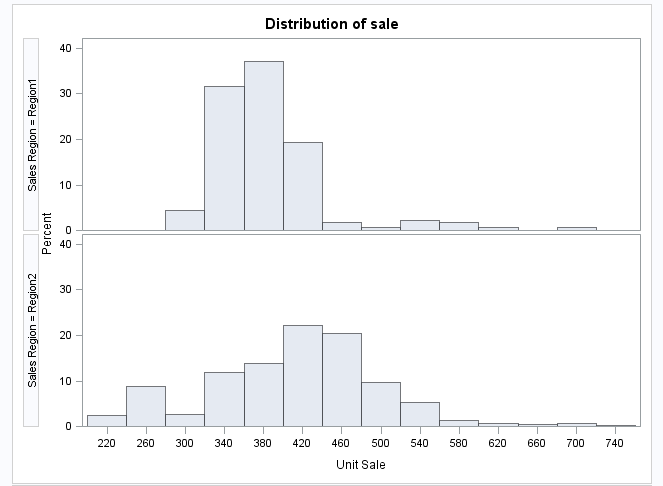
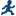Distribution Analysis Task
Example: Distribution Analysis of Sales for Each Region
Assigning Data to Roles
To run the Distribution
Analysis task, you must assign a column to the Analysis
variables and select a plot or test on the Options tab.
|
Role
|
Description
|
|---|---|
|
Roles
|
|
|
Analysis
variables
|
specifies the analysis
variables and their order in the results.
|
|
Additional Roles
|
|
|
Frequency
count
|
specifies a numeric
variable whose value represents the frequency of the observation.
The Distribution Analysis task assumes that each observation represents n observations,
where n is the value of the variable.
|
|
Group analysis
by
|
specifies the variables
that the Distribution Analysis task uses to form groups.
|
Setting Options
|
Option Name
|
Description
|
|---|---|
|
Exploring Data
|
|
|
By default, the task
creates a histogram of the data. In the Classification
variables role, specify the variables that are used to
group the analysis variables into classification levels. You can assign
a maximum of two columns to this role.
You can also specify
whether to superimpose a kernel density estimate and the normal density
curve on the histogram. Finally, you can specify whether to include
an inset box of selected statistics in the graph.
|
|
|
Checking for Normality
Note: If you select any of these
options, you can also specify whether to include these inset statistics:
number of observations, goodness-of-fit test, mean, median, standard
deviation, variance, skewness, and kurtosis.
|
|
|
Histogram
and goodness-of-fit tests
|
requests tests for normality
that include a series of goodness-of-fit tests based on the empirical
distribution function. The table provides test statistics and p-values
for the Shapiro-Wilk test (provided the sample size is less than or
equal to 2,000), the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test, the Anderson-Darling
test, and the Cramér-von Mises test.
|
|
Normal probability
plot
|
creates a probability
plot, which compares ordered variable values with the percentiles
of the normal distribution. If the data distribution matches the normal
distribution, the points on the plot form a linear pattern. Probability
plots are preferable for graphical estimation of percentiles.
The distribution reference
line on the plot is created from the maximum likelihood estimate for
the parameter.
You can also specify
whether to include an inset box of selected statistics in the graph.
|
|
Normal quantile-quantile
plot
|
creates quantile-quantile
plots (Q-Q plots) and compares ordered variable values with quantiles
of the normal distribution. If the data distribution matches the normal
distribution, the points on the plot form a linear pattern. Q-Q plots
are preferable for graphical estimation of distribution parameters.
The distribution reference
line on the plot is created from the maximum likelihood estimate for
the parameter.
You can also specify
whether to include an inset box of selected statistics in the graph.
|
|
Fitting Distributions
Note: If you select a plot option
for any of these distributions, you can also specify whether to include
these inset statistics: number of observations, mean, median, standard
deviation, and variance.
|
|
|
Beta
|
|
|
Histogram
and goodness-of-fit tests
|
fits beta distribution
with threshold parameter
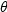 , scale parameter , scale parameter  , and shape parameters , and shape parameters 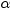 and and 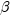 . .
|
|
Probability
plot
|
specifies a beta probability
plot for shape parameters
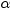 and and 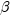 . .
|
|
Quantile-quantile
plot
|
specifies a beta Q-Q
plot for shape parameters
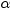 and and 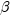 . .
|
|
Exponential
|
|
|
Histogram
and goodness-of-fit tests
|
fits exponential distribution
with threshold parameter
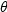 and scale parameter and scale parameter  . .
|
|
Probability
plot
|
specifies an exponential
probability plot.
|
|
Quantile-quantile
plot
|
specifies an exponential
Q-Q plot.
|
|
Gamma
|
|
|
Histogram
and goodness-of-fit tests
|
fits gamma distribution
with threshold parameter
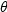 , scale parameter , scale parameter  , and shape parameter , and shape parameter 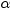 . .
|
|
Probability
plot
|
specifies a gamma probability
plot for shape parameter
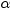 . .
|
|
Quantile-quantile
plot
|
specifies a gamma Q-Q
plot for shape parameter
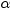 . .
|
|
Lognormal
|
|
|
Histogram
and goodness-of-fit tests
|
fits lognormal distribution
with threshold parameter
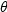 , scale parameter , scale parameter 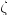 , and shape parameter , and shape parameter  . .
|
|
Probability
plot
|
specifies a lognormal
probability plot for shape parameter
 . .
|
|
Quantile-quantile
plot
|
specifies a lognormal
Q-Q plot for shape parameter
 . .
|
|
Weibull
|
|
|
Histogram
and goodness-of-fit tests
|
fits Weibull distribution
with threshold parameter
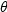 , scale parameter , scale parameter 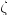 , and shape parameter , and shape parameter  . .
|
|
Probability
plot
|
specifies a two-parameter
Weibull probability plot.
|
|
Quantile-quantile
plot
|
specifies a two-parameter
Weibull Q-Q plot.
|
Copyright © SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved.