The EXPAND Procedure
- Overview
-
Getting Started
 Converting to Higher Frequency Series Aggregating to Lower Frequency Series Combining Time Series with Different Frequencies Interpolating Missing Values Requesting Different Interpolation Methods Using the ID Statement Specifying Observation Characteristics Converting Observation Characteristics Creating New Variables Transforming Series
Converting to Higher Frequency Series Aggregating to Lower Frequency Series Combining Time Series with Different Frequencies Interpolating Missing Values Requesting Different Interpolation Methods Using the ID Statement Specifying Observation Characteristics Converting Observation Characteristics Creating New Variables Transforming Series -
Syntax

-
Details

-
Examples

- References
Example 15.3 Interpolating Irregular Observations
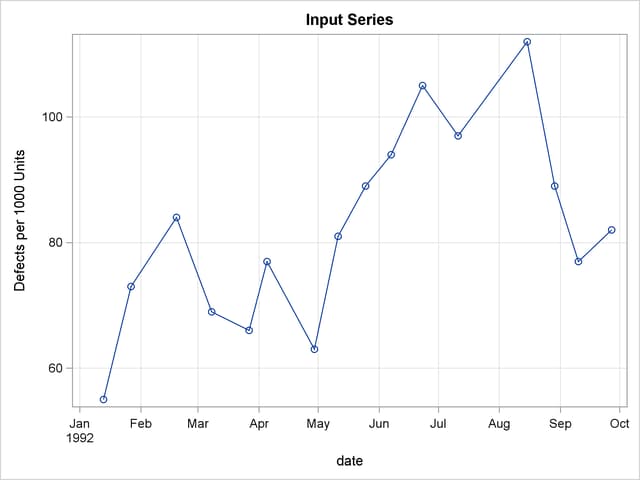
This example shows the interpolation of a series of values measured at irregular points in time. The data are hypothetical. Assume that a series of randomly timed quality control inspections are made and defect rates for a process are measured. The problem is to produce two reports: estimates of monthly average defect rates for the months within the period covered by the samples, and a plot of the interpolated defect rate curve over time.
The following statements read and print the input data, as shown in Output 15.3.1.
data samples; input date : date9. defects @@; label defects = "Defects per 1000 Units"; format date date9.; datalines; ... more lines ...
title "Sampled Defect Rates"; proc print data=samples; run;
| Sampled Defect Rates |
| Obs | date | defects |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 13JAN1992 | 55 |
| 2 | 27JAN1992 | 73 |
| 3 | 19FEB1992 | 84 |
| 4 | 08MAR1992 | 69 |
| 5 | 27MAR1992 | 66 |
| 6 | 05APR1992 | 77 |
| 7 | 29APR1992 | 63 |
| 8 | 11MAY1992 | 81 |
| 9 | 25MAY1992 | 89 |
| 10 | 07JUN1992 | 94 |
| 11 | 23JUN1992 | 105 |
| 12 | 11JUL1992 | 97 |
| 13 | 15AUG1992 | 112 |
| 14 | 29AUG1992 | 89 |
| 15 | 10SEP1992 | 77 |
| 16 | 27SEP1992 | 82 |
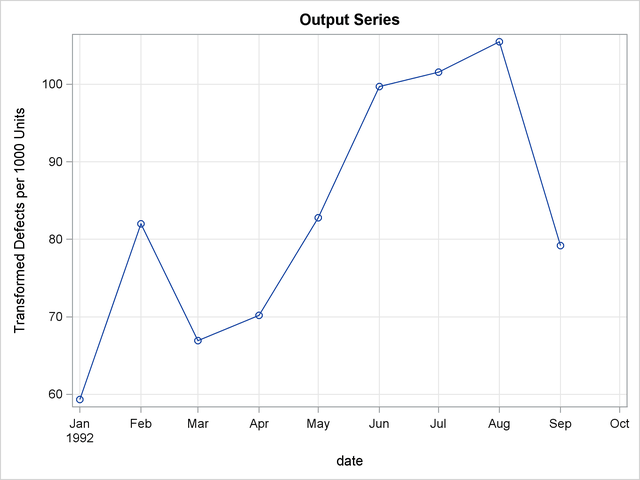
To compute the monthly estimates, use PROC EXPAND with the TO=MONTH option and specify OBSERVED=(BEGINNING,AVERAGE). The following statements interpolate the monthly estimates.
proc expand data=samples
out=monthly
to=month
plots=(input output);
id date;
convert defects / observed=(beginning,average);
run;
The following PROC PRINT step prints the results, as shown in Output 15.3.2.
title "Estimated Monthly Average Defect Rates"; proc print data=monthly; run;
| Estimated Monthly Average Defect Rates |
| Obs | date | defects |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | JAN1992 | 59.323 |
| 2 | FEB1992 | 82.000 |
| 3 | MAR1992 | 66.909 |
| 4 | APR1992 | 70.205 |
| 5 | MAY1992 | 82.762 |
| 6 | JUN1992 | 99.701 |
| 7 | JUL1992 | 101.564 |
| 8 | AUG1992 | 105.491 |
| 9 | SEP1992 | 79.206 |
The plots produced by PROC EXPAND are shown in Output 15.3.3.