ERP and CRM Systems
Overview of ERP and CRP Systems
New Data Surveyors
Previously,
SAS provided data surveyors that relied on accessing the underlying
database—Oracle, DB2, and SQL Server—and not the application
APIs. SAS provides, through software from Composite Software, both
Service Oriented Architecture (SOA) and SQL data services that unlock
the data in Oracle Applications, Siebel, as well as Salesforce.com.
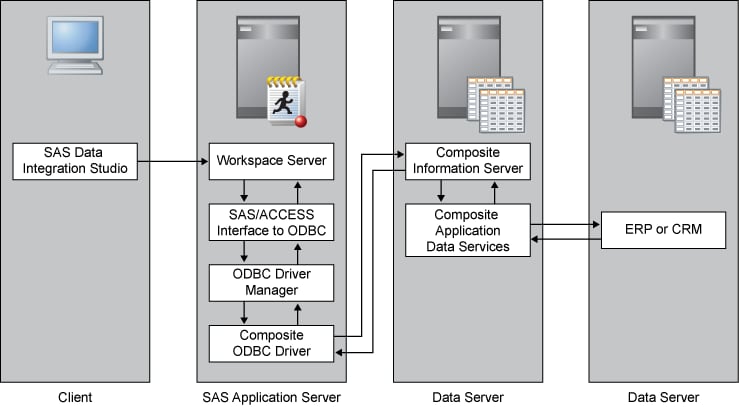
The following figure shows how SAS interacts with Composite Software:
The Composite Information Server uses a Data Service to access a data
source through the data source's API. The Composite Information Server
then offers the data through an ODBC interface. You configure an ODBC
data source name on the SAS Application Server with the Composite
ODBC driver. Then you use SAS Management Console to register an ODBC
server and an ODBC library. For a detailed example of a Composite
Information Server connection to Salesforce.com, See Establishing Connectivity to a Composite Information Server.
Data Surveyor for SAP
The Data Surveyor for SAP remains as
in previous versions. It contains Java plug-ins to SAS Data Integration
Studio and SAS Management Console, plus the required SAS/ACCESS engine
necessary to get the information out of the DBMS system. Understanding
the metadata of these business applications is at the heart of the
data surveyor. The SAP Data Surveyor has knowledge about the structure
of the tables deployed in SAP. This knowledge contains information
about the ERP metadata that enables you to do the following:
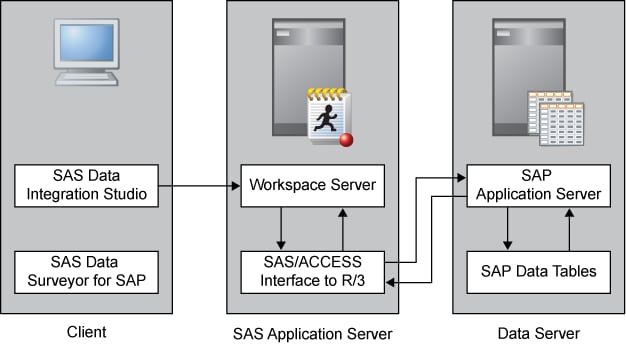
The following figure shows how connectivity to SAP
servers is established:
For a detailed example
of an SAP server connection, see Establishing Connectivity to an SAP Server.