The Decomposition Algorithm
- Overview
-
Getting Started

-
Syntax
 Decomposition Algorithm Options in the PROC OPTLP Statement or the SOLVE WITH LP Statement in PROC OPTMODELDecomposition Algorithm Options in the PROC OPTMILP Statement or the SOLVE WITH MILP Statement in PROC OPTMODELDECOMP StatementDECOMP_MASTER StatementDECOMP_MASTER_IP StatementDECOMP_SUBPROB Statement
Decomposition Algorithm Options in the PROC OPTLP Statement or the SOLVE WITH LP Statement in PROC OPTMODELDecomposition Algorithm Options in the PROC OPTMILP Statement or the SOLVE WITH MILP Statement in PROC OPTMODELDECOMP StatementDECOMP_MASTER StatementDECOMP_MASTER_IP StatementDECOMP_SUBPROB Statement -
Details

-
Examples
 Multicommodity Flow Problem and METHOD=NETWORKGeneralized Assignment ProblemBlock-Diagonal Structure and METHOD=CONCOMP in Single-Machine ModeBlock-Diagonal Structure and METHOD=CONCOMP in Distributed ModeBlock-Angular Structure and METHOD=AUTOBin Packing ProblemResource Allocation ProblemVehicle Routing ProblemATM Cash Management in Single-Machine ModeATM Cash Management in Distributed ModeKidney Donor Exchange and METHOD=SET
Multicommodity Flow Problem and METHOD=NETWORKGeneralized Assignment ProblemBlock-Diagonal Structure and METHOD=CONCOMP in Single-Machine ModeBlock-Diagonal Structure and METHOD=CONCOMP in Distributed ModeBlock-Angular Structure and METHOD=AUTOBin Packing ProblemResource Allocation ProblemVehicle Routing ProblemATM Cash Management in Single-Machine ModeATM Cash Management in Distributed ModeKidney Donor Exchange and METHOD=SET - References
DECOMP Statement
-
DECOMP <decomp-options>;
The DECOMP statement controls the overall decomposition algorithm.
Table 15.4 summarizes the decomp-options available in the DECOMP statement. These options control the overall decomposition algorithm process flow during the solution of an LP or a MILP. (As indicated, you can specify the data set options only in the OPTLP or OPTMILP procedure, and you can specify some control options only for a MILP.)
Table 15.4: Options in the DECOMP Statement
|
Description |
decomp-option |
|---|---|
|
Data Set Options (OPTLP and OPTMILP procedures only) |
|
|
Specifies the blocks input data set |
|
|
Control Options |
|
|
Specifies the stopping criterion based on an absolute objective gap |
|
|
Specifies the frequency of removing ineffective columns from the master LP |
|
|
Specifies whether or not to first process the root node by using standard MILP techniques |
|
|
Specifies whether to initialize the columns by solving each block with the original cost vector |
|
|
Specifies the level of detail of solution progress to print in the log |
|
|
Specifies the maximum number of blocks to allow |
|
|
Specifies the maximum number of new columns to allow into the master each pass |
|
|
Specifies the maximum amount of time spent in the decomposition algorithm |
|
|
Specifies the decomposition algorithm method |
|
|
Specifies the number of blocks to search for by using METHOD=AUTO |
|
|
Specifies the number of block threads to use in the decomposition algorithm |
|
|
Specifies the stopping criterion based on relative objective gap |
|
|
Control Options (MILP only) |
|
|
Specifies how frequently to print the continuous iteration log |
|
|
Specifies whether the master problem is solved as a MILP with the current set of columns at the beginning of phase II |
|
|
Specifies whether the master problem is solved as a MILP with the current set of columns at the end of phase II |
|
|
Specifies the frequency of solving the master problem as a MILP with the current set of columns |
|
|
Specifies the maximum number of outer iterations for the decomposition algorithm |
The following list describes the decomp-options in detail.
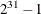

![\[ \mid \mbox{MasterObjective} - \mbox{BestBound}\mid / \left(\mbox{1E$-$10}~ + \mid \mbox{BestBound}\mid \right) \]](images/ormpug_decomp0036.png)