| The Unconstrained Nonlinear Programming Solver |
Example 13.3 Solving a Bound-Constrained Optimization Problem
Consider the following optimization problem, where 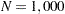 :
:
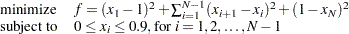 |
As you can see, this problem has 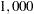 variables. Also the first
variables. Also the first 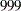 are allowed to take values only in the interval
are allowed to take values only in the interval 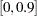 . In other words there are bounds on the values of the variables. Optimization problems that contain only this type of constraints are called bound-constrained problems. To solve the preceding problem you can use the following statements:
. In other words there are bounds on the values of the variables. Optimization problems that contain only this type of constraints are called bound-constrained problems. To solve the preceding problem you can use the following statements:
proc optmodel;
number N=1000;
var x{1..N} >= - 1.5 <= 3.0;
minimize f = sum {i in 1..N - 1} ( - 1.5 * x[i] + 2.5 * x[i + 1] +
1.0 + (x[i] - x[i + 1])^2 + sin(x[i] + x[i + 1]));
Solve with nlpu / tech=cgtr;
quit;
The optimal solution is displayed in Output 13.3.1.
| Problem Summary | |
|---|---|
| Objective Sense | Minimization |
| Objective Function | f |
| Objective Type | Nonlinear |
| Number of Variables | 1000 |
| Bounded Above | 0 |
| Bounded Below | 0 |
| Bounded Below and Above | 1000 |
| Free | 0 |
| Fixed | 0 |
| Number of Constraints | 0 |
Copyright © SAS Institute, Inc. All Rights Reserved.