The Network Solver
- Overview
- Getting Started
-
Syntax

-
Details
 Input Data for the Network SolverSolving over Subsets of Nodes and Links (Filters)Numeric LimitationsBiconnected Components and Articulation PointsCliqueConnected ComponentsCycleLinear Assignment (Matching)Minimum-Cost Network FlowMinimum CutMinimum Spanning TreeShortest PathTransitive ClosureTraveling Salesman ProblemMacro Variable _OROPTMODEL_
Input Data for the Network SolverSolving over Subsets of Nodes and Links (Filters)Numeric LimitationsBiconnected Components and Articulation PointsCliqueConnected ComponentsCycleLinear Assignment (Matching)Minimum-Cost Network FlowMinimum CutMinimum Spanning TreeShortest PathTransitive ClosureTraveling Salesman ProblemMacro Variable _OROPTMODEL_ -
Examples
 Articulation Points in a Terrorist NetworkCycle Detection for Kidney Donor ExchangeLinear Assignment Problem for Minimizing Swim TimesLinear Assignment Problem, Sparse Format versus Dense FormatMinimum Spanning Tree for Computer Network TopologyTransitive Closure for Identification of Circular Dependencies in a Bug Tracking SystemTraveling Salesman Tour through US Capital Cities
Articulation Points in a Terrorist NetworkCycle Detection for Kidney Donor ExchangeLinear Assignment Problem for Minimizing Swim TimesLinear Assignment Problem, Sparse Format versus Dense FormatMinimum Spanning Tree for Computer Network TopologyTransitive Closure for Identification of Circular Dependencies in a Bug Tracking SystemTraveling Salesman Tour through US Capital Cities - References
General Options
You can specify the following general options, which have the same meaning for multiple algorithms.
-
GRAPH_DIRECTION=DIRECTED | UNDIRECTED
DIRECTION=DIRECTED | UNDIRECTED -
specifies directed or undirected graphs.
Table 9.5: Values for the GRAPH_DIRECTION= Option
Option Value
Description
DIRECTED
Requests a directed graph. In a directed graph, each link
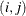 has a direction that defines how something (for example, information) might flow over that link. In link
has a direction that defines how something (for example, information) might flow over that link. In link 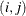 , information flows from node i to node j (
, information flows from node i to node j (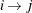 ). The node i is called the source (tail) node, and node j is called the sink (head) node.
). The node i is called the source (tail) node, and node j is called the sink (head) node.
UNDIRECTED
Requests an undirected graph. In an undirected graph, each link
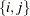 has no direction and information can flow in either direction. That is,
has no direction and information can flow in either direction. That is, 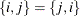 .
.
By default, GRAPH_DIRECTION=UNDIRECTED.
- INCLUDE_SELFLINK
-
includes self links in the graph definition—for example,
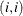 —when an input graph is read. By default, when the network solver reads the LINKS=
data, it removes all self links.
—when an input graph is read. By default, when the network solver reads the LINKS=
data, it removes all self links.
- LOGFREQ=number
-
controls the frequency with which an algorithm reports progress from its underlying solver. This setting is recognized by the traveling salesman problem and minimum-cost flow algorithms. You can set number to 0 to turn off log updates from underlying algorithms.
- LOGLEVEL=number | string
-
controls the amount of information that is displayed in the SAS log. This setting sets the log level for all algorithms. Table 9.6 describes the valid values for this option.
Table 9.6: Values for LOGLEVEL= Option
number
string
Description
0
NONE
Turns off all procedure-related messages in the SAS log
1
BASIC
Displays a basic summary of the input, output, and algorithmic processing
2
MODERATE
Displays a summary of the input, output, and algorithmic processing
3
AGGRESSIVE
Displays a detailed summary of the input, output, and algorithmic processing
By default, LOGLEVEL=BASIC.
- MAXTIME=number
-
specifies the maximum time spent calculating results. The type of time (either CPU time or real time) is determined by the value of the TIMETYPE= option. The value of number can be any positive number; the default value is the positive number that has the largest absolute value that can be represented in your operating environment. The clique, cycle, minimum-cost network flow, and traveling salesman problem algorithms recognize the MAXTIME= option.
- TIMETYPE=number | string
-
specifies whether CPU time or real time is used for the MAXTIME= option for each applicable algorithm. Table 9.7 describes the valid values of the TIMETYPE= option.
Table 9.7: Values for TIMETYPE= Option
number
string
Description
0
CPU
Specifies units of CPU time
1
REAL
Specifies units of real time
By default, TIMETYPE=CPU.