Usage Note 43070: Creating a DBMS library in SAS® Management Console to Access it from a third-party ODBC application using the SAS ODBC driver
 |  |  |
You can access DBMS library that is defined in SAS Management from third party ODBC application using SAS ODBC driver and SAS/Share.®
You access the library as follows:
Step 1: Define a DBMS Library
First you need to define a DBMS library in SAS® Management Console. For details about how to define such a library, see "Assigning Libraries" in the SAS® 9.2 Intelligence Platform: Data Administration Guide.
You use SAS Management Console or the METALIB procedure to register the database tables that you want to access from a third-party application. To register tables with SAS Management Console, see Registering and Verifying Tables" in the SAS(R) 9.2 Intelligence Platform: Data Administration Guide. To register tables with PROC METALIB, see "Overview: METALIB Procedure" in the SAS(R) 9.2 Languages Interface to Metadata.
The following display shows five tables that are registered for the Teradata library in SAS Management Console.
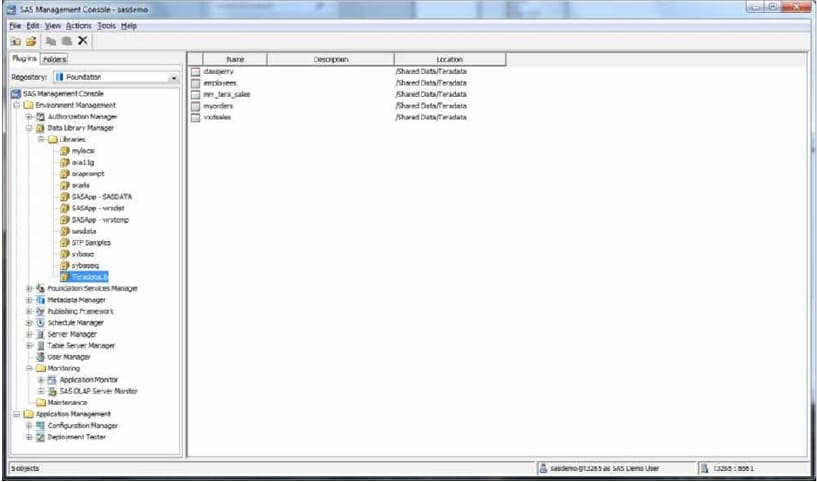
As you follow the steps to define your library, make sure that the library is assigned to a SAS/SHARE server, as shown below.

Step 2: Configure the SAS ODBC Driver
Configure the SAS ODBC driver so that it creates an ODBC data source. For details, see "Defining Your Data Sources" in the SAS® 9.2 Drivers for ODBC: User's Guide, Second Edition.To configure the driver, follow these steps:
- In the Windows operating environment, locate the ODBC Data Sources or the ODBC Administrator icon. This icon might be located in the Control Panel group, an ODBC group, or in Administrative Tools. Most commonly, you can find it by selecting Start ► Settings ► ► Control Panel ► Administrative Tools ► Data Sources(ODBC). The result should be the ODBC Data Source Administrator dialog box. In this dialog box, click the Add button to open the SAS ODBC Driver Configuration dialog box.
This dialog box contains three tabs: General, Servers, and Libraries. On each tab, provide information about the data source that you want to access.
- On the General tab, provide a name in the Data Source Name text box, as shown in the following display:
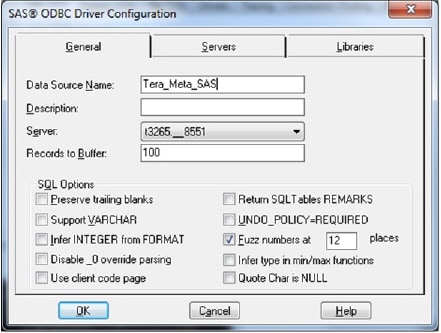
- On the Servers tab, enter a value for the Name list box. In Windows operating environments, the SAS ODBC driver requires special syntax for the server name. You must specify the two-part name, using the syntax machine-name__server-ID. Each part of the name must be eight characters or fewer, as shown in the example in the following display:
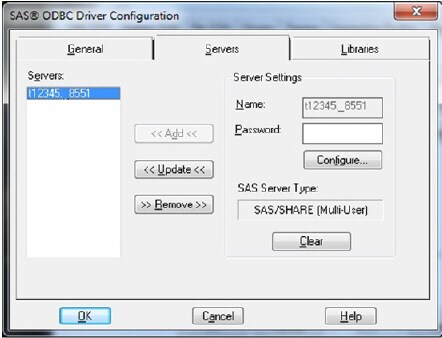
The SAS ODBC Driver interprets machine-name (in this case, t12345 as the host name of the SAS/SHARE server. It interprets server-ID (in this case, __8551) as the service name.
- Click the Configure button to display the SAS/SHARE Options dialog box.
- The Server Address text box is automatically filled with the alias for the TCP/IP network machine name that you specify in the Name text box on the Servers tab. Replace that value with the fully qualified domain name for your SAS/SHARE server (for example, machine.domain.com).
- The value for the User Name text box is your user ID for the system where the server is running. A value is required here if the server is running in secure mode. Otherwise, the system ignores the value in this box.
- The value for the User Password box is your password for the system on which the server is running. If you provide a user name without a user password, then the system prompts you for a password at connection time.
- The Connect Options text box uses a value for the SAS/SHARE server connection. Leave this box empty.
- The Userid/Password Override check box requests that the UID keyword and PWD keyword be used in the ODBC client application. The driver passes the value of the PWD keyword as the user logon password, and the value of the UID keyword as the user ID.
- When you finish entering all of the data, click OK to return to the Servers tab.
Important: Click the Add button to save the server definition.
- Click the Libraries tab, as shown in the following display:
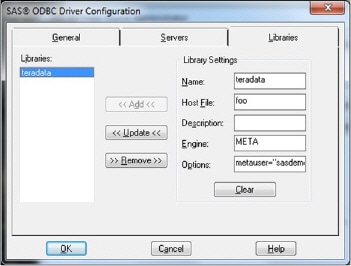
- Define a library for each data library that you want to access with this data source name, as follows:
- In the Name text box, enter a name for the library. This text box corresponds to the libref in a SAS LIBNAME statement.
- Enter a name for the host in the Host File text box.
- The Description text box is optional.
- In the Engine text box, enter META.
- In the Options text box, enter the following option:
metauser="metadata-user-ID" metapass="metadata-password" library="exact-library-name-as-defined-in-SAS-Management-Console"
- Click Add to save your library information. The saved library name is added then to the list of libraries in the Libraries list box on the left.

In this dialog box:
After you complete all of the steps above, you can query your database tables from any ODBC application (for example, Microsoft Access).
Operating System and Release Information
| Product Family | Product | System | Product Release | SAS Release | ||
| Reported | Fixed* | Reported | Fixed* | |||
| SAS System | SAS Drivers for ODBC | Microsoft® Windows® for x64 | 9.23 | 9.2 TS2M3 | ||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Datacenter Edition | 9.23 | 9.2 TS2M3 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Enterprise Edition | 9.23 | 9.2 TS2M3 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Standard Edition | 9.23 | 9.2 TS2M3 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2003 for x64 | 9.23 | 9.2 TS2M3 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2008 | 9.23 | 9.2 TS2M3 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2008 for x64 | 9.23 | 9.2 TS2M3 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows XP Professional | 9.23 | 9.2 TS2M3 | ||||
| Windows 7 Enterprise 32 bit | 9.23 | 9.2 TS2M3 | ||||
| Windows 7 Enterprise x64 | 9.23 | 9.2 TS2M3 | ||||
| Windows 7 Home Premium 32 bit | 9.23 | 9.2 TS2M3 | ||||
| Windows 7 Home Premium x64 | 9.23 | 9.2 TS2M3 | ||||
| Windows 7 Professional 32 bit | 9.23 | 9.2 TS2M3 | ||||
| Windows 7 Professional x64 | 9.23 | 9.2 TS2M3 | ||||
| Windows 7 Ultimate 32 bit | 9.23 | 9.2 TS2M3 | ||||
| Windows 7 Ultimate x64 | 9.23 | 9.2 TS2M3 | ||||
| Windows Vista | 9.23 | 9.2 TS2M3 | ||||
| Windows Vista for x64 | 9.23 | 9.2 TS2M3 | ||||
| Type: | Usage Note |
| Priority: | |
| Topic: | Data Management ==> Data Sources ==> External Databases |
| Date Modified: | 2011-08-10 13:37:17 |
| Date Created: | 2011-04-25 15:46:51 |