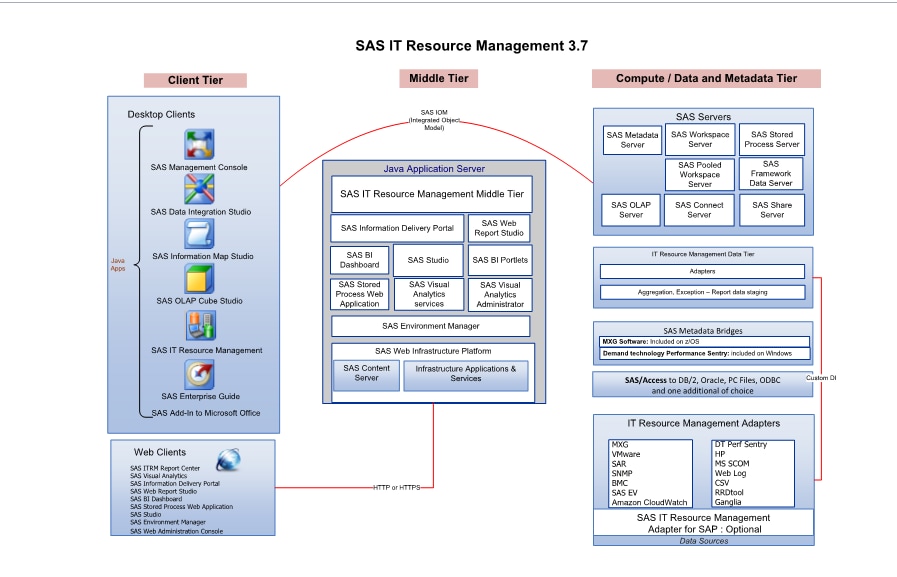
Architecture and Basic Principles for Data Administrators
The Architecture of SAS IT Resource Management
SAS IT Resource Management
uses data integration and business intelligence components that are
provided by the SAS Intelligence Platform. It also uses additional
software that was designed specifically for the processing of IT resource
data. At installation time, users can deploy these components across
multiple tiers. Using a multi-tier architecture to separate major
software functions supports flexible processing schemes. The following
functions can be supported on the tiers that SAS IT Resource Management
uses:
-
The client tier provides the interface between the user and SAS IT Resource Management. The client software enables you to perform data administration tasks, build reports, and view reports.
-
The middle tier provides web-based interfaces for report creation and information delivery. The web-based ITRM Report Center application runs on this tier.Note: SAS IT Resource Management supports both secured (https) and unsecured (http) middle tiers.
-
The server tier provides services that access data and perform background processing, such as managing the metadata, executing stored processes, and performing resource aggregation calculations. In addition, the server tier provides the metadata for the files and tables that are input to and generated by the SAS IT Resource Management software.
-
SAS Visual Analytics server and middle tiers are typically deployed to dedicated hardware resources. They can run on Linux x64 and Windows x64 operating environments.
With multi-tier processing, the tiers can be separated so that the
processing can be done on multiple machines.
-
The SAS IT Resource Management client must run on the Windows operating environment.
-
The SAS IT Resource Management middle tier can run in Windows or UNIX operating environments.
-
The SAS IT Resource Management server can run in Windows, UNIX, or z/OS operating environments.
Therefore, those software
components for the server tiers and the middle tiers can be installed
on different machines according to the site requirements of an enterprise
and the platforms that are supported by SAS for each tier of the SAS
software architecture. For example, in a Windows environment, all
of the processes that are needed by SAS IT Resource Management can
be installed on a single PC. Other sites might prefer to install the
client applications and middle tier on a PC and install the remaining
components on the mainframe. Another option is to install the components
needed for web-based functions on a UNIX processor. The SAS representative
can discuss these options and ensure the most appropriate configuration
for a site.
The architectural components
that constitute the clients, middle tier, and servers that are used
by SAS IT Resource Management are presented in the detail and summary
diagrams of the plan files for the SAS IT Resource Management solution.
Here is a sample of the diagrams that are delivered:
Note: The multiple tiers shown
in this diagram represent categories of software that perform similar
functions. They do not necessarily represent separate machines or
processors. In addition, your site might not need to use all of these
software components. For example, if your site does not use the SAS
Add-In for Microsoft Office, you do not need to install it.
The Basic Principles and Components of SAS IT Resource Management
Using IT Resource Management
After the initial setup
is complete, you can use IT Resource Management to process and evaluate
IT resource data. SAS IT Resource Management provides the processes
and the supporting technology that are required to regularly collect,
aggregate, analyze, and report on the IT performance evaluation data
that is vital to the health of an enterprise.
To start SAS IT Resource Management from Windows, select Start Programs
Programs SAS
SAS SAS IT Resource Management.
SAS IT Resource Management.
In general, the processes
that gather and monitor IT performance evaluation data consist of
the following steps.
-
IT performance data is information about IT resources, such as hardware, operating system software, networks, web servers, databases, and applications. Raw (or unprocessed) data about the usage or performance of these resources is generated by the logging mechanisms that are inherent to IT resources. The data can also be created by the Enterprise Systems Management tools that are used to manage the IT infrastructure. The raw data is input to SAS IT Resource Management transformations that are supplied with SAS IT Resource Management software.For information about how to generate and reference the raw data for supported adapters, see the various adapter-specific "Accessing Raw Data" topics in Data Sources Supported by SAS IT Resource Management Adapters.
-
The raw data is processed (or staged) by adapters that are customized for the data sources that they process. The adapter's staging code performs functions, such as normalizing measurement units, generating computed columns from the raw data, and checking for duplicate data. Staging is performed by transformations that are set up in jobs. The job that actually executes the transformation can run interactively but is normally scheduled to run in batch mode, depending on the requirements of your enterprise.A unique staging transformation is supplied for each adapter that is supported by SAS IT Resource Management. It contains the code and can access the associated templates that are needed to process and load the raw data into staged tables. For data sources that are not natively supported by the solution, the User-Written Staging transformation is available. The staged tables can then be used as input to an Aggregation transformation or other SAS Data Integration Studio and SAS IT Resource Management transformations.Information about these staging components is available in the following topics.
-
For a list of the adapters that are supported by SAS IT Resource Management, see Supported Adapters.
-
For more information about the staging transformations that are available for the supported adapters, see About Staging the Data..
-
For more information about user-written staging code, see User-Written Staging Transformations.
-
-
After the raw data is staged, it can be input to the aggregation step. An aggregation is the act or process of grouping data, using an operation that produces a statistic, such as a sum, average, minimum, or maximum. The term aggregation can also refer to the grouped data that results from such an operation. Aggregation transformations can generate summarized aggregated tables or simple aggregated tables.Jobs that contain Aggregation transformations are created and updated in SAS Data Integration Studio.
-
Simple aggregations do not undergo any summarizations; they simply append new data as it was read by the staging transformation to an existing aggregation table. (These tables are typically called detail aggregation tables.)
-
Summarized aggregations read data from a staged or user-defined table and then categorize and aggregate data according to the specifications of the Aggregation transformation.
An Aggregation transformation can contain multiple aggregations that each generate an aggregation table of data. SAS IT Resource Management provides the ability to customize Aggregation transformations based on a site's requirements. An Aggregation transformation can be customized to perform aging and filtering of the aggregated data. It can perform calculations that create additional columns of data and join columns from different tables. It can support summarizations of data into any choice of time periods. The Aggregation transformation can also compute statistics on the data, calculate percent of change of a statistic over a specified period of time, calculate the rank of a statistic or a class or ID column, and more.An unlimited number of aggregations can be created for each staged table. For example, the same data source can be input to both a daily aggregation and a weekly aggregation within the same or separate Aggregation transformations. For more information about working with Aggregation transformations and aggregation tables, see About Aggregation Tables. -
-
Incoming data can be evaluated by an exception analysis process that detects user-defined conditions. Typically, the source data to an Exception transformation is a staged table. However, it can be any table that users need to examine for exceptional conditions. (Information maps are not valid input to the Exception transformation.)The Exception transformation can be customized to filter the data and define the occurrence level and type of exception that is to be detected. The transformation supports the creation of exception definitions. The expression that is specified in the exception definition defines the condition being evaluated. These conditions are supported: constant threshold, other column, range, statistic bounds, and free form values. (Some exception definitions are supplied with the software.)When an exception is detected, SAS IT Resource Management can generate reports and tables. The reports are stored in the SAS Content Server.Report jobs are usually run in batch mode.
-
After the performance data has been aggregated, it is ready for the reporting processes. For a supported adapter, SAS IT Resource Management generates transformations that create information maps that reference the tables of data that are generated by that adapter's Aggregation transformations. Information maps provide clearly labeled references for all data fields that are used to create and view reports. Information maps can be used in SAS Enterprise Guide and SAS Intelligence Platform applications, such as SAS Web Report Studio in order to generate reports. These reports can provide domain intelligence about the adapters, such as CPU utilization, threshold analysis, and peak period analysis.For more information about working with Information Map transformations to create and customize information maps, see About Information Maps.
-
SAS IT Resource Management generates tabular and graphical reports from report definitions that are supplied with the software, or created in SAS Enterprise Guide. Report definitions can be accessed by the Performance Report transformation. When the job that contains that Performance Report transformation is run, the reports are generated and stored in the SAS Content Server. Report jobs are usually run in batch mode.Report definitions can be run directly from SAS Enterprise Guide, and the resulting reports can be viewed interactively from the SAS Enterprise Guide Project window or from a web browser. The reports can also be published to your web server.
-
Using ITRM Report Center, reports that are generated by running the Performance Report or the Exception transformation can be accessed and managed. This web application enables information consumers to organize their reports into gallery folders, galleries, and albums. Galleries can be filtered so that they display only a subset of the available reports.ITRM Report Center requires that users of this web application be assigned to users, groups, and roles in the metadata. SAS IT Resource Management delivers groups and roles that are necessary to use ITRM Report Center. For more information, see SAS IT Resource Management 3.7: Report Center Guide..For more information about the reporting capabilities that are available using SAS IT Resource Management data, see SAS IT Resource Management 3.7: Reporting Guide.
Information consumers
and performance analysts can also use these additional processes:
-
Generate and view ad hoc reports.SAS Web Report Studio is a web-based interface that can use information maps to select and report on data. Information maps are generated by Information Map transformations.
-
Use Microsoft Office products.SAS Add-In for Microsoft Office enables SAS functionality to be accessed directly from the menus and toolbars of Microsoft Office word processing and spreadsheet products.Performance analysts and information consumers frequently work with Microsoft Office products, such as Microsoft Word and Microsoft Excel. They can use SAS to access, analyze, and report on IT performance data that is available in information maps. SAS can then distribute the results to other people in the enterprise.
-
Use SAS Visual Analytics to actively interact with data produced by SAS IT Resource Management.
Copyright © SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved.