The FREQ Procedure
| OUTPUT Statement |
- OUTPUT <OUT= SAS-data-set> options ;
The OUTPUT statement creates a SAS data set that contains statistics computed by PROC FREQ. You specify which statistics to store in the output data set with the OUTPUT statement options. The output data set contains one observation for each two-way table or stratum, and one observation for summary statistics across all strata. For more information about the contents of the output data set, see the section Contents of the OUTPUT Statement Output Data Set.
Only one OUTPUT statement is allowed for each execution of PROC FREQ. You must specify a TABLES statement with the OUTPUT statement. If you use multiple TABLES statements, the contents of the OUTPUT data set correspond to the last TABLES statement. If you use multiple table requests in a TABLES statement, the contents of the OUTPUT data set correspond to the last table request.
Note that you can use the Output Delivery System (ODS) to create a SAS data set from any piece of PROC FREQ output. For more information, see the section ODS Table Names.
Also note that the output data set created by the OUTPUT statement is not the same as the output data set created by the OUT= option in the TABLES statement. The OUTPUT statement creates a data set that contains statistics (such as the Pearson chi-square and its p-value), and the OUT= option in the TABLES statement creates a data set that contains frequency table counts and percentages. See the section Output Data Sets for more information.
You can specify the following options in the OUTPUT statement:
- OUT=SAS-data-set
names the output data set. If you omit the OUT= option, the data set is named DATAn, where n is the smallest integer that makes the name unique.
- options
-
specify the statistics you want in the output data set. Table 36.7 lists the available options, together with the TABLES statement options needed to produce the statistics. You can output groups of statistics by using group options identical to those available in the TABLES statement, which include the AGREE, ALL, CHISQ, CMH, and MEASURES options. Or you can request statistics individually.
When you specify an option in the OUTPUT statement, the output data set contains all statistics from that analysis—the estimate or test statistic plus any associated standard error, confidence limits, p-values, and degrees of freedom. See the section Contents of the OUTPUT Statement Output Data Set for details.
If you want to store a statistic in the output data set, you must also request computation of that statistic with the appropriate TABLES or EXACT statement option. For example, you cannot specify the option PCHI (Pearson chi-square) in the OUTPUT statement without also specifying a TABLES or EXACT statement option to compute the Pearson chi-square test. The TABLES statement option ALL or CHISQ requests the Pearson chi-square test. If you have only one TABLES statement, the EXACT statement option CHISQ or PCHI also requests the Pearson chi-square test. Table 36.7 lists the TABLES statement options required to produce the OUTPUT data set statistics. Note that the ALL option in the TABLES statement invokes the CHISQ, MEASURES, and CMH options.
Table 36.7 OUTPUT Statement Options Option
Output Data Set Statistics
Required TABLES Statement Option
AGREE
McNemar’s test, Bowker’s test, simple and
weighted kappas; for multiple strata, overall
simple and weighted kappas, tests for equal
kappas, and Cochran’s
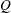
AJCHI
Continuity-adjusted chi-square (
 tables)
tables) ALL
CHISQ, MEASURES, and CMH statistics; N
BDCHI
Breslow-Day test (
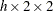 tables)
tables) BINOMIAL
Binomial statistics for one-way tables
CHISQ
For one-way tables, goodness-of-fit test;
for two-way tables, Pearson, likelihood-ratio,
continuity-adjusted, and Mantel-Haenszel
chi-squares, Fisher’s exact test (
 tables),
tables), phi and contingency coefficients, Cramer’s

CMH
Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel (CMH) correlation,
row mean scores (ANOVA), and general
association statistics; for
 tables, logit and
tables, logit and Mantel-Haenszel adjusted odds ratios and
relative risks, Breslow-Day test
CMH1
CMH output, except row mean scores (ANOVA)
and general association statistics
CMH2
CMH output, except general association statistic
CMHCOR
CMH correlation statistic
CMHGA
CMH general association statistic
CMHRMS
CMH row mean scores (ANOVA) statistic
COCHQ
Cochran’s
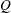 (
(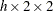 tables)
tables) CONTGY
Contingency coefficient
CRAMV
Cramer’s

EQKAP
Test for equal simple kappas
EQOR | ZELEN
Zelen’s test for equal odds ratios (
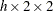 tables)
tables) CMH and EXACT EQOR
EQWKP
Test for equal weighted kappas
FISHER
Fisher’s exact test
GAILSIMON
Gail-Simon test
GAMMA
Gamma
JT
Jonckheere-Terpstra test
KAPPA
Simple kappa coefficient
KENTB
Kendall’s tau-

LAMCR
Lambda asymmetric
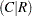
LAMDAS
Lambda symmetric
LAMRC
Lambda asymmetric
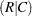
LGOR
Adjusted logit odds ratio (
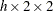 tables)
tables) LGRRC1
Adjusted column 1 logit relative risk
LGRRC2
Adjusted column 2 logit relative risk
LRCHI
Likelihood-ratio chi-square
MCNEM
McNemar’s test (
 tables)
tables) MEASURES
Gamma, Kendall’s tau-
 , Stuart’s tau-
, Stuart’s tau- ,
, Somers’
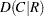 and
and 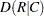 , Pearson and
, Pearson and Spearman correlations, lambda asymmetric
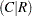 and
and 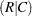 , lambda symmetric,
, lambda symmetric, uncertainty coefficients
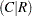 and
and 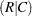 ,
, symmetric uncertainty coefficient;
odds ratio and relative risks (
 tables)
tables) MHCHI
Mantel-Haenszel chi-square
MHOR | COMOR
Adjusted Mantel-Haenszel odds ratio
(
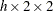 tables)
tables) MHRRC1
Adjusted column 1 Mantel-Haenszel relative risk
MHRRC2
Adjusted column 2 Mantel-Haenszel relative risk
N
Number of nonmissing observations
NMISS
Number of missing observations
OR
Odds ratio (
 tables)
tables) PCHI
Chi-square goodness-of-fit test for one-way tables,
Pearson chi-square for two-way tables
PCORR
Pearson correlation coefficient
PHI
Phi coefficient
PLCORR
Polychoric correlation coefficient
RDIF1
Column 1 risk difference (row 1 - row 2)
RDIF2
Column 2 risk difference (row 1 - row 2)
RELRISK
Odds ratio and relative risks (
 tables)
tables) RISKDIFF
Risks and risk differences (
 tables)
tables) RISKDIFF1
Column 1 risks and risk difference
RISKDIFF2
Column 2 risks and risk difference
RRC1
Column 1 relative risk
RRC2
Column 2 relative risk
RSK1
Column 1 risk, overall
RSK11
Column 1 risk, for row 1
RSK12
Column 2 risk, for row 1
RSK2
Column 2 risk, overall
RSK21
Column 1 risk, for row 2
RSK22
Column 2 risk, for row 2
SCORR
Spearman correlation coefficient
SMDCR
Somers’
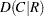
SMDRC
Somers’
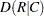
STUTC
Stuart’s tau-

TREND
Cochran-Armitage test for trend
TSYMM
Bowker’s test of symmetry
U
Symmetric uncertainty coefficient
UCR
Uncertainty coefficient
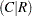
URC
Uncertainty coefficient
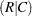
WTKAP
Weighted kappa coefficient

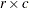 tables.
tables.