| Variable Transformations |
Variance Stabilizing Transformations
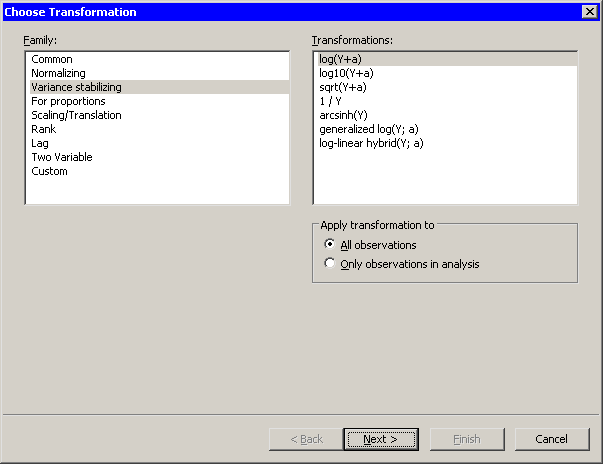
Figure 32.13 shows the transformations that are available
when you select Variance stabilizing from the Family list.
Variance stabilizing transformations
are often used to transform a variable whose variance depends on the
value of the variable. For example, the variability
of a variable ![]() might increase as
might increase as ![]() increases.
Equations for these transformations are
given in Table 32.3.
increases.
Equations for these transformations are
given in Table 32.3.
|
Figure 32.13: Variance Stabilizing Transformations
| Default | Name of | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Transformation | Parameter | New Variable | Equation |
| log(Y+a) | Log_Y | ||
| log10(Y+a) | Log10_Y | ||
| sqrt(Y+a) | Sqrt_Y | ||
| 1 / Y | Inv_Y | ||
| arcsinh(Y) | Arcsinh_Y | ||
| generalized log(Y;a) | GLog_Y | ||
| log-linear hybrid(Y;a) | LogLin_Y | See text. |
The log-linear hybrid transformation is defined for ![]() as follows:
as follows:
The generalized log and the log-linear hybrid transformations were introduced in the context of gene-expression microarray data by Rocke and Durbin (2003).
Copyright © 2008 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.