranges. For example,
range maps can be used when representing the body weight of males
across different ranges: underweight, healthy, overweight, and obese.
Each data point should fall into one of these ranges on the map.
|
|
|
Alerts are supported. For information, see Customizing Alerts.
|
|
|
This indicator type can be used to define a link or as the
destination of a link.For
more information about defining an indicator with a hyperlink, see Adding Links to Indicators or Other Content.
|
|
|
Filtering multiple items is supported.For
more information, see Supporting Multiple Selections in a Filtered Data Interaction.
|
General Settings
Display Settings
The following display settings are used in the preceding
figure. For more information, see “Sample Data Structure”
for this indicator.
You can customize the
following display settings for this indicator:
-
(Required) From the X-axis value list, select the column in your data that you want to use for the X-axis value in the indicator. When you view your indicator data, the columns in the data set are described by the values in the Column Name column. The selections available in the X-axis value list are all of the values in the Column Name column.
-
(Required) From the Y-axis value list, select the column in your data that you want to use for the Y-axis value in the indicator. When you view your indicator data, the columns in the data set are described by the values in the Column Name column. The selections available in the Y-axis value list are all of the values in the Column Name column.
-
In the X-axis title field, type the title to use for the X axis in the indicator. If you do not specify a title, the value that you selected from the X-axis value list is used by default. If you do not want a title, type a space in the field. If you select Scale X axis, a measurement label is added to the title.
-
In the Y-axis title field, type the title to use for the Y axis in the indicator. If you do not specify a title, the value that you selected from the Y-axis value list is used by default. If you do not want a title, type a space in the field. If you select Scale Y axis, a measurement label is added to the title.