The NPAR1WAY Procedure
Hodges-Lehmann Estimation of Location Shift
If you specify the HL option, PROC NPAR1WAY computes the Hodges-Lehmann estimate of location shift for two-sample data. This option also provides asymptotic confidence limits for the location shift (which are sometimes known as Moses confidence limits). You can specify the confidence level in the ALPHA= option in the PROC NPAR1WAY statement. By default, ALPHA=0.05, which produces 95% confidence limits. Additionally, you can request exact confidence limits for the location shift by specifying the HL option in the EXACT statement.
The Hodges-Lehmann estimator of location shift is associated with the Wilcoxon linear rank statistic. For more information, see Hollander and Wolfe (1999) and Hodges and Lehmann (1983).
PROC NPAR1WAY computes the Hodges-Lehmann estimate 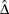 as the median of all paired differences between observations in the two samples (classes), which can be written as
as the median of all paired differences between observations in the two samples (classes), which can be written as
![\[ \hat{\Delta } = \mr{median} \left( ~ ( Y_ j - X_ i ) \quad \mr{where} \hspace{.1in} j = 1,2,\ldots ,n_1; ~ i = 1,2,\ldots ,n_2 ~ \right) \]](images/statug_npar1way0061.png)
The 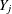 are observations in class 1, the
are observations in class 1, the 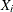 are observations in class 2, and
are observations in class 2, and 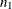 and
and 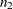 denote the number of observations in class 1 and class 2, respectively.
denote the number of observations in class 1 and class 2, respectively.
By default, PROC NPAR1WAY uses the larger of the two classes as the reference class X (class 2). If both class have the same number of observations, PROC NPAR1WAY uses the class that appears second in the input data set as the reference class. You can specify the reference class by using the HL(REFCLASS=) option. REFCLASS=1 refers to the first class that is listed in the "Wilcoxon Scores" table, and REFCLASS=2 refers to the second class in the table. REFCLASS=class-value identifies the reference class by the formatted value of the CLASS variable.
Let m denote the total number of differences (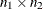 ), and let
), and let 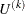 denote the kth value of
denote the kth value of 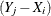 among the ordered differences. When m is an odd number, the median difference is the value that has rank
among the ordered differences. When m is an odd number, the median difference is the value that has rank 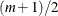 ,
,
![\[ \hat{\Delta } = U^{(k)} \quad \mr{where} \hspace{.1in} k = (m + 1) / 2 \]](images/statug_npar1way0068.png)
When m is an even number, the median difference is the average of the values that have ranks 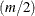 and
and 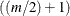 ,
,
![\[ \hat{\Delta } = \left( U^{(k)} + U^{(k+1)} \right) / 2 \quad \mr{where} \hspace{.1in} k = m / 2 \]](images/statug_npar1way0071.png)
Following Hollander and Wolfe (1999), the asymptotic lower and upper confidence limits for the location shift are
![\[ \left( ~ \Delta _{\mi{L}} = U^{(C_{\alpha })}, \hspace{.10in} \Delta _{\mi{U}} = U^{(m + 1 - C_{\alpha })} ~ \right) \]](images/statug_npar1way0072.png)
where 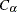 is the largest integer less than or equal to
is the largest integer less than or equal to 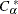 , which is computed as
, which is computed as
![\[ C_{\alpha }^{~ *} = \mr{E_0}(S) - z_{\alpha /2} \sqrt { \mr{Var_0}(S) } \]](images/statug_npar1way0075.png)
where 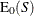 and
and 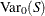 are the expected value and variance, respectively, of the Wilcoxon statistic S under the null hypothesis (as described in the section Simple Linear Rank Tests for Two-Sample Data), and
are the expected value and variance, respectively, of the Wilcoxon statistic S under the null hypothesis (as described in the section Simple Linear Rank Tests for Two-Sample Data), and 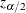 is the
is the 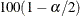 th percentile of the standard normal distribution. For Wilcoxon rank scores,
th percentile of the standard normal distribution. For Wilcoxon rank scores,
![\[ \mr{E_0}(S) = n_1 n_2 / 2 \]](images/statug_npar1way0078.png)
When there are no tied values, 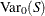 for Wilcoxon scores equals
for Wilcoxon scores equals
![\[ \mr{Var_0}(S) = n_1 n_2 ( n_1 + n_2 + 1 ) / 12 \]](images/statug_npar1way0079.png)
PROC NPAR1WAY displays the midpoint of the confidence interval 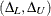 , which can also be used as an estimate of location shift. For more information, see Lehmann (1963). Additionally, PROC NPAR1WAY provides an estimate of the asymptotic standard error of
, which can also be used as an estimate of location shift. For more information, see Lehmann (1963). Additionally, PROC NPAR1WAY provides an estimate of the asymptotic standard error of 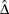 based on the length of the confidence interval, which is computed as
based on the length of the confidence interval, which is computed as
![\[ \mr{se}(\hat{\Delta }) = ( \Delta _{\mi{U}} - \Delta _{\mi{L}} ) ~ / ~ (2 ~ z_{\alpha /2}) \]](images/statug_npar1way0081.png)
Exact Confidence Limits
If you specify the HL option in the EXACT statement, PROC NPAR1WAY computes exact confidence limits for the location shift between the two samples. You can specify the level of the confidence limits in the ALPHA= option in the PROC NPAR1WAY statement. By default, ALPHA=0.05, which produces 95% confidence limits.
PROC NPAR1WAY computes exact confidence limits for the location shift as described in Randles and Wolfe (1979, p. 180). PROC NPAR1WAY first generates the exact conditional distribution of the Mann-Whitney U statistic, which equals the number of pairwise differences 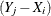 that are positive, plus half the number of pairwise differences that are 0. The Mann-Whitney statistic is defined as
that are positive, plus half the number of pairwise differences that are 0. The Mann-Whitney statistic is defined as
![\[ \mi{MW} = \sum _{j=1}^{n_1} \sum _{i=i}^{n_2} \phi \left( Y_ j, X_ i \right) \]](images/statug_npar1way0082.png)
where
![\[ \phi (Y_ j, X_ i) = \left\{ \begin{array}{ll} 1 & \mr{if} \hspace{.1in} Y_ j > X_ i \\[0.10in] 1 / 2 & \mr{if} \hspace{.1in} Y_ j = X_ i \\[0.10in] 0 & \mr{otherwise} \\ \end{array} \right. \]](images/statug_npar1way0083.png)
From the exact conditional distribution of the Mann-Whitney statistic 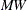 , PROC NPAR1WAY chooses
, PROC NPAR1WAY chooses 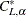 as the smallest value such that
as the smallest value such that 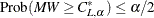 . Rounding
. Rounding 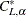 up to the nearest integer
up to the nearest integer 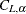 , the lower confidence limit equals the difference
, the lower confidence limit equals the difference 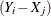 that has a rank of
that has a rank of 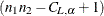 .
.
To find the upper confidence limit, PROC NPAR1WAY chooses 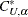 as the largest Mann-Whitney value such that
as the largest Mann-Whitney value such that 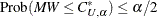 . Rounding
. Rounding 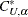 down to the nearest integer
down to the nearest integer 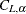 , the upper confidence limit equals the difference
, the upper confidence limit equals the difference 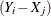 that has a rank of
that has a rank of 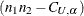 .
.
Because this is a discrete problem, the confidence coefficient is not exactly (1 –  ) but is at least (1 –
) but is at least (1 –  ); thus, these confidence limits are conservative.
); thus, these confidence limits are conservative.
