KPI (Key Performance Indicator)
Definition
KPI Subtypes
Usage Information
|
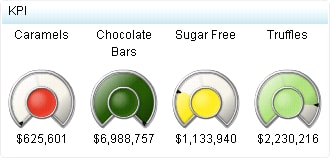
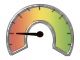
A gauge displays the
status or measure of a variable or variables in relation to a target,
goal, or interval. Gauges are designed to achieve this goal in a way
that is familiar to the user: Many gauges can be found in real-life
objects such as cars and machines. Gauges can be used to display
a quantity, range, variable, or status.
Gauges are most effective
when they are used to instantly alert the business user of a status,
without the user having to know many details. Business users should
be able to grasp information at a glance. Gauges, especially round
ones, can use up quite a bit of screen real estate, so keep this in
mind. They are commonly used, however, due to their familiarity and
ease of use.
|
|
|
KPI gauges are not suitable
for significant amounts of data. KPI gauges appear best with indicator
data that produces summarized data with a limited number of data rows.
If you use indicator data with significant amounts of data to drive
a KPI, SAS BI Dashboard attempts to produce one KPI gauge representation
for each row of data in the indicator data. For significant amounts
of data, an indicator type that automatically summarizes the data
is preferable. Bar charts are an example of this type of indicator.
|
|
|
Some audiences might
not be familiar with gauges. However, gauges are not difficult to
interpret, so even if users are unfamiliar with this indicator type,
they should be able to understand it. Be sure to label the value,
the interval threshold values, and colors used to represent intervals
(red for below target, yellow for on target, and green for above target).
|
|
|
Alerts are supported. For information, see Customizing Alerts.
|
|
|
This indicator type can be used to define a link or as the
destination of a link.For
more information about defining an indicator with a hyperlink, see Adding Links to Indicators or Other Content.
|
|