The NLMIXED Procedure
-
Overview

-
Getting Started

-
Syntax

-
Details
 Modeling Assumptions and NotationIntegral ApproximationsBuilt-in Log-Likelihood FunctionsHierarchical Model SpecificationOptimization AlgorithmsFinite-Difference Approximations of DerivativesHessian ScalingActive Set MethodsLine-Search MethodsRestricting the Step LengthComputational ProblemsCovariance MatrixPredictionComputational ResourcesDisplayed OutputODS Table Names
Modeling Assumptions and NotationIntegral ApproximationsBuilt-in Log-Likelihood FunctionsHierarchical Model SpecificationOptimization AlgorithmsFinite-Difference Approximations of DerivativesHessian ScalingActive Set MethodsLine-Search MethodsRestricting the Step LengthComputational ProblemsCovariance MatrixPredictionComputational ResourcesDisplayed OutputODS Table Names -
Examples

- References
References
-
Abramowitz, M., and Stegun, I. A., eds. (1972). Handbook of Mathematical Functions with Formulas, Graphs, and Mathematical Tables. 10th printing. New York: Dover.
-
Anderson, D. A., and Aitkin, M. (1985). “Variance Component Models with Binary Response: Interviewer Variability.” Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B 47:203–210.
-
Beal, S. L., and Sheiner, L. B. (1982). “Estimating Population Kinetics.” CRC Critical Reviews in Biomedical Engineering 8:195–222.
-
Beal, S. L., and Sheiner, L. B. (1988). “Heteroscedastic Nonlinear Regression.” Technometrics 30:327–338.
-
Beal, S. L., and Sheiner, L. B. (1992). NONMEM User’s Guide. San Francisco: NONMEM Project Group, University of California, San Francisco.
-
Beale, E. M. L. (1972). “A Derivation of Conjugate Gradients.” In Numerical Methods for Nonlinear Optimization, edited by F. A. Lootsma, 39–43. London: Academic Press.
-
Beitler, P. J., and Landis, J. R. (1985). “A Mixed-Effects Model for Categorical Data.” Biometrics 41:991–1000.
-
Billingsley, P. (1986). Probability and Measure. 2nd ed. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Booth, J. G., and Hobert, J. P. (1998). “Standard Errors of Prediction in Generalized Linear Mixed Models.” Journal of the American Statistical Association 93:262–272.
-
Breslow, N. E., and Clayton, D. G. (1993). “Approximate Inference in Generalized Linear Mixed Models.” Journal of the American Statistical Association 88:9–25.
-
Burnham, K. P., and Anderson, D. R. (1998). Model Selection and Inference: A Practical Information-Theoretic Approach. New York: Springer-Verlag.
-
Cox, C. (1998). “Delta Method.” In Encyclopedia of Biostatistics, edited by P. Armitage, and T. Colton. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Cox, D. R., and Oakes, D. (1984). Analysis of Survival Data. London: Chapman & Hall.
-
Cramer, J. S. (1986). Econometric Applications of Maximum Likelihood Methods. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
-
Crouch, E. A. C., and Spiegelman, D. (1990). “The Evaluation of Integrals of the Form
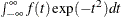 : Application to Logistic-Normal Models.” Journal of the American Statistical Association 85:464–469.
: Application to Logistic-Normal Models.” Journal of the American Statistical Association 85:464–469.
-
Davidian, M., and Gallant, A. R. (1993). “The Nonlinear Mixed Effects Model with a Smooth Random Effects Density.” Biometrika 80:475–488.
-
Davidian, M., and Giltinan, D. M. (1995). Nonlinear Models for Repeated Measurement Data. New York: Chapman & Hall.
-
Dennis, J. E., Gay, D. M., and Welsch, R. E. (1981). “An Adaptive Nonlinear Least-Squares Algorithm.” ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software 7:348–368.
-
Dennis, J. E., and Mei, H. H. W. (1979). “Two New Unconstrained Optimization Algorithms Which Use Function and Gradient Values.” Journal of Optimization Theory and Applications 28:453–482.
-
Dennis, J. E., and Schnabel, R. B. (1983). Numerical Methods for Unconstrained Optimization and Nonlinear Equations. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
-
Diggle, P. J., Liang, K.-Y., and Zeger, S. L. (1994). Analysis of Longitudinal Data. Oxford: Clarendon Press.
-
Draper, D. (1996). “Discussion of the Paper by Lee and Nelder.” Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B 58:662–663.
-
Draper, N. R., and Smith, H. (1981). Applied Regression Analysis. 2nd ed. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Engel, B., and Keen, A. (1992). A Simple Approach for the Analysis of Generalized Linear Mixed Models, vol. LWA-92-6. Wageningen, Netherlands: Agricultural Mathematics Group (GLW-DLO).
-
Eskow, E., and Schnabel, R. B. (1991). “Algorithm 695: Software for a New Modified Cholesky Factorization.” ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software 17:306–312.
-
Ezzet, F., and Whitehead, J. (1991). “A Random Effects Model for Ordinal Responses from a Crossover Trial.” Statistics in Medicine 10:901–907.
-
Fletcher, R. (1987). Practical Methods of Optimization. 2nd ed. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Galecki, A. T. (1998). “NLMEM: New SAS/IML Macro for Hierarchical Nonlinear Models.” Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine 55:207–216.
-
Gallant, A. R. (1987). Nonlinear Statistical Models. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Gaver, D. P., and O’Muircheartaigh, I. G. (1987). “Robust Empirical Bayes Analysis of Event Rates.” Technometrics 29:1–15.
-
Gay, D. M. (1983). “Subroutines for Unconstrained Minimization.” ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software 9:503–524.
-
Ghebretinsae, A. H., Faes, C., Molenberghs, G., De Boeck, M., and Geys, H. (2013). “A Bayesian, Generalized Frailty Model for Comet Assays.” Journal of Biopharmaceutical Statistics 23:618–636.
-
Gilmour, A. R., Anderson, R. D., and Rae, A. L. (1985). “The Analysis of Binomial Data by Generalized Linear Mixed Model.” Biometrika 72:593–599.
-
Goldstein, H. (1991). “Nonlinear Multilevel Models, with an Application to Discrete Response Data.” Biometrika 78:45–51.
-
Golub, G. H., and Welsch, J. H. (1969). “Calculation of Gaussian Quadrature Rules.” Mathematical Computing 23:221–230.
-
Harville, D. A., and Mee, R. W. (1984). “A Mixed-Model Procedure for Analyzing Ordered Categorical Data.” Biometrics 40:393–408.
-
Hedeker, D., and Gibbons, R. D. (1994). “A Random Effects Ordinal Regression Model for Multilevel Analysis.” Biometrics 50:933–944.
-
Hurvich, C. M., and Tsai, C.-L. (1989). “Regression and Time Series Model Selection in Small Samples.” Biometrika 76:297–307.
-
Lin, X., and Breslow, N. E. (1996). “Bias Correction in Generalized Linear Mixed Models with Multiple Components of Dispersion.” Journal of the American Statistical Association 91:1007–1016.
-
Lindstrom, M. J., and Bates, D. M. (1990). “Nonlinear Mixed Effects Models for Repeated Measures Data.” Biometrics 46:673–687.
-
Littell, R. C., Milliken, G. A., Stroup, W. W., Wolfinger, R. D., and Schabenberger, O. (2006). SAS for Mixed Models. 2nd ed. Cary, NC: SAS Institute Inc.
-
Liu, Q., and Pierce, D. A. (1994). “A Note on Gauss-Hermite Quadrature.” Biometrika 81:624–629.
-
Longford, N. T. (1994). “Logistic Regression with Random Coefficients.” Computational Statistics and Data Analysis 17:1–15.
-
McCulloch, C. E. (1994). “Maximum Likelihood Variance Components Estimation for Binary Data.” Journal of the American Statistical Association 89:330–335.
-
McGilchrist, C. A. (1994). “Estimation in Generalized Mixed Models.” Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B 56:61–69.
-
Molenberghs, G., Verbeke, G., Demetrio, C. G. B., and Vieira, A. M. C. (2010). “A Family of Generalized Linear Models for Repeated Measures with Normal and Conjugate Random Effects.” Statistical Science 25:325–347.
-
Moré, J. J. (1978). “The Levenberg-Marquardt Algorithm: Implementation and Theory.” In Lecture Notes in Mathematics, vol. 30, edited by G. A. Watson, 105–116. Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
-
Moré, J. J., and Sorensen, D. C. (1983). “Computing a Trust-Region Step.” SIAM Journal on Scientific and Statistical Computing 4:553–572.
-
Ochi, Y., and Prentice, R. L. (1984). “Likelihood Inference in a Correlated Probit Regression Model.” Biometrika 71:531–543.
-
Pierce, D. A., and Sands, B. R. (1975). Extra-Bernoulli Variation in Binary Data. Technical Report 46, Department of Statistics, Oregon State University.
-
Pinheiro, J. C., and Bates, D. M. (1995). “Approximations to the Log-Likelihood Function in the Nonlinear Mixed-Effects Model.” Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics 4:12–35.
-
Polak, E. (1971). Computational Methods in Optimization. New York: Academic Press.
-
Powell, M. J. D. (1977). “Restart Procedures for the Conjugate Gradient Method.” Mathematical Programming 12:241–254.
-
Pringle, R. M., and Rayner, A. A. (1971). Generalized Inverse Matrices with Applications to Statistics. New York: Hafner Publishing.
-
Rodriguez, G., and Goldman, N. (1995). “An Assessment of Estimation Procedures for Multilevel Models with Binary Response.” Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series A 158:73–89.
-
Roe, D. J. (1997). “Comparison of Population Pharmacokinetic Modeling Methods Using Simulated Data: Results from the Population Modeling Workgroup.” Statistics in Medicine 16:1241–1262.
-
Schall, R. (1991). “Estimation in Generalized Linear Models with Random Effects.” Biometrika 78:719–727.
-
Schittkowski, K., and Stoer, J. (1979). “A Factorization Method for the Solution of Constrained Linear Least Squares Problems Allowing Subsequent Data Changes.” Numerische Mathematik 31:431–463.
-
Self, S. G., and Liang, K.-Y. (1987). “Asymptotic Properties of Maximum Likelihood Estimators and Likelihood Ratio Tests under Nonstandard Conditions.” Journal of the American Statistical Association 82:605–610.
-
Serfling, R. J. (1980). Approximation Theorems of Mathematical Statistics. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Sheiner, L. B., and Beal, S. L. (1980). “Evaluation of Methods for Estimating Population Pharmacokinetic Parameters, Part I: Michaelis-Menten Model—Routine Clinical Pharmacokinetic Data.” Journal of Pharmacokinetics and Biopharmaceutics 8:553–571.
-
Sheiner, L. B., and Beal, S. L. (1985). “Pharmacokinetic Parameter Estimates from Several Least Squares Procedures: Superiority of Extended Least Squares.” Journal of Pharmacokinetics and Biopharmaceutics 13:185–201.
-
Smith, S. P. (1995). “Differentiation of the Cholesky Algorithm.” Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics 4:134–147.
-
Stiratelli, R., Laird, N. M., and Ware, J. H. (1984). “Random Effects Models for Serial Observations with Binary Response.” Biometrics 40:961–971.
-
Vonesh, E. F. (1992). “Nonlinear Models for the Analysis of Longitudinal Data.” Statistics in Medicine 11:1929–1954.
-
Vonesh, E. F. (1996). “A Note on Laplace’s Approximation for Nonlinear Mixed-Effects Models.” Biometrika 83:447–452.
-
Vonesh, E. F., and Chinchilli, V. M. (1997). Linear and Nonlinear Models for the Analysis of Repeated Measurements. New York: Marcel Dekker.
-
Weil, C. S. (1970). “Selection of the Valid Number of Sampling Units and Consideration of Their Combination in Toxicological Studies Involving Reproduction, Teratogenesis, or Carcinogenesis.” Food and Cosmetic Toxicology 8:177–182.
-
White, H. (1982). “Maximum Likelihood Estimation of Misspecified Models.” Econometrica 50:1–25.
-
Williams, D. A. (1975). “The Analysis of Binary Responses from Toxicological Experiments Involving Reproduction and Teratogenicity.” Biometrics 31:949–952.
-
Wolfinger, R. D. (1993). “Laplace’s Approximation for Nonlinear Mixed Models.” Biometrika 80:791–795.
-
Wolfinger, R. D. (1997). “Comment: Experiences with the SAS Macro NLINMIX.” Statistics in Medicine 16:1258–1259.
-
Wolfinger, R. D., and Lin, X. (1997). “Two Taylor-Series Approximation Methods for Nonlinear Mixed Models.” Computational Statistics and Data Analysis 25:465–490.
-
Wolfinger, R. D., and O’Connell, M. A. (1993). “Generalized Linear Mixed Models: A Pseudo-likelihood Approach.” Journal of Statistical Computation and Simulation 48:233–243.
-
Yuh, L., Beal, S. L., Davidian, M., Harrison, F., Hester, A., Kowalski, K., Vonesh, E., and Wolfinger, R. D. (1994). “Population Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Methodology and Applications: A Bibliography.” Biometrics 50:566–575.