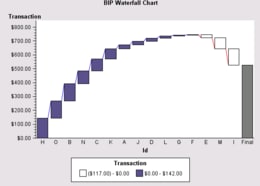
The main responsibility of a WaterfallChartTableDataModel is to determine which data variables are used in the bar chart and what role each variable plays. A WaterfallChartTableDataModel's primary roles are
The following code fragment graphs company transactions for various income and expense categories by assigning the Category and Response variable roles to variables named Id and Transaction:
// Create a data source that must contain a string column
// named Id and a numeric column named Transaction
javax.swing.table.TableModel dataTable = <...>;
// Create a data model and attach the data source to it
WaterfallChartTableDataModel dataModel =
new WaterfallChartTableDataModel();
dataModel.setModel(dataTable);
// Assign the Category and Response variable roles
// to appropriate variable(s)
dataModel.setCategoryVariable(
new ClassificationVariable("Id"));
dataModel.setResponseVariable(
new AnalysisVariable("Transaction"));
// Create a WaterfallChart and attach the data model to it
WaterfallChart waterfallChart = new WaterfallChart();
waterfallChart.setDataModel(dataModel);
When a data model is assigned to a WaterfallChart, the chart summarizes the data before displaying it. During summarization
The following statistics are the default calculations:
The AnalysisVariable constructor can be used to specify a statistic to calcuate. The following code fragment specifies a mean:
AnalysisVariable response=new AnalysisVariable(
"Var1" // column for Response role
,GraphConstants.STATISTIC_MEAN // statistic to calculate
);
WaterfallChartTableDataModel dataModel=new WaterfallChartTableDataModel();
dataModel.setResponseVariable(response);
By default, a WaterfallChart summarizes the data, even if the TableModel's data values have already been summarized. When the values in the data source have already been summarized, you can improve performance by turning off data summarization. Do this by setting the StatisticEnabled boolean to false as follows:
WaterfallChartTableDataModel dataModel=new WaterfallChartTableDataModel();
dataModel.setStatisticEnabled(false);
To set bar styles so that they represent a chart variable's values, assign the WaterfallChartModel's StyleBy role to an appropriate variable. Bar colors in the chart then represent the values of the StyleBy variable.

For example, if the bars in a chart represent transaction amounts, the response variable might be assigned the StyleBy role. The assignment would resemble the following:
dataModel.setStyleByVariable(dataModel.getResponseVariable());
The chart would then use one color for bars that represent positive transactions, and a different color for bars that represent negative transactions. In this case, you might also want to sort bars according to the values of the response variable:
dataModel.setCategorySortVariable(dataModel.getResponseVariable());
By default, a discrete categorization is performed when a numeric data column is specified for the CategoryVariable role. The format parameter on the ClasificationVariable's constructor can be used to specify the type of categorization (or midpointing) operation to use.
For example, for a numeric data column named Sample, the following code fragment formats the numeric values into categories Initial, Interim, and Final, and then specifies the numeric variable for the Category role:
try {
com.sas.text.SASUserDefinedFormat.createFormat(
"value myFormat 1 - 2 = 'Initial'"
+ "3 - 4 = 'Interim'"
+ "5 - 6 = 'Final'");
} catch (java.text.ParseException e) {
java.lang.System.out.println("error=" + e.getMessage());
}
ClassificationVariable myFormattedVar=
new ClassificationVariable("Sample", "myFormat");
WaterfallChartTableDataModel dataModel=new WaterfallChartTableDataModel();
dataModel.setCategoryVariable(myFormattedVar);
Multiple Response variables can be plotted against the same Category variable by adding the variables to an AnalysisVariableList, and then assigning that list rather than an individual variable to the Response role.
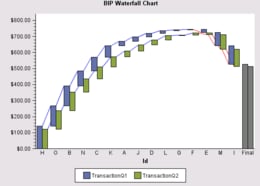
The following code fragment assigns the Category role to variable Id, and the Response role to variables named TransactionQ1 and TransactionQ2:
dataModel.setCategoryVariable(
new ClassificationVariable("Id"));
AnalysisVariableList multiResponse=new AnalysisVariableList(
new AnalysisVariable[] {
new AnalysisVariable("TransactionQ1"),
new AnalysisVariable("TransactionQ2")
} );
dataModel.setResponseVariable(multiResponse);
For each value of the category variable, the response-variable bars are positioned side-by-side for ease of comparison. A different color bar is used for each response variable, and a legend is displayed by default to indicate which color represents each variable.
Separate WaterfallCharts can be generated for each value of a ClassificationVariable by assigning either the ColumnVariable or RowVariable role to that variable.
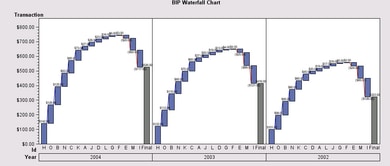
For example, when charting company transactions, a variable named Year might be assigned to the Column role so that a separate chart is generated for the transactions in each year. The assignment would resemble the following:
dataModel.setColumnVariable(new ClassificationVariable("Year"));
If the Column role is assigned, charts are aligned horizontally by the variable's values. Each column has its own category-axis scale, and the charts share the same response axis.
If the Row role is assigned, charts are aligned vertically by the variable's values. Each row has its own category and response axes.
The Column and Row variable roles can both be assigned to the same graph. In that case, a separate bar chart is produced for each unique pair of (column, row) values, and the plots are displayed in a grid. For example, when charting company transactions, a variable named Year might be assigned to the Column role and a variable named Region might be assigned the Row role. In this case, a separate chart is generated for each region's transactions in each year.
The following table summarizes the WaterfallChartTableDataModel variable roles and the type of data each role supports.
| Variable Role | Class Type | Numeric | String | Multiple Variables |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CategoryVariable* Assigns category-axis variable |
ClassificationVariable | Yes | Yes | No |
| ResponseVariable Assigns response-axis variable |
AnalysisVariable | Yes | No | Yes |
| CategorySortVariable Determines sort order for bars |
Variable | Yes | Yes | No |
| ColumnVariable Aligns multiple charts in columns |
ClassificationVariable | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| InsideBarLabelVariable Sets bar labels inside the bar element |
Variable | Yes | Yes | No |
| OutsideBarLabelVariable Sets bar labels outside the bar element |
Variable | Yes | Yes | No |
| RowVariable Aligns multiple charts in rows |
ClassificationVariable | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| StyleByVariable Maps style properties onto bar elements |
Variable | Yes | Yes | No |
| * required variable | ||||
To generate a graph, a WaterfallChart needs a data column for the CategoryVariable role. If the role is not assigned in the program code, a WaterfallChart selects the first string column found in the WaterfallChartTableDataModel and uses it as its Category variable. If there is no string column in the data, then it selects the first numeric column.
This default behavior occurs only when the Category role is not assigned. If the role is assigned to a variable that does not exist in the data, the WaterfallChart cannot display a graph.
If the ResponseVariable role is not assigned in the program code, then the bar heights represent a frequency count of the Category values. If the ResponseVariable role is assigned, then the default statistic for the bar heights is the sum of the response values for each category value.
A WaterfallChartTableDataModel fires property change events when
For example, if the name property is changed in the ClassificationVariable that has been assigned the CategoryVariable role, the WaterfallChartTableDataModel fires a ProeprtyChangeEvent stating that the CategoryVariable has changed.
When variable roles are assigned, the WaterfallChartTableDataModel does not confirm that the variables exist in the TableModel. Thus, assigning a non-existent data column to a variable role may mean that the WaterfallChart cannot display a graph. For example, if the CategoryVariable role is assigned to an Id column but the TableModel does not contain an Id column, then the WaterfallChart fails to produce a graph.
If the CategoryVariable role is correctly assigned to an existing variable but another role is incorrectly assigned, the WaterfallChart displays a graph without the incorrect role. For example, if the CategoryVariable role is correctly assigned but the ColumnVariable role is not, a graph using the Category role is generated, but the Column role is ignored.