| The TIMESERIES Procedure |
Example 27.2 Trend and Seasonal Analysis
This example illustrates using the TIMESERIES procedure for trend and seasonal analysis of time-stamped transactional data.
Suppose that the data set SASHELP.AIR contains two variables: DATE and AIR. The variable DATE contains sorted SAS date values recorded at no particular frequency. The variable AIR contains the transaction values to be analyzed.
The following statements accumulate the transactional data on an average basis to form a quarterly time series and perform trend and seasonal analysis on the transactions.
proc timeseries data=sashelp.air
out=series
outtrend=trend
outseason=season print=seasons;
id date interval=qtr accumulate=avg;
var air;
run;
The time series is stored in the data set WORK.SERIES, the trend statistics are stored in the data set WORK.TREND, and the seasonal statistics are stored in the data set WORK.SEASON. Additionally, the seasonal statistics are printed (PRINT=SEASONS) and the results of the seasonal analysis are shown in Output 27.2.1.
| Season Statistics for Variable AIR | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Season Index | N | Minimum | Maximum | Sum | Mean | Standard Deviation |
| 1 | 36 | 112.0000 | 419.0000 | 8963.00 | 248.9722 | 95.65189 |
| 2 | 36 | 121.0000 | 535.0000 | 10207.00 | 283.5278 | 117.61839 |
| 3 | 36 | 136.0000 | 622.0000 | 12058.00 | 334.9444 | 143.97935 |
| 4 | 36 | 104.0000 | 461.0000 | 9135.00 | 253.7500 | 101.34732 |
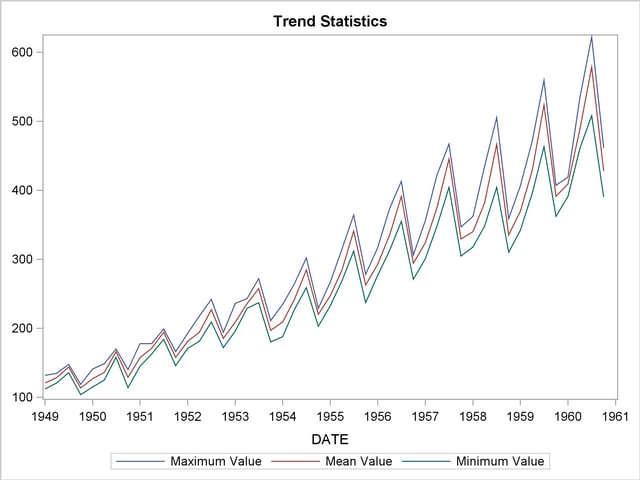
Using the trend statistics stored in the WORK.TREND data set, the following statements plot various trend statistics associated with each time period over time.
title1 "Trend Statistics";
proc sgplot data=trend;
series x=date y=max / lineattrs=(pattern=solid);
series x=date y=mean / lineattrs=(pattern=solid);
series x=date y=min / lineattrs=(pattern=solid);
yaxis display=(nolabel);
format date year4.;
run;
The results of this trend analysis are shown in Output 27.2.2.
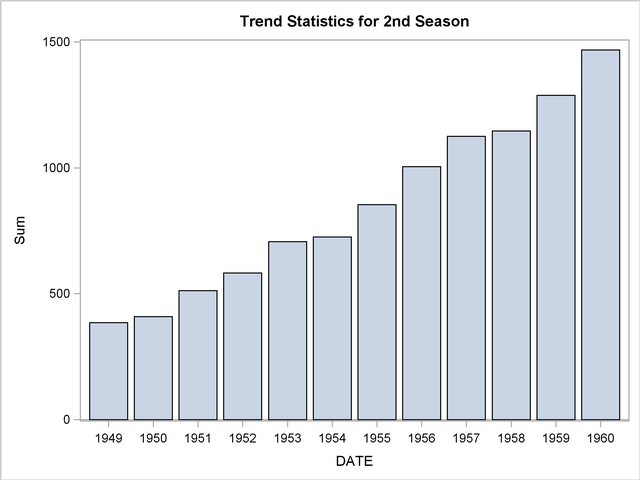
Using the trend statistics stored in the WORK.TREND data set, the following statements chart the sum of the transactions associated with each time period for the second season over time.
title1 "Trend Statistics for 2nd Season";
proc sgplot data=trend;
where _season_ = 2;
vbar date / freq=sum;
format date year4.;
yaxis label='Sum';
run;
The results of this trend analysis are shown in Output 27.2.3.
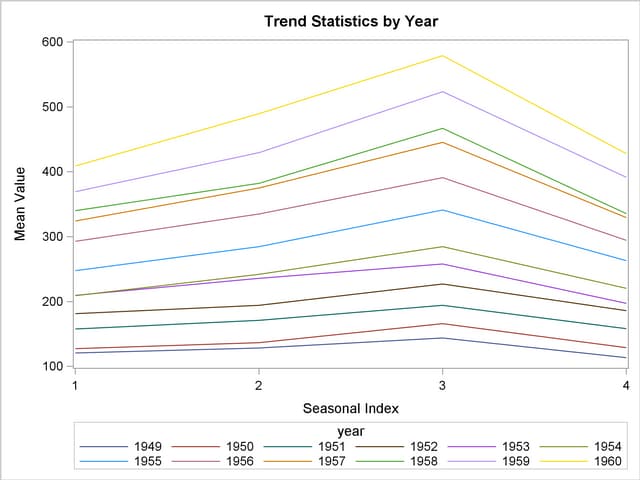
Using the trend statistics stored in the WORK.TREND data set, the following statements plot the mean of the transactions associated with each time period by each year over time.
data trend;
set trend;
year = year(date);
run;
title1 "Trend Statistics by Year";
proc sgplot data=trend;
series x=_season_ y=mean / group=year lineattrs=(pattern=solid);
xaxis values=(1 to 4 by 1);
run;
The results of this trend analysis are shown in Output 27.2.4.
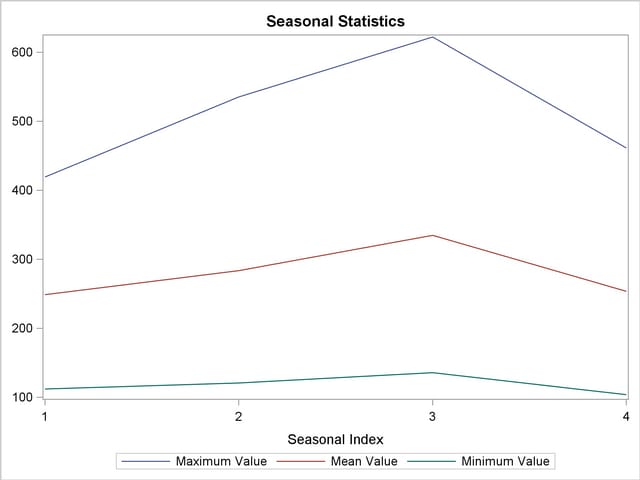
Using the season statistics stored in the WORK.SEASON data set, the following statements plot various season statistics for each season.
title1 "Seasonal Statistics";
proc sgplot data=season;
series x=_season_ y=max / lineattrs=(pattern=solid);
series x=_season_ y=mean / lineattrs=(pattern=solid);
series x=_season_ y=min / lineattrs=(pattern=solid);
yaxis display=(nolabel);
xaxis values=(1 to 4 by 1);
run;
The results of this seasonal analysis are shown in Output 27.2.5.
Copyright © 2008 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.