SAS 9.1.3 Integration Technologies » Server Administrator's Guide
|
Pooling and Load Balancing
Overview of Load BalancingWhat Is Load Balancing?Load balancing is a feature of the object spawner that balances workloads across server processes and across server machines. When a logical SAS Workspace Server or a logical SAS Stored Process Server is configured as a load-balancing cluster, client requests to any of the servers in the cluster are directed to the server that has the least load. The amount of load on a server is determined by a load-balancing algorithm.
How Load Balancing WorksFor SAS Workspace Servers, load balancing distributes work equally across server machines. For SAS Stored Process Servers, load balancing distributes work equally across server processes. These server processes can exist on the same machine or across multiple machines. Load balancing occurs within a group of servers called a cluster. Each machine in the cluster runs an object spawner that handles client requests for connections. All of the spawners in the cluster are connected together, and they share their server load information. A load balancer routine runs in each object spawner and directs client requests to the server or server process that is least loaded at the time the client request is made. Subsequent calls are performed as direct calls between the client and SAS. Note: Each client's credentials must be able to authenticate against any server in the load-balancing cluster. Therefore, when you define server connections within a load-balancing cluster, you must use the same authentication domain for each connection. When you launch a load-balancing spawner, you must specify a metadata configuration file that contains information for accessing a SAS Metadata Server. The spawner processes information as follows: 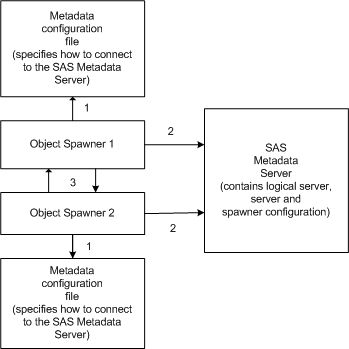
Each spawner then has the server metadata in order to launch new server processes for client requests. If one machine in the cluster becomes unavailable, then the other machines in the cluster detect that the machine is unavailable and continue to run and process any client requests. Note: You can launch load-balancing spawners at any time, as follows:
Note: Because a client can connect to any machine, client programs should not depend on being able to reconnect to the same server. Example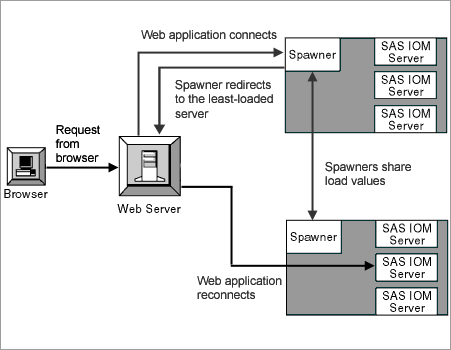
The following scenario assumes a load-balancing cluster that contains two server machines. The spawner on each machine is running, and each spawner has started three server processes. A Web application connects to SAS using the Windows Object Manager (or the Java Connection Factory) as follows:
When the Web application disconnects from the server, the load for that server returns to its previous value. MultiBridge Connections (SAS Stored Process Servers Only)When you configure load balancing for SAS Stored Process Servers, you must define at least one MultiBridge connection for each server in the cluster. Each MultiBridge connection represents a separate server process within a Stored Process Server definition, and each MultiBridge connection runs on a specific port. The Bridge connection for a stored process server is only used for the initial server request. After the spawner determines which server process has the least load, the client is redirected to the appropriate MultiBridge connection. That is, a client requests the Bridge connection for a stored process server, and then the spawner redirects the client to the appropriate MultiBridge connection. Note: MultiBridge connections use the server's multi-user login credentials. When using MultiBridge connections, you must specify multi-user login credentials on the server definition. SecurityWith load balancing, every connection to the server is authenticated with the credentials of the client. However, the credentials that server runs under depends on the type of server:
You can use normal server security mechanisms to protect sensitive data. For more information about load-balancing security, see Planning the Load Balancing Security. Administration (SAS Stored Process Servers Only)For SAS Stored Process Servers, you can use the administrator command Note: The AlgorithmsLoad balancing supports two different types of load-balancing algorithms:
For more details about load-balancing algorithms, see Planning the Load-Balancing Algorithm Properties. Setting up Load BalancingTo plan and set up load balancing, see Planning and Configuring a Load-Balancing Cluster. |
 Credentials
Credentials