IMSTAT Procedure (Analytics)
- Syntax
 Procedure SyntaxPROC IMSTAT (Analytics) StatementAGGREGATE StatementARM StatementASSESS StatementBOXPLOT StatementCLUSTER StatementCORR StatementCROSSTAB StatementDECISIONTREE StatementDISTINCT StatementFORECAST StatementFREQUENCY StatementGENMODEL StatementGLM StatementGROUPBY StatementHISTOGRAM StatementKDE StatementLOGISTIC StatementMDSUMMARY StatementOPTIMIZE StatementPERCENTILE StatementRANDOMWOODS StatementREGCORR StatementSUMMARY StatementTEXTPARSE StatementTOPK StatementQUIT Statement
Procedure SyntaxPROC IMSTAT (Analytics) StatementAGGREGATE StatementARM StatementASSESS StatementBOXPLOT StatementCLUSTER StatementCORR StatementCROSSTAB StatementDECISIONTREE StatementDISTINCT StatementFORECAST StatementFREQUENCY StatementGENMODEL StatementGLM StatementGROUPBY StatementHISTOGRAM StatementKDE StatementLOGISTIC StatementMDSUMMARY StatementOPTIMIZE StatementPERCENTILE StatementRANDOMWOODS StatementREGCORR StatementSUMMARY StatementTEXTPARSE StatementTOPK StatementQUIT Statement - Overview
- Examples
 Calculating Percentiles and QuartilesRetrieving Box ValuesRetrieving Box Plot Values with the NOUTLIERLIMIT= OptionRetrieving Distinct Value Counts and GroupingPerforming a Cluster AnalysisPerforming a Pairwise CorrelationCrosstabulation with Measures of Association and Chi-Square TestsTraining and Validating a Decision TreeStoring and Scoring a Decision TreePerforming a Multi-Dimensional SummaryFitting a Regression ModelForecasting and Automatic ModelingForecasting with Goal SeekingAggregating Time Series Data
Calculating Percentiles and QuartilesRetrieving Box ValuesRetrieving Box Plot Values with the NOUTLIERLIMIT= OptionRetrieving Distinct Value Counts and GroupingPerforming a Cluster AnalysisPerforming a Pairwise CorrelationCrosstabulation with Measures of Association and Chi-Square TestsTraining and Validating a Decision TreeStoring and Scoring a Decision TreePerforming a Multi-Dimensional SummaryFitting a Regression ModelForecasting and Automatic ModelingForecasting with Goal SeekingAggregating Time Series Data
Example 13: Forecasting with Goal Seeking
Details
Goal seeking is based
on numerical optimization of control variables in order to produce
a desired forecast. You can think of it as an inverse prediction method.
Normal prediction techniques produce a predicted value when given
a series of inputs. An inverse prediction method specifies the desired
predicted value and then asks to find the inputs that generate it.
For time series forecasting, the inverse prediction method is called
goal seeking. Instead of producing a forecast for values of independent
variables that you provide, you provide the target forecast (the goal).
Then, the numerical optimization attempts to find the values of the
independent variables that generate the goal values for the chosen
model.
The independent variables
in the time series model are divided into two categories. Those whose
values can be modified during goal seeking are called controllable
variables. The values of other independent variables are immutable
during goal seeking. You specify the variables that can be modified
during goal seeking in the CONTROL= option. You specify the variable
that cannot be modified (the target) with the GOAL= option.
Program
data work.pricedata; 1 set sashelp.pricedata; where region=1 and product=1 and line=1; run; data work.goalsale; retain slast 0; keep region product line; keep date gsale; set pricedata end=last; if sale ne . then slast=sale; if last then do; gsale=slast; do i=1 to 4; 2 gsale=1.05 * gsale; date=intnx("month", date, 1); output; end; stop; end; run; data work.merged; merge pricedata goalsale; by date; run; /* proc print data=merged; 3 var date sale price discount gsale; where date > '01jul2002'd; run; */ proc imstat; forecast data=merged date / dep =sale 4 control=(price discount) goal =gsale info lead =4 host ="grid001.example.com" 5 port =10010; quit;
Program Description
-
The DATA step places a subset of the Sashelp.Pricedata data set into the temporary Work library.
-
The purpose of this DATA step is to generate four additional observations for the variable Gsale. The values for this variable represent the sales goal to attain.
-
The PRINT procedure can be used to view the last few observations from the original data set with the observed values for Sale and the target values for variable Gsale.
-
The FORECAST statement requests a goal seeking analysis for time stamp Date, with dependent variable Sale, control variables Price and Discount, and the goal variable Gsale.
-
This example also demonstrates how the DATA= option can be used with the HOST= and PORT= option to analyze a data set that is not in memory. This feature is unique to this statement. In this example, the Merged data set is transferred from the temporary Work library to the server and then analyzed.
Output
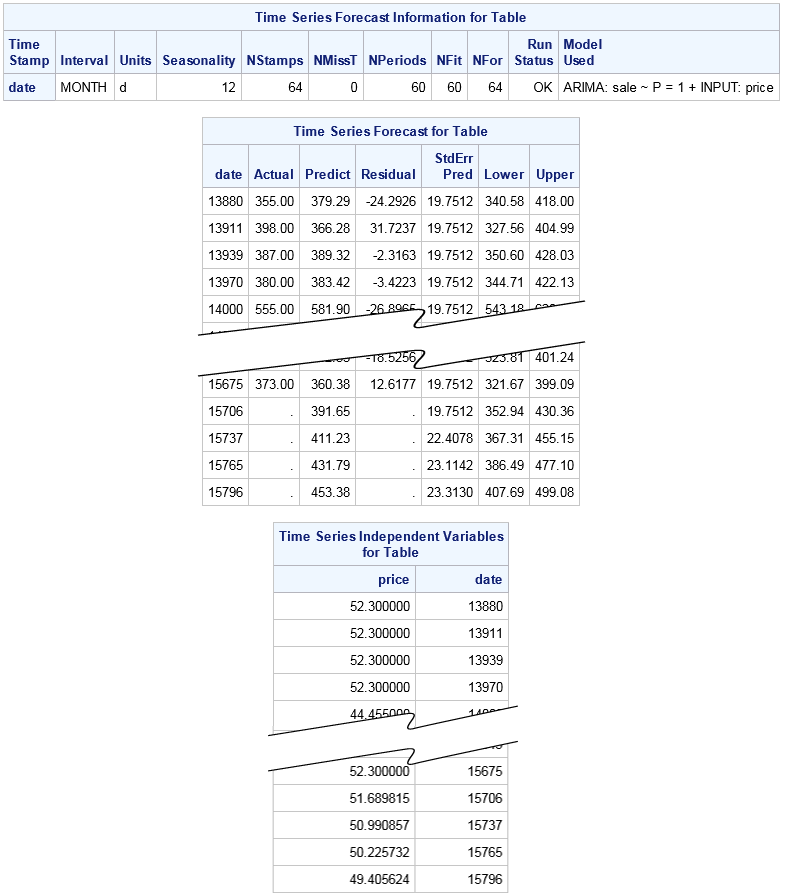
The forecast information
table shows that the automatic modeling step determined that the best-fitting
model was an ARIMA model with independent variable Price.
Based on this model,
the missing values for the control variables are replaced with forecasted
values and the result is passed to the goal-seeking analysis. It produces
the second and third tables.
The first sixty observations
in the forecast table are the forecasted values from the automatic
modeling step. The four observations at the end of the table are the
result of goal seeking. Notice that the values in the Predict column
for these four observations match the values for the Gsale column
in the Merged data set. (The data set is not shown here, but is available
if you remove the comments from the PROC PRINT statement.) The numerical
optimization converged and the goal was met.
Copyright © SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved.