| The LP Procedure |
PROC LP Statement
- PROC LP options ;
This statement invokes the procedure. The following options can appear in the PROC LP statement.
Data Set Options
- ACTIVEIN=SAS-data-set
-
names the SAS data set containing the active nodes in
a branch-and-bound tree that is to be used to restart
an integer program.
- ACTIVEOUT=SAS-data-set
-
names the SAS data set in which to save the current
branch-and-bound tree of active nodes.
- DATA=SAS-data-set
-
names the SAS data set containing the problem
data. If the DATA= option is not specified, PROC LP uses the
most recently created SAS data set.
- DUALOUT=SAS-data-set
-
names the SAS data set that contains
the current dual solution (shadow prices)
on termination of PROC LP. This data set
contains the current dual solution only if PROC LP terminates
successfully.
- MPSOUT=SAS-data-set
-
names the SAS data set that contains converted sparse or
dense format input data in MPS format. Invoking this option directs the
LP procedure to halt before attempting optimization. For more information
about the MPS-format SAS data set, see
Chapter 14, "The MPS-Format SAS Data Set."
- PRIMALIN=SAS-data-set
-
names the SAS data set that contains a feasible solution
to the problem defined by the DATA= data set.
The data set specified in the PRIMALIN= option should have
the same format as a data set saved using
the PRIMALOUT= option.
Specifying the PRIMALIN= option is particularly useful for continuing
iteration on a problem previously attempted.
It is also useful for performing sensitivity analysis
on a previously solved problem.
- PRIMALOUT=SAS-data-set
-
names the SAS data set that contains
the current primal solution
when PROC LP terminates.
- SPARSEDATA
-
tells PROC LP that the data are in the sparse input format.
If this option is not specified,
PROC LP assumes that the data are
in the dense input format.
See the section "Sparse Data Input Format" for information about the sparse
input format.
- TABLEAUOUT=SAS-data-set
-
names the SAS data set in which to save the final tableau.
Display Control Options
- FLOW
-
requests that a journal of pivot information (the Iteration Log)
be displayed after every PRINTFREQ= iterations.
This includes the names of the variables entering and leaving the basis,
the reduced cost of the entering variable, and the current objective value.
- FUZZ=e
-
displays all numbers within e of zero as
zeros. The default value is 1.0E-10.
- NOFLOW
-
is the inverse of the FLOW option.
- NOPARAPRINT
-
is the inverse of the PARAPRINT option.
- NOPRINT
-
suppresses the display of the Variable, Constraint,
and Sensitivity Analysis summaries.
This option is equivalent to the PRINTLEVEL=0 option.
- NOTABLEAUPRINT
-
is the inverse of the TABLEAUPRINT option.
- PARAPRINT
-
indicates that the solution be displayed at each pivot when
performing parametric programming.
-
is the inverse of the NOPRINT option.
- PRINTFREQ=m
-
indicates that after every mth iteration, a
line in the (Integer) Iteration Log be displayed.
The default value is 1.
- PRINTLEVEL=i
-
indicates the amount of displaying that the procedure should perform.
- PRINTLEVEL=-2
- only messages to the SAS log are displayed
- PRINTLEVEL=-1
- is equivalent to NOPRINT unless the problem is infeasible. If it is infeasible, the infeasible rows are displayed in the Constraint Summary along with the Infeasible Information Summary.
- PRINTLEVEL=0
- is identical to NOPRINT
- PRINTLEVEL=1
- all output is displayed
- TABLEAUPRINT
-
indicates that the final tableau be displayed.
Interactive Control Options
- ENDPAUSE
-
requests that PROC LP pause before displaying the solution.
When this pause occurs, you can enter the RESET,
SHOW, PRINT, RUN,
and QUIT statements.
- FEASIBLEPAUSE
-
requests that PROC LP pause after a feasible (not necessarily
integer feasible) solution has been found. At a pause,
you can enter the RESET,
SHOW, PRINT,
PIVOT, RUN,
and QUIT statements.
- IFEASIBLEPAUSE=n
-
requests that PROC LP pause
after every n integer feasible solutions.
At a pause, you can enter the RESET,
SHOW, PRINT,
IPIVOT, PIVOT,
RUN, and QUIT statements.
The default value is 99999999.
- IPAUSE=n
-
requests that PROC LP pause after every
n integer iterations.
At a pause, you can enter RESET,
SHOW, PRINT,
IPIVOT, PIVOT,
RUN, and QUIT statements.
The default value is 99999999.
- NOENDPAUSE
-
is the inverse of the ENDPAUSE option.
- NOFEASIBLEPAUSE
-
is the inverse of the FEASIBLEPAUSE option.
- PAUSE=n
-
requests that PROC LP pause after every n iterations.
At a pause, you can enter the RESET,
SHOW, PRINT,
IPIVOT, PIVOT,
RUN, and QUIT statements.
The default value is 99999999.
- PROXIMITYPAUSE=r
-
causes the procedure to pause if at least one integer feasible
solution has been found and the objective value of the current best integer
solution can be determined to be within r units of the
optimal integer solution.
This distance, called proximity, is also displayed on the
Integer Iteration Log.
Note that the proximity is calculated using the minimum (maximum if the
problem is maximization)
objective value among the nodes that remain to be explored in the
branch-and-bound tree as a bound on the value of the optimal integer
solution.
Following the first PROXIMITYPAUSE= pause, in order to avoid a pause
at every iteration thereafter, it is recommended that you reduce this
measure through the use of a RESET statement.
Otherwise, if any other option
or statement that causes the procedure to pause is used while the
PROXIMITYPAUSE= option is in effect, pause interferences may occur.
When this pause occurs,
you can enter the RESET,
SHOW, PRINT,
IPIVOT, PIVOT,
RUN, and QUIT statements.
The default value is 0.
- READPAUSE
-
requests that PROC LP pause after the data have been read and the
initial basis inverted. When this pause occurs,
you can enter the RESET,
SHOW, PRINT,
IPIVOT, PIVOT,
RUN, and QUIT statements.
Preprocessing Control Options
- NOPREPROCESS
-
is the inverse of the PREPROCESS option.
- PEPSILON=e
-
specifies a positive number close to zero.
This value is an error tolerance in the preprocessing.
If the value is too small, any marginal changes
may cause the preprocessing to repeat itself.
However, if the value is too large, it may alter the
optimal solution or falsely claim that the problem is
infeasible.
The default value is 1.0E-8.
- PMAXIT=n
-
performs at most n preprocessings. Preprocessing
repeats itself if it improves some bounds or fixes some variables.
However when a problem is large and dense, each preprocessing may take a
significant amount of CPU time. This option limits the number of
preprocessings PROC LP performs.
It can also reduce the build-up of round-off errors.
The default value is 100.
- PREPROCESS
-
performs preprocessing techniques.
See the section "Preprocessing" for further discussion.
Branch-and-Bound Algorithm Control Options
- AUTO, AUTO(m,n)
-
automatically sets and adjusts the value of
the CONTROL= option. Initially, it sets
CONTROL=0.70, concentrating
on finding an integer feasible solution or an upper bound.
When an upper bound is found, it sets
CONTROL=0.5, concentrating on efficiency and lower
bound improvement. When the number of active problems
exceeds m, it starts to gradually increase the value
of the CONTROL= option to keep the size of active
problems under control.
When total active problems exceed n, CONTROL=1
will keep the active problems from growing further. You can
alter the automatic process by resetting the
value of the CONTROL= option interactively.
The default values of m and n are 20000 and 250000, respectively. You can change the two values according to your computer's space and memory capacities. - BACKTRACK=rule
-
specifies the rule used to choose the next active problem
when backtracking is required.
One of the following can be specified:
The default value is OBJ.
See the section "Integer Programming" for further discussion.
- BINFST
-
requests that PROC LP branch on binary variables first
when integer and binary variables are present.
The reasoning behind this is that
a subproblem will usually be fathomed or found integer
feasible after less than 20% of its variables have been fixed.
Considering binary variables first attempts to reduce the size
of the branch-and-bound tree. It is a heuristic technique.
- CANSELECT=rule
-
specifies the rule used to choose the next active problem
when backtracking is not required or used.
One of the following can be specified:
The default value is LIFO. See the section "Integer Programming" for further discussion. - CONTROL=r
-
specifies a number between 0 and 1. This option combines
CANSELECT= and other rules to choose the next active
problem. It takes into consideration three factors: efficiency,
improving lower bounds, and improving upper bounds. When r is
close to 0, PROC LP concentrates on improving lower bounds (upper bounds
for maximization). However, the efficiency per integer
iteration is usually the worst. When r is close to 1, PROC LP
concentrates on improving upper bounds (lower bounds for
maximization). In addition, the growth of active problems will be
controlled and stopped at r = 1. When its value is around 0.5,
PROC LP will be in the most efficient state in terms of CPU time
and integer number of iterations. The CONTROL= option will be automatically
adjusted when the AUTO option is applied.
- DELTAIT=r
-
is used to modify the exploration of the
branch-and-bound tree.
If more than r integer iterations have
occurred since the last integer solution was found, then
the procedure uses the backtrack strategy
in choosing the next node to be explored.
The default value is 3 times the number of integer variables.
- DOBJECTIVE=r
-
specifies that PROC LP should discard active nodes
that cannot lead to an integer solution with the objective
at least as small (or as large for maximizations) as
the objective of the
relaxed problem plus (minus) r. The default value is
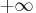 .
. - IEPSILON=e
-
requests that PROC LP
consider an integer variable as having
an integer value if its value is within e
units of an integer.
The default value is 1.0E-7.
- IMAXIT=n
-
performs at most n integer iterations.
The default value is 100.
- IOBJECTIVE=r
-
specifies that PROC LP should discard active nodes unless
the node could lead to an integer solution with the objective
smaller (or larger for maximizations) than r.
The default value is
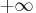 for minimization (
for minimization (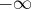 for maximization).
for maximization).
- LIFOTYPE=c
-
specifies the order in which to add the two newly branched
active nodes to the LIFO list.
- LIFOTYPE=0
- add the node with minimum penalty first
- LIFOTYPE=1
- add the node with maximum penalty first
- LIFOTYPE=2
- add the node resulting from adding
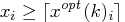 first
first
- LIFOTYPE=3
- add the node resulting from adding
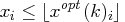 first
first
The default value is 0. - NOAUTO
-
is the inverse of the AUTO option.
- NOBINFST
-
is the inverse of the BINFST option.
- NOPOSTPROCESS
-
is the inverse of the POSTPROCESS option.
- PENALTYDEPTH=m
-
requests that PROC LP
examine m variables as branching candidates
when VARSELECT=PENALTY. If the
PENALTYDEPTH= option is not specified when
VARSELECT=PENALTY, then
all of the variables are considered branching candidates.
The default value is the number of integer variables.
See the section "Integer Programming" for further discussion.
- POBJECTIVE=r
-
specifies that PROC LP should discard active nodes that cannot
lead to an integer solution with objective
at least as small as
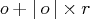 (at least as large as
(at least as large as 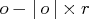 for maximizations)
where
for maximizations)
where 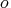 is the objective of
the relaxed noninteger constrained problem.
The default value is
is the objective of
the relaxed noninteger constrained problem.
The default value is 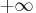 .
. - POSTPROCESS
-
attempts to fix binary variables globally based on the
relationships among the reduced cost and objective
value of the relaxed problem and the objective
value of the current best integer feasible solution.
- PWOBJECTIVE=r
-
specifies a percentage for use in the
automatic update of the WOBJECTIVE= option.
If the WOBJECTIVE= option is not specified in
PROC LP, then when an integer feasible solution is found, the value of
the option is updated to be b + q
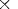 r
where b is the best bound on the value
of the optimal integer solution and q is the current proximity.
Note that for maximizations, b - q
r
where b is the best bound on the value
of the optimal integer solution and q is the current proximity.
Note that for maximizations, b - q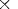 r
is used. The default value is 0.95.
r
is used. The default value is 0.95.
- TREETYPE=i
-
specifies a data compression algorithm.
- TREETYPE=0
- no data compression
- TREETYPE=1
- Huffman coding compression routines
- TREETYPE=2
- adaptive Huffman coding compression routines
- TREETYPE=3
- adaptive arithmetic coding compression routines
For IP or MIP problems, the basis and bounds information of each active node is saved to a utility file. When the number of active nodes increases, the size of the utility file becomes larger and larger. If PROC LP runs into a disk problem, like "disk full ..." or "writing failure ...", you can use this option to compress the utility file. For more information on the data compression routines, refer to Nelson (1992). The default value is 0. - VARSELECT=rule
-
specifies the rule used to choose the branching variable
on an integer iteration.
The default value is FAR.
See the section "Integer Programming" for further discussion.
- WOBJECTIVE=r
-
specifies that PROC LP should delay examination of active
nodes that cannot lead to an integer solution with
objective at least as small
(as large for maximizations) as r, until all
other active nodes have been explored.
The default value is
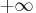 for minimization
(
for minimization
(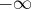 for maximization).
for maximization).
Sensitivity/Parametric/Ranging Control Options
- NORANGEPRICE
-
is the inverse of the RANGEPRICE option.
- NORANGERHS
-
is the inverse of the RANGERHS option.
-
PRICEPHI=
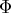
- specifies the limit for parametric programming when perturbing the price vector. See the section "Parametric Programming" for further discussion. See Example 3.5 for an illustration of this option.
- RANGEPRICE
-
indicates that range analysis is to be performed on the
price coefficients.
See the section "Range Analysis" for further discussion.
- RANGERHS
-
indicates that range analysis is to be performed on the
right-hand-side vector.
See the section "Range Analysis" for further discussion.
-
RHSPHI=
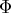
-
specifies the limit for parametric programming when perturbing
the right-hand-side vector.
See the section "Parametric Programming" for further discussion.
Simplex Algorithm Control Options
- DEVEX
-
indicates that the devex method of weighting the reduced costs
be used in pricing (Harris 1975).
- EPSILON=e
-
specifies a positive number close to zero. It is used in
the following instances:
During phase 1, if the sum of the basic artificial variables is within e of zero, the current solution is considered feasible. If this sum is not exactly zero, then there are artificial variables within e of zero in the current solution. In this case, a note is displayed on the SAS log.
During phase 1, if all reduced costs are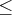 e for nonbasic variables at their lower bounds and
e for nonbasic variables at their lower bounds and
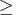 e for nonbasic variables at their upper bounds
and the sum of infeasibilities is greater than e,
then the problem is considered infeasible.
If the maximum reduced cost
is within e of zero, a note is displayed on the SAS log.
e for nonbasic variables at their upper bounds
and the sum of infeasibilities is greater than e,
then the problem is considered infeasible.
If the maximum reduced cost
is within e of zero, a note is displayed on the SAS log.
During phase 2, if all reduced costs are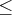 e for
nonbasic variables at their lower bounds and
e for
nonbasic variables at their lower bounds and 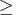 e for
nonbasic variables at their upper bounds, then the
current solution is considered optimal.
e for
nonbasic variables at their upper bounds, then the
current solution is considered optimal.
During phases 1, 2, and 3, the EPSILON= option is also used to test if the denominator is different from zero before performing the ratio test to determine which basic variable should leave the basis.
The default value is 1.0E-8. - GOALPROGRAM
-
specifies that multiple objectives in the input data set are
to be treated as sequential objectives in a goal-programming model.
The value of the right-hand-side variable in the objective
row gives the priority of the objective. Lower numbers have
higher priority.
- INFINITY=r
-
specifies the largest number PROC LP uses in computation.
The INFINITY= option is used to determine when a problem
has an unbounded variable value. The default value is
the largest double precision number.
*
- INVFREQ=m
-
reinverts the current basis matrix after
m major and minor iterations.
The default value is 100.
- INVTOL=r
-
reinverts the current basis matrix if the largest element
in absolute value in the decomposed basis matrix is greater than
r.
If after reinversion this condition still holds, then
the value of the INVTOL= option is increased by a factor of 10 and
a note indicating this modification is displayed on the SAS log.
When r is frequently exceeded,
this may be an indication of a numerically unstable problem.
The default value is 1000.
- MAXIT=n
-
simultaneously sets the values of the
MAXIT1=, MAXIT2=,
MAXIT3=, and IMAXIT= options.
- MAXIT1=n
-
performs at most n
 phase 1 iterations.
The default value is 100.
phase 1 iterations.
The default value is 100.
- MAXIT2=n
-
performs at most n
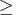 phase 2
iterations. If MAXIT2=0, then only phase 1 is entered so that on
successful termination PROC LP will have found a feasible, but not
necessarily optimal, solution.
The default value is 100.
phase 2
iterations. If MAXIT2=0, then only phase 1 is entered so that on
successful termination PROC LP will have found a feasible, but not
necessarily optimal, solution.
The default value is 100.
- MAXIT3=n
-
performs at most n
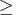 phase 3
iterations. All dual pivots are counted as phase 3 pivots.
The default value is 99999999.
phase 3
iterations. All dual pivots are counted as phase 3 pivots.
The default value is 99999999.
- NODEVEX
-
is the inverse of the DEVEX option.
- PARARESTORE
-
indicates that following a parametric programming analysis,
PROC LP should restore the basis.
- PHASEMIX=r
-
specifies a number between 0 and 1. When the number is
positive, PROC LP tries to improve the objective function
of phase 2 during phase 1. The PHASEMIX= option is a weight factor of
the phase 2 objective function in phase 1.
The default value is 0.
- PRICE=m
-
specifies the number of columns
to subset when multiple pricing
is used in selecting the column to enter the basis (Greenberg 1978).
The type of suboptimization used is determined by the
PRICETYPE= option.
See the section "Pricing" for a description of this process.
- PRICETYPE=pricetype
-
specifies the type of multiple pricing to be performed.
If this option is specified and the PRICE= option is not
specified, then PRICE= is assumed to be 10. Valid values for the
PRICETYPE= option are
The default value is PARTIAL.
See the section "Pricing" for a description of this process.
- RANDOMPRICEMULT=r
-
specifies a number between 0 and 1.
This option sets a limit, in phase 1, on the number
of iterations when PROC LP will randomly pick the entering variables.
The limit equals r times the number of nonbasic
variables, or the number of basic variables, whichever is
smaller.
The default value of the RANDOMPRICEMULT= option is 0.01.
- REPSILON=e
-
specifies a positive number close to zero.
The REPSILON= option is used in the ratio test to determine which basic
variable is to leave the basis.
The default value is 1.0E-10.
- SCALE=scale
-
specifies the type of scaling to be used. Valid values for the SCALE= option
are
The default value is BOTH.
See the section "Scaling" for further discussion.
- SMALL=e
-
specifies a positive number close to zero.
Any element in a matrix with a value less than e
is set to zero. The default value is machine dependent.
- TIME=t
-
checks at each iteration to see if t seconds
have elapsed since PROC LP began.
If more than t seconds have elapsed,
the procedure pauses and displays the current solution.
The default value is 120 seconds.
- U=r
-
enables PROC LP to control the choice of pivots during LU
decomposition and updating the basis matrix. The variable r
should take values between EPSILON and 1.0 because small values
of r bias the algorithm toward maintaining sparsity at
the expense of numerical stability and vice versa. The more sparse
the decomposed basis is, the less time each iteration takes.
The default value is 0.1.
Copyright © 2008 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.