Sample 33146: Dynamically selecting a table for a SAS® Information Map using a SAS® Stored Process with prompts
 |  |  |
Overview
You might have many tables that have the same data structure but vary in content. In such a case, it is not always efficient to join all of the tables together in an information map. This sample demonstrates how to create an information map that selects which table to use based on a parameter selected from a prompt.
This sample uses a stored process to preprocess the information map. The stored process uses a lookup table in order to determine which table to use for the information map based on the selected prompt value. All of your tables must have a similar structure for this sample to work. The sample uses the following tables in the SASHELP library: PRDSALE, PRDSAL2, and PRDSAL3. The following figure shows how the input table is chosen based on the prompt value.
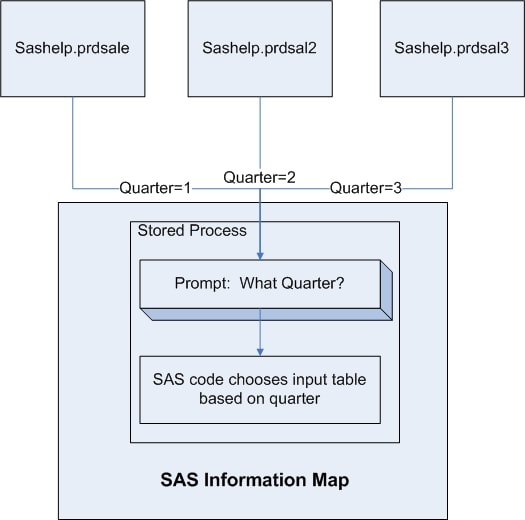
Here are the major steps that you will perform:
- Create and register the stored process in SAS® Enterprise Guide
- Create and register metadata for the result table.
- Create the information map by using the metadata for the result table and the stored process.
Note: For another example of how to associate a stored process with an information map, see SAS Sample 26175.
Create and Register the Stored Process in SAS Enterprise Guide
- Open SAS Enterprise Guide.
- Select File ► New ► Code.
- Include the following code:
- Select the Project Designer tab.
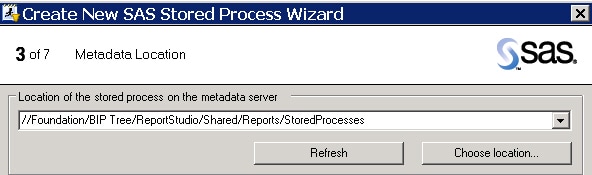
- Right-click on the code icon and select Create Stored Process to launch a wizard that will guide you through creating the stored process. There are seven pages in the wizard, but the following screen captures show only the major modifications.
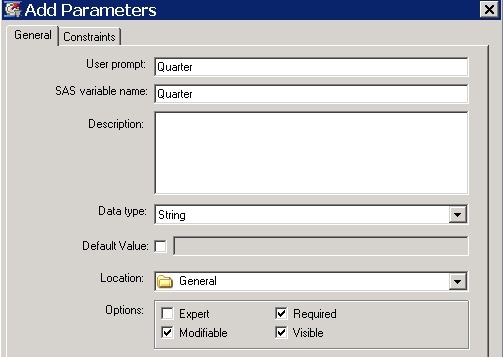
- Add a parameter called Quarter.
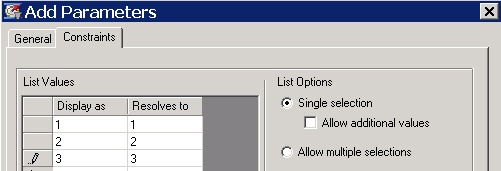
- Click the Constraints tab and create a list that contains 1, 2 and 3.
- Select None for output.
- Deselect the Run stored process when finished option, and then click Finish.
*ProcessBody;
%stpbegin;
%global quarter; /* passed in from the prompt and turned into a SAS macro */
libname biout (work);
/*
This first step creates a parameter driven table for the parameter. Normally
This table would be created in advance and not included in the stored process
for performance reasons.
*/
data work.driver;
length quarter $1 table $30;
quarter = '1';
table='sashelp.prdsale';
output;
quarter = '2';
table='sashelp.prdsal2';
output;
quarter = '3';
table='sashelp.prdsal3';
output;
run;
/* ******* end of parameter table code ************** */
/* loop through the driver table and pick out the table from the quarter */
data _NULL_;
set work.driver (where=(quarter=compress("&quarter")));
/* ***************************************************************************
There should now only be 1 row in the table so grab the table value and
store it in a macro variable.
**************************************************************************** */
call symput("mytable",table);
run;
/* **********************************************************************
Create the table for the map. Keep in mind that the table that is
included in the map should be biout.sales
*********************************************************************** */
data biout.sales;
length table $30; /* create the table column to list the table that was chosen */
table = compress("&mytable");
set &mytable ;
run;
%stpend;
|

Note: Make sure that the Execution Server is a Workspace Server. You might have to select the Modify button to change that.

Note: If you are creating the stored process in SAS 9.3, then, in SAS Management Console, right-click on the stored process and select Make Compatible. Using the Make Compatible option is the easiest way to ensure that stored processes created with SAS 9.3 can be used with information maps.
Create and Register Metadata for the Result Table
- Create a new code object by selecting File ► New ► Code.
- Insert and submit the following code on your remote server:
- Open SAS® Management Console and register the BIOUT.SALES table.
/* ******************************************************************************
Note: Your location to the biout library will be different from mine. keep in
mind that this library needs to be registered in the SAS Management Console
******************************************************************************** */
LIBNAME biout BASE "C:\orion\orgold\biout" ;
run; |
Create the Information Map by Using the Metadata for the Result Table and the Stored Process
- Open SAS® Information Map Studio.
- Insert the biout.sales table.
- Select Tools ► Stored Processes and select the stored process that you created.
- Select Tools ► Test and verify that the prompt is displayed.
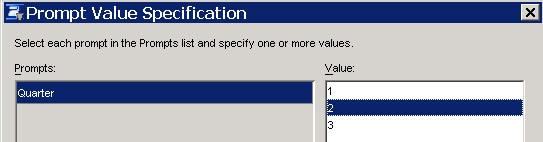
The table that is displayed should include a Table column and it should change based on the value of the Quarter prompt.
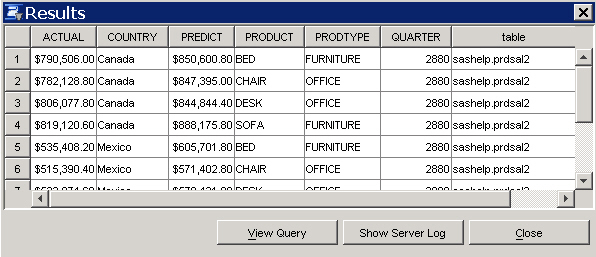
Note: The Quarter prompt value is not the same as the "Quarter" column in the PRDSALE, PRDSAL2, and PRDSAL3 tables.
Additional Documentation
For a list of available documentation for SAS Enterprise Guide, see http://support.sas.com/documentation/onlinedoc/guide/.
For a list of available documentation for SAS Information Map Studio, see http://support.sas.com/documentation/onlinedoc/ims/index.html.
These sample files and code examples are provided by SAS Institute Inc. "as is" without warranty of any kind, either express or implied, including but not limited to the implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose. Recipients acknowledge and agree that SAS Institute shall not be liable for any damages whatsoever arising out of their use of this material. In addition, SAS Institute will provide no support for the materials contained herein.
These sample files and code examples are provided by SAS Institute Inc. "as is" without warranty of any kind, either express or implied, including but not limited to the implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose. Recipients acknowledge and agree that SAS Institute shall not be liable for any damages whatsoever arising out of their use of this material. In addition, SAS Institute will provide no support for the materials contained herein.
| Type: | Sample |
| Date Modified: | 2008-09-11 17:03:58 |
| Date Created: | 2008-09-03 22:02:24 |
Operating System and Release Information
| Product Family | Product | Host | Product Release | SAS Release | ||
| Starting | Ending | Starting | Ending | |||
| SAS System | SAS Information Map Studio | Microsoft® Windows® for x64 | 3.1 | 9.1 TS1M3 SP4 | ||
| Microsoft Windows 2000 Advanced Server | 3.1 | 9.1 TS1M3 SP4 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows 2000 Datacenter Server | 3.1 | 9.1 TS1M3 SP4 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows 2000 Server | 3.1 | 9.1 TS1M3 SP4 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows 2000 Professional | 3.1 | 9.1 TS1M3 SP4 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Datacenter Edition | 3.1 | 9.1 TS1M3 SP4 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Enterprise Edition | 3.1 | 9.1 TS1M3 SP4 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Standard Edition | 3.1 | 9.1 TS1M3 SP4 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows XP Professional | 3.1 | 9.1 TS1M3 SP4 | ||||
| Windows Vista | 3.1 | 9.1 TS1M3 SP4 | ||||