Recovering the SAS Metadata Server
About Metadata Server Recovery
You can use SAS Management
Console to recover the SAS Metadata Server. The following options
are available:
-
You can use the roll-forward recovery to apply metadata updates that are stored in the journal file.
The recovery facility
provides safeguards to ensure the integrity of the backup files from
which you are recovering. The recovery operation checks to make sure
that the backup directory contains all of the correct files and that
the files have the correct name and file sizes. In addition, each
backup file contains a universal unique identifier that is used to
make sure that you are recovering files for the correct metadata server.
If any problems exist, the recovery is not started and a warning message
is displayed.
During recovery operations,
the metadata server is automatically paused to a RECOVERY state. This
state is similar to an OFFLINE state but more restrictive. External
systems such as Windows Services Manager report the server as paused.
After the recovery, the metadata server automatically takes a new
backup. If the recovery was successful, the server is automatically
returned to the state that it was in before the recovery process.
About Roll-Forward Recovery
When recovering the metadata server,
you can choose to use roll-forward recovery to update the recovered
metadata repository files with transactions from the journal file.
Roll-forward recovery uses the journal file that is located in the
same directory as the backup files. The updates that are applied include
additions, modifications, and deletions of metadata, as well as additions
and deletions of metadata repositories. You can choose to apply all
transactions that are in the journal file, or you can apply all transactions
through a specified date and time.
Executing a Metadata Server Recovery
To recover the SAS metadata
server from a backup, either with or without roll-forward recovery,
follow these steps:
-
If you start the recovery while the server in the ADMINISTRATION state, the server changes the state to RECOVERY, performs the recovery, and then returns the server to the ADMINISTRATION state. You can then verify system readiness before clients reconnect. When readiness has been verified, you can manually resume the server.
-
Use one of the following methods to start the recovery process:
-
If you want to recover using backup files that are in the configured backup location, follow these steps:
-
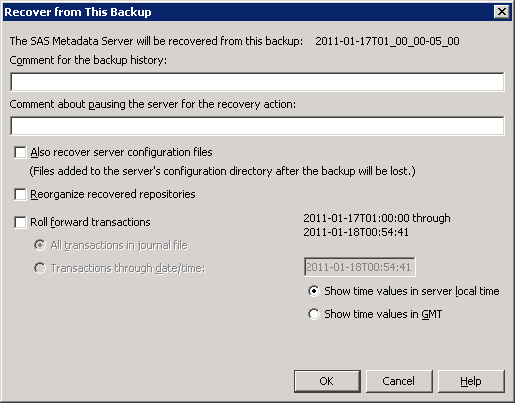
On the backup history list in the right panel, find the backup from which you want to recover. To determine its status, either double-click the backup entry or right-click and select Properties. If the files are usable for a recovery, the Verification field of the Properties dialog box displays this message:
All files in this backup are currently correct.
-
-
If you want to recover from a different location (for example, the location that contains your system backups), right-click the Server Backup node (located on the Plug-ins tab under Metadata Utilities), and select Recover from Alternate Location. In the Recover from Alternate Location dialog box, enter the complete pathname for the directory that contains the backup. You can specify any network location that is accessible from the metadata server. If the backups are remote to the metadata server, then specify a UNC path, as in the following example:
-
-
After you select Recover from This Backup (or after you enter a pathname in the Recover from Alternate Location dialog box and click OK), the server accesses the backup directory and attempts to validate the backup files. It checks to make sure that all of the backup files are present and that they have the correct filenames, file sizes, and universal unique identifier.Note: If the validation is not successful, one of the following messages is displayed:
-
If appropriate, select the check boxes for the following options:Also recover server configuration filesReorganize recovered repositoriesThis option reorganizes the metadata repositories when they are backed up following the recovery. The reorganization reclaims any unused disk space that is left from previously deleted metadata objects. See About the Reorganize Repositories Backup Option.Roll forward transactionsIn addition to restoring the repository files from the backup, this option recovers transactions that were recorded in the metadata server journal file after the backup was created. If you select this option, the following additional options become available:All transactions in journal fileThis option recovers all transactions that are recorded in the journal file. The time period that is covered by the journal file is displayed on the right side of the dialog box in server local time. (If you want to display the time period in Greenwich Mean Time (GMT), select Show time values in GMT.)Transactions through date/timeThis option recovers all transactions through a date and time that you specify. This option is useful if you want to recover the server to the state that it was in just before a specific problematic transaction. You can use the metadata server log to determine the exact time that the transaction occurred. See Use the Log Tab in the Server Manager.Enter the roll-forward ending date and time in the format yyyy-mm-dd
Thh:mm:ss. You can either edit the default values that are displayed in the field, or you can cut and paste the date and time from the appropriate event in the metadata server log. Most log events use server local time.The dialog box enables you to specify the time in either server local time or GMT, depending on which of the following radio buttons is selected:
Troubleshooting Metadata Server Recovery Jobs
If a recovery does not finish successfully, an e-mail
with the subject line
Metadata Server Recovery Failed is
sent to the designated recipients for metadata server alerts. The
e-mail specifies the server’s host name, the path to the server’s
configuration directory, and the recovery name. For details about
the failure, refer to the metadata server log and search for the recovery
name. The log is typically located in the Logs subdirectory
of the server’s configuration directory.
When a recovery fails,
an “x” icon ( ) also appears in the Status column of the backup
and recovery history panel in SAS Management Console. To determine
why the recovery failed, right-click the recovery and select Properties.
On the Properties dialog box, the Error
Summary field provides high-level information to help
resolve the problem. If more details are available, then the Full
Report button is activated. Click this button to obtain
a text report that you can browse, copy, and paste.
) also appears in the Status column of the backup
and recovery history panel in SAS Management Console. To determine
why the recovery failed, right-click the recovery and select Properties.
On the Properties dialog box, the Error
Summary field provides high-level information to help
resolve the problem. If more details are available, then the Full
Report button is activated. Click this button to obtain
a text report that you can browse, copy, and paste.
The ConfigurationFiles
subdirectory of each backup contains files called MetadataServerBackupHistory.xml,
MetadataServerBackupConfiguration.xml and MetadataServerRecoveryManifest.xml.
These files might be useful to SAS Technical Support if you require
troubleshooting assistance.
Note: In a Windows environment,
the recovery operation cannot update a READONLY file. If you have
manually set any of the metadata server files to READONLY, recovery
errors will be reported. In this situation, the recovery might still
be valid if no changes have been made to the READONLY file since the
backup was taken.